Recherche
Recherche simple
La barre de recherche que le personnel verra le plus souvent est la barre de recherche répétée située en haut de la page dans l’interface professionnelle.

Note
Si la préférence système IntranetAddMastheadLibraryPulldown est positionnée sur “Ajouter”, la barre de recherche simple dans l’interface professionnelle inclura un choix de bibliothèque.

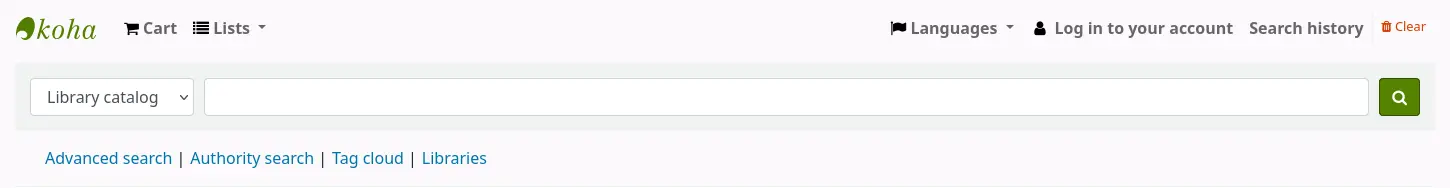
Dans l’OPAC, les adhérents de la bibliothèque verront une barre de recherche en haut de la plupart des pages.
Note
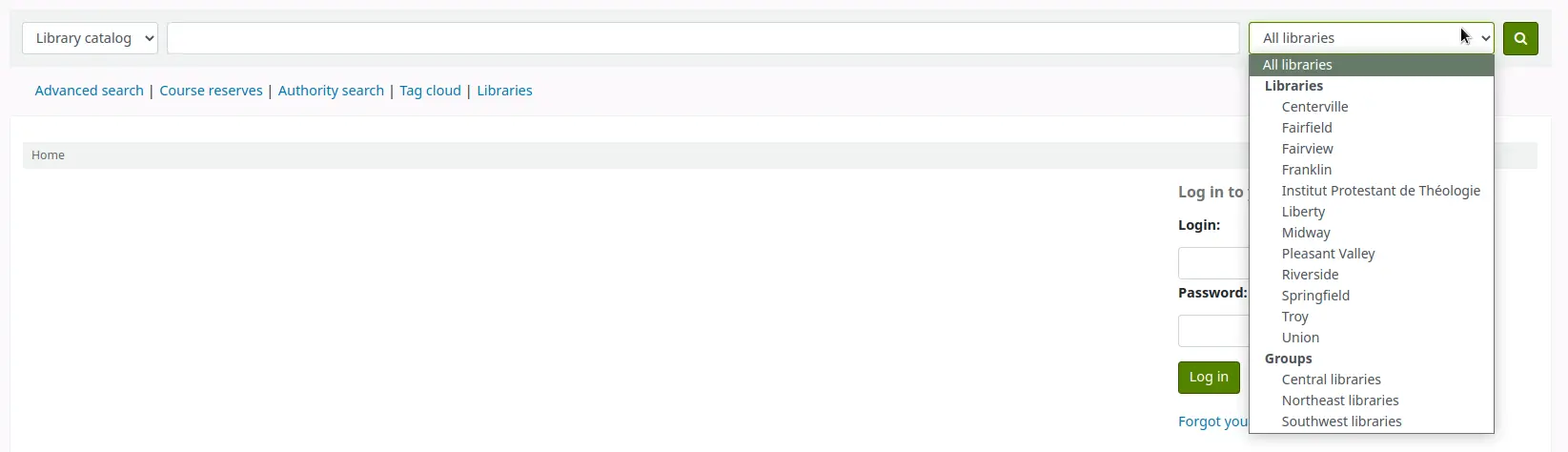
Si la préférence système OpacAddMastheadLibraryPulldown est positionnée sur “Ajouter”, la barre de recherche simple dans l’OPAC inclura un choix de bibliothèques et de groupes de bibliothèques.
Pour rechercher, saisir un mot ou plusieurs mots dans la barre de recherche. Quand aucun index de recherche n’est spécifié, une recherche par mot-clé est effectuée.
Note
Vous pouvez le vérifier en lançant une recherche avec un seul terme dans le formulaire et noter le nombre de résultats. Répétez ensuite la recherche avec un changement mineur : devant le mot recherché, ajoutez “kw=” suivi par le même mot recherché. Les résultats seront identiques.
Lorsque vous saisissez plus d’un mot dans la barre de recherche, Koha effectuera toujours une recherche par mot-clé, mais avec l’opérateur Booléen “ET”. Ceci restreindra votre recherche uniquement aux notices qui contiennent tous les mots.
Au moment de la recherche, sélectionnez les mots les plus importants que vous recherchez et saisissez-les dans la barre de recherche persistante.

Koha will perform the search and return the results.
L’ordre des mots n’affecte pas les résultats de recherche.

Trop de mots saisis dans la barre de recherche génèreront très peu de résultats.
Recherche avancée
La recherche avancée peut aider lorsque la recherche simple renvoie trop de résultats.
Aller à : Recherche ou Recherche avancée
Le formulaire de recherche avancée propose plusieurs façons de limiter votre recherche. Vous pouvez utiliser les opérateurs booléens ET, OU, SAUF ; limiter par type de document ; limiter par année et langue ; limiter par les données de public, contenu, format ou types de contenu supplémentaires ; par localisation et par disponibilité.
Vous pouvez utiliser autant de sections que nécessaire, aucune n’est obligatoire, tant qu’il y a au moins un mot de recherche ou une limite sélectionnée.
L’option permettant de voir l’Historique de recherche dans la Recherche avancée est disponible si la préférence système EnableSearchHistory est paramétrée sur “Conserver”. Cette préférence système contrôle si l’interface professionnelle conserve l’historique de recherche pour les adhérents authentifiés. L’historique de recherche sera accessible sous le lien de votre compte en haut à droite de l’interface professionnelle et également sous l’option de Recherche avancée.
Mots de recherche
Dans la première section du formulaire de recherche avancée il y a plusieurs barres de recherche pour rechercher différents index en même temps.
Si la préférence système expandedSearchOption est positionnée sur “afficher”, les options pour choisir les opérateurs booléens seront automatiquement affichées. Si la préférence est positionnée sur “ne pas afficher”, il faudra cliquer sur “Plus d’options” pour les faire apparaître.

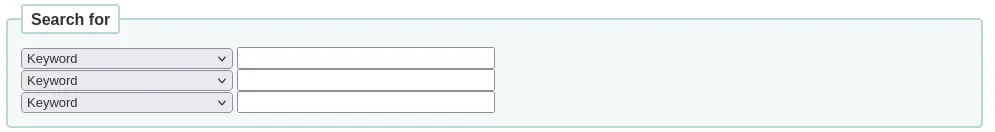
Dans cette section, vous pouvez choisir parmi plusieurs indexes en cliquant sur les flèches dans le premier menu déroulant. Le champ vierge qui suit ce menu correspond au champ dans lequel vous allez entrer votre recherche. Sur la ligne suivante, vous pouvez choisir l’opérateur Booléen que vous souhaitez utiliser dans votre recherche. Les options sont “et”, “ou”, “sauf”. Ensuite, vous pouvez de nouveau choisir un index, suivi d’un ou plusieurs termes de recherche. Si vous avez plusieurs concepts à saisir dans votre recherche, vous pouvez cliquer sur les [+] pour ajouter une nouvelle ligne de recherche.
Par exemple, c’est une recherche pour les notices où l’auteur est Twain et le titre contient soit “Huckleberry Finn” soit “Tom Sawyer”.
Les opérateurs booléens élargissent ou restreignent les recherches.
ET : restreint les résultats car la recherche ne retournera que les notices qui contiennent tous les termes de recherche.
OU : augmente les résultats car la recherche cherchera les occurrences de tous les termes recherchés, qu’ils soient dans la même notice ou pas.
SAUF : exclut les notices qui contiennent le terme recherché.
The indexes available in the advanced search form are the following (see more about indexes and which MARC fields are indexed in each in the Koha search indexes section below):
Option de l’index |
Recherche d’index |
Type de recherche |
|---|---|---|
Mot-clef |
Tout |
Mot clé |
Mot-clé comme phrase |
Tout |
phrase exacte |
Auteur |
auteur |
Mot clé |
Auteur comme expression |
auteur |
phrase exacte |
Raison sociale |
raison sociale |
Mot clé |
Nom de congrès |
nom de congrès |
Mot clé |
Raison sociale comme expression |
raison sociale |
phrase exacte |
Nom de congrès comme expression |
nom de congrès |
phrase exacte |
Nom de personne |
nom de personne |
Mot clé |
Nom de personne comme expression |
nom de personne |
phrase exacte |
Titre |
titre |
Mot clé |
Titre comme phrase |
titre |
phrase exacte |
Titre de collection |
title-series |
Mot clé |
Sujet |
sujet |
Mot clé |
Sujet comme expression |
sujet |
phrase exacte |
Barcode |
code à barres |
Mot clé |
Localisation |
localisation (voir note) |
Mot clé |
numéro standardisé |
identifier-standard |
numéro |
ISBN |
isbn |
isbn |
ISSN |
issn |
numéro |
cote |
classification locale |
Mot clé |
Langue |
ln |
Mot clé |
Notes/Commentaires |
note |
Mot clé |
Curriculum |
curriculum |
Mot clé |
Editeur |
éditeur |
Mot clé |
Lieu d’édition |
pl |
Mot clé |
Date d’édition |
date de plublication |
date |
Date d’acquisition |
date d’acquisition |
date |
Note
If using LOC authorized values in the item location field, the location indexed is the authorized value code.
Types de documents, localisations et limites de collections
Sous les barres de recherche, il y a des zones qui vous permettent de limiter votre recherche par type de document, localisation ou collection.
Préfixes de recherche avancée
Les zones affichées ici, ainsi que leur ordre, sont contrôlées par la préférence système AdvancedSearchTypes (ou OpacAdvancedSearchTypes pour le formulaire de recherche avancée à l’OPAC).
Note
Dans l’OPAC, cette section peut être masquée avec les préférences système OpacAdvSearchMoreOptions ou OpacAdvSearchOptions (décocher l’option “Types de documents”).
Il n’est pas possible de le masquer dans l’interface professionnelle.
Il est possible, au moment de la recherche, de cocher plusieurs options dans plusieurs zones. Dans ce cas, les options de la même zone sont recherchées avec un opérateur OU et les options de différentes zones sont recherchées avec un opérateur ET. Par exemple, si un utilisateur coche les types de documents “Livres” et “Référence” ainsi que les localisations “Espace enfants” et “Généralités”, les options seront reliées ainsi : (Livres OU Référence) ET (Espace enfants OU Généralités).
For each tab, the following indexes are searched (see more about indexes and which MARC fields are indexed in each in the Koha search indexes section below):
Onglet |
Recherche d’index |
|---|---|
Type de document |
itype |
Localisation |
location |
Code de collection |
ccode |
Limites de date et de langue
La section suivante n’apparaît que si vous cliquez sur “Plus d’options” ou si la préférence système expandedSearchOption est positionnée sur “afficher”. Cela vous permet de limiter votre recherche par date de publication ou par langue.
Note
Dans l’OPAC, cette section peut être masquée avec les préférences système OpacAdvSearchMoreOptions ou OpacAdvSearchOptions (décocher l’option “Date de publication” ou “Langue”).
Il n’est pas possible de le masquer dans l’interface professionnelle.
La limitation “Année” vous permet de chercher des titres publiés dans une année en particulier tout comme dans un intervalle d’années.
“2005” recherchera les titres publiés en 2005
“2005-2010” recherchera les titres publiés entre 2005 et 2010 (y compris 2005 et 2010)
“-2010” recherchera les titres publiés en 2010 et avant
“<2010” recherchera les titres publiés avant 2010 (2010 exclus)
“2005-” recherchera les titres publiés en 2005 et après
“>2005” recherchera les titres publiés après 2005 (2005 exclu)
Les limités “Langue” et “Langue de l’original” vous permettent de rechercher des titres dans des langues spécifiques ou traduites de langues spécifiques.
Note
Par défaut, les menus déroulants des langues sont remplis avec toutes les langues. Il est possible de limiter la liste avec la préférence système AdvancedSearchLanguages.
For each search field, the following indexes are searched (see more about indexes and which MARC fields are indexed in each in the Koha search indexes section below):
Période de recherche |
Recherche d’index |
|---|---|
Année |
date de plublication |
Langue |
ln |
langue original |
language-original |
Limites de sous-type
La sections suivante vous permet de limiter votre recherche avec des données codées.

Note
Dans l’OPAC, cette section peut être masquée avec les préférences système OpacAdvSearchMoreOptions ou le OpacAdvSearchOptions (décocher l’option “Sous-types”).
Il n’est pas possible de le masquer dans l’interface professionnelle.
Le menu déroulant “Public” peut être utilisé pour limiter les résultats à un public cible spécifique.
Préscolaire
Primaire
Pré-adolescent
Adolescent
Adulte
Spécialisé
Généralités
Jeunesse
Le menu déroulant “Contenu” peut être utilisé pour limiter les résultats à un type de contenu spécifique.
Fiction
Non Fiction
Biographie
Enregistrement musical
mus:j Enregistrement non-musical
Le menu déroulant “Format” peut être utilisé pour limiter les résultats à un type de format spécifique.
Impression normale
Gros caractères
Braille
CD audio
Cassette audio
Bande VHS / Videocassette
DVD Vidéo / Vidéodisque
CD logiciel
Site Web
Le menu déroulant “Types de contenu additionnels” peut être utilisé pour limiter ultérieurement les résultats à un type de contenu spécifique.
Résumé / Sommaires
Bibliographies
Catalogues
Encyclopédies
Manuels
Articles juridiques
Index
Brevets
Discographies
Contenu légal
Thèses
Enquêtes
Comptes rendus critiques
Textes programmés
Filmographies
Répertoires
Statistiques
Rapports techniques
Causes juridiques, notes de causes
Recueils de jurisprudence, lois et compilations
Traités
For each search field, the following indexes are searched (see more about indexes and which MARC fields are indexed in each in the Koha search indexes section below):
Période de recherche |
Recherche d’index |
|---|---|
Public ciblé |
ta |
Contenu |
Si bio rtype |
Format |
ff7-01-02 |
Types de contenus additionnels |
ctype |
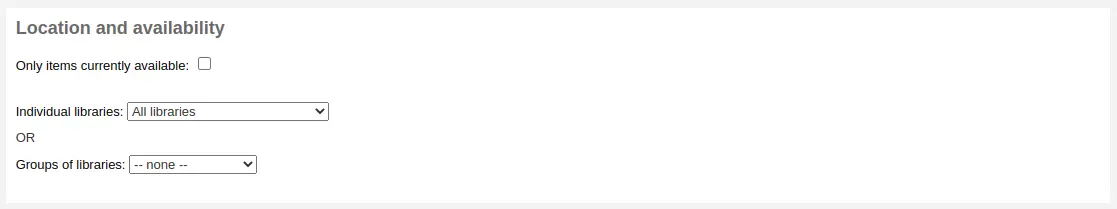
Localisation et disponibilité
La section “localisation et disponibilité” vous permet de limiter ultérieurement votre recherche.
Note
Dans l’OPAC, cette zone peut être masquée avec les préférences système OpacAdvSearchMoreOptions ou OpacAdvSearchOptions (décocher l’option “Localisation et disponibilité”).
Il n’est pas possible de le masquer dans l’interface professionnelle.
La case “Limiter aux exemplaires disponibles” peut être cochée pour afficher uniquement les exemplaires disponibles dans les résultats.
Avertissement
L’option “Limiter aux exemplaires disponibles” enlève uniquement les exemplaires qui sont actuellement prêtés. Elle n” enlève pas les exemplaires qui sont retirés des collections, perdus ou bien pas en prêt.
Le menu déroulant “Bibliothèques” peut être utilisé pour limiter la recherche à une bibliothèque spécifique.
If you have library groups that are selected to be search groups, they will appear under “Groups of libraries”.
Note
Par défaut, la limite par localisation recherche le site de rattachement de l’exemplaire. Ceci peut être modifié avec la préférence système SearchLimitLibrary.
For each search field, the following indexes are searched (see more about indexes and which MARC fields are indexed in each in the Koha search indexes section below):
Période de recherche |
Recherche d’index |
|---|---|
Exemplaires disponibles |
onloan |
Bibliothèques ou groupes de bibliothèques |
Site de rattachement |
Tri
Enfin, vous pouvez choisir comment les résultats seront triés.
Recherche avancée
Note
Dans l’OPAC, cette zone peut être masquée avec les préférences système OpacAdvSearchMoreOptions ou OpacAdvSearchOptions (décocher l’option “Tri”).
Il n’est pas possible de le masquer dans l’interface professionnelle.
Le tri par défaut est paramétré dans les préférences système defaultSortField et defaultSortOrder, mais vous pouvez choisir de trier par auteur, par titre, par cote, par dates, ou par popularité (ce tri utilise les informations trouvées dans le champ total issues de la table items).
Pertinence : si vous utilisez ElasticSearch, la pertinence est calculée avec le poids des champs et le nombre d’occurrences des termes de recherche dans chaque champ.
Popularité : ce tri utilise l’index des prêts, le nombre de prêts pour chaque exemplaire d’une notice.
Auteur : ce tri utilise l’index auteur
Cote : ce tri utilise l’index cn-sort, qui est construit en utilisant le schéma de classification et la cote
Date de publication/date de copyright : ce tri utilise l’index date-of-publication
Date d’acquisition : ce tri utilise l’index date-of-acquisition
Titre : ce tri utilise l’index title
See more about indexes and which MARC fields are indexed in each in the Koha search indexes section below.
Elasticsearch advanced search syntax
If you use the Elasticsearch search engine, you can use the following advanced search syntax:
Fuzzy: add a tilde (~) to the end of each word
wierd~ searches for wired, weird
liberry~ searches for library, liberty
midevil~ searches medieval
Wildcards: question mark (?) stands in for one character
c?t searches for cat, cot, cut
c?at searches for chat, coat
Asterisk (*): stands in for zero or more characters
c*t searches for ct, cat, cot, coat, cut, connecticut, court, cormorant
c*at searches for cat, chat, coat, cheat
cat* searches for cat, cats, catapult, catastrophe, caterer
*cat searches for scat, wildcat, bobcat
Phrases: surround a phrase with quotation marks (“”) to force an exact match
“Pete the cat” only shows titles that have the exact phrase Pete the cat in the record
“The Road” only shows titles where the is directly left of road
Minus sign (-): add to the start of each word you want to remove
cat -dog searches for titles with cat but not dog
fantasy -romance searches for fantasy titles without romance in the record
Recherche d’exemplaires
Si vous cherchez des exemplaires spécifiques, vous pouvez utilisez le moteur de recherche d’exemplaires situé dans l’interface professionnelle pour les trouver.
Aller à : Rechercher > Recherche d’exemplaires

Vous pouvez également accéder à la recherche d’exemplaires depuis le lien “Rechercher sur les exemplaires” en haut de la page de recherche avancée dans l’interface professionnelle.

En cliquant sur l’un ou l’autre de ces liens, vous ouvrirez un moteur de recherche spécifique à la recherche d’exemplaires.
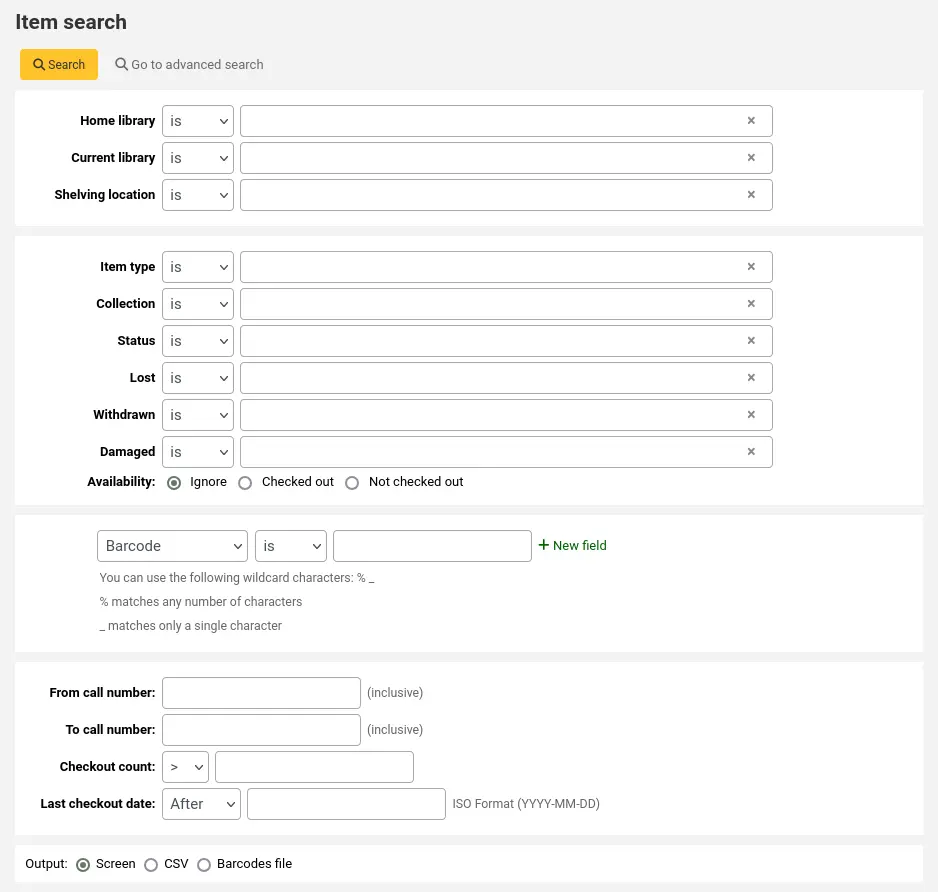
En utilisant le formulaire de recherche qui vous est proposé, vous pouvez trouver une liste d’exemplaires spécifiques que vous pourrez afficher à l’écran, dans un fichier CSV ou dans un fichier de codes à barres.
Vous pouvez ajouter des champs de recherche supplémentaires à ce formulaire en vous rendant dans la section champs de recherche sur les exemplaires dans le module Administration.
Si vos résultats sont affichés à l’écran vous aurez la possibilité de restreindre davantage votre recherche en utilisant les filtres en haut.
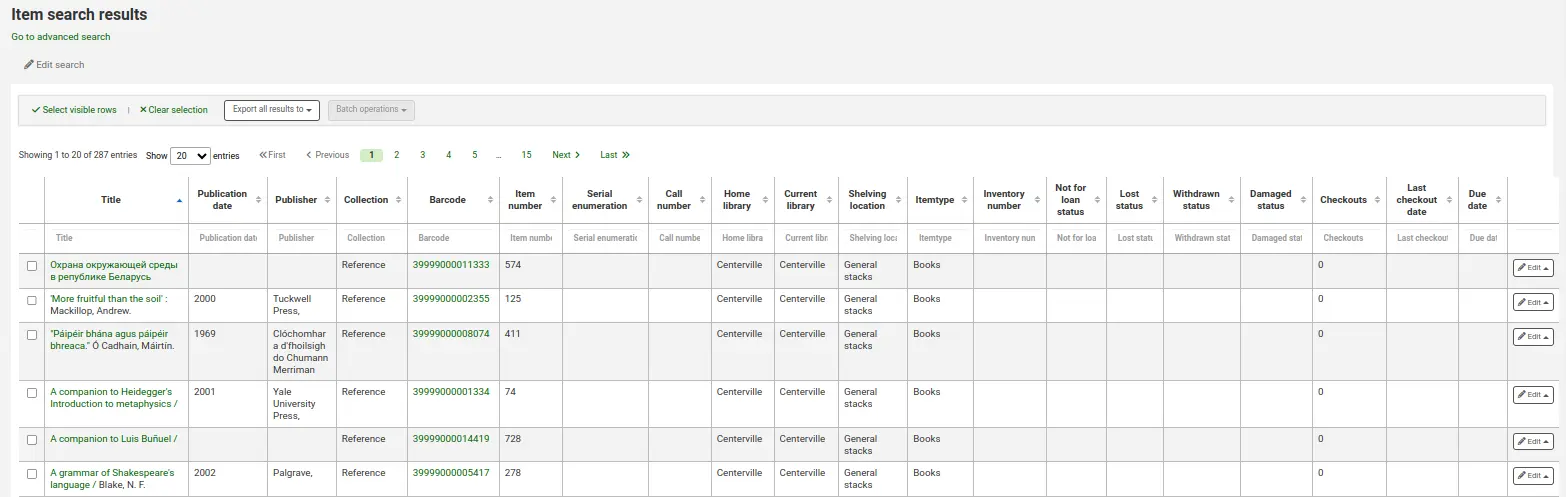
Depuis la recherche, vous pouvez sélectionner un exemplaire, puis :
exporter ses informations dans un fichier CSV ou un fichier de code a barre;
les modifier grâce à l’outil de modification par lot ou les supprimer grâce à l’outil de suppression par lot
Note
Les exemplaires sélectionnés resteront sauvegardés dans la mémoire cache de votre navigateur jusqu’à votre déconnexion, le nettoyage de la sélection, ou le nettoyage de la mémoire cache de votre navigateur.
pb: Navigation dans la recherche de l’OPAC
Quand Elasticsearch est utilisé, une option de recherche par navigation est disponible à l’Opac. Elle s’active en utilisant la préférence système OpacBrowseSearch. L’option apparaît alors comme un lien dans la zone « Plus de recherches » de l’Opac.
Sur la page de recherche, saisissez l’objet de votre recherche dans la boite « Recherche ». Utiliser le menu « Type de recherche » pour faire une recherche spécifique par auteur, par sujet ou par titre. Sous la boîte de recherche, des boutons vous permette de choisir entre une recherche par terme « exact », « approximatif » ou « très approximatif ».
Par défaut, la recherche par auteur et de manière approximative sont sélectionnées.
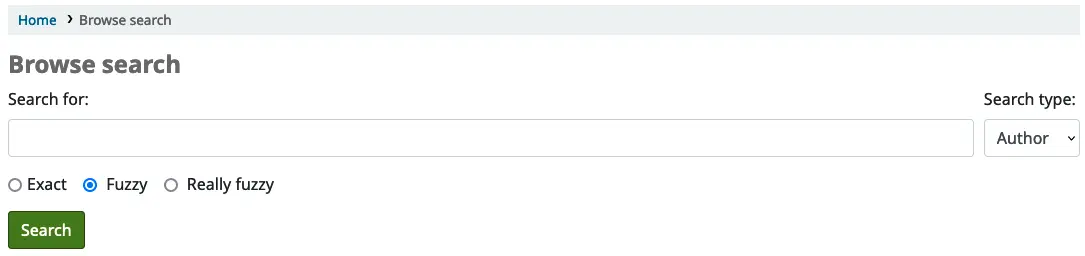
Lorsque vous cliquez sur le bouton « Rechercher », vous verrez une liste de résultat débutant par le texte saisi précédemment dans la boîte de recherche. Cliquer sur un résultat ouvrira une partie listant toutes les entrées du catalogue en lien avec votre recherche. De là, il est possible de naviguer dans la notice détaillée.
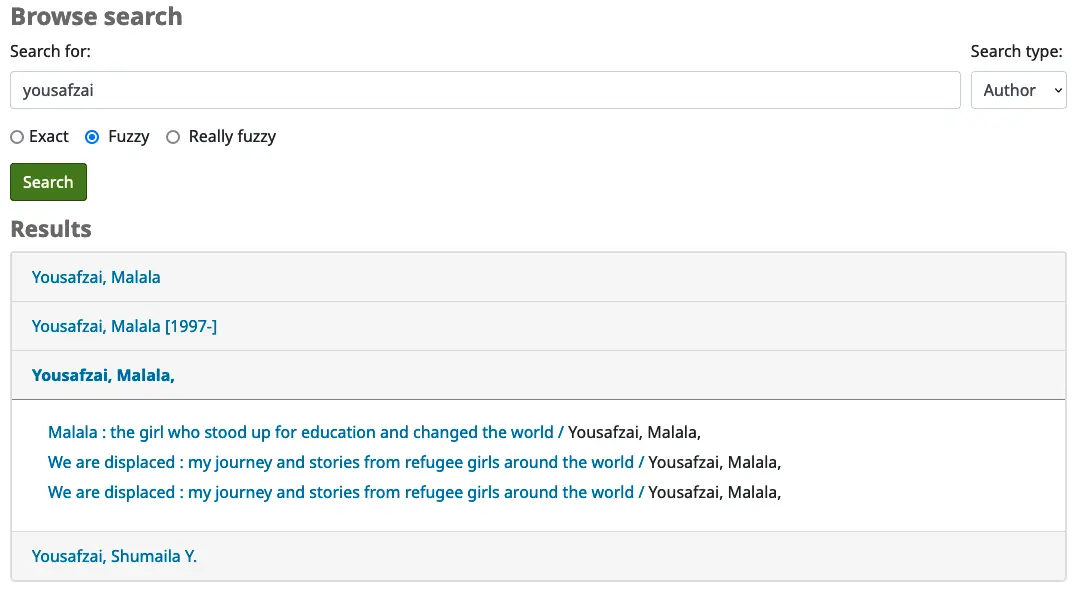
Résultats de la recherche
Après avoir lancé une recherche, le nombre de résultats trouvés au-dessus des résultats.
Quand la recherche ne rend qu’un résultat, la notice détaillée sera affichée et non la liste des résultats. Ce comportement peut être modifié avec la préférence système RedirectToSoleResult.
Il y aura aussi un lien pour revenir à l’écran de recherche avancée pour modifier la recherche.
Si la préférence système SavedSearchFilters est activée, il y aura aussi un lien pour enregistrer la recherche comme filtre.

Il y a la possibilité de rechercher parmi les résultats. Cette boîte de recherche prendra la requête et l’ajoutera aux limites de la précédente recherche.
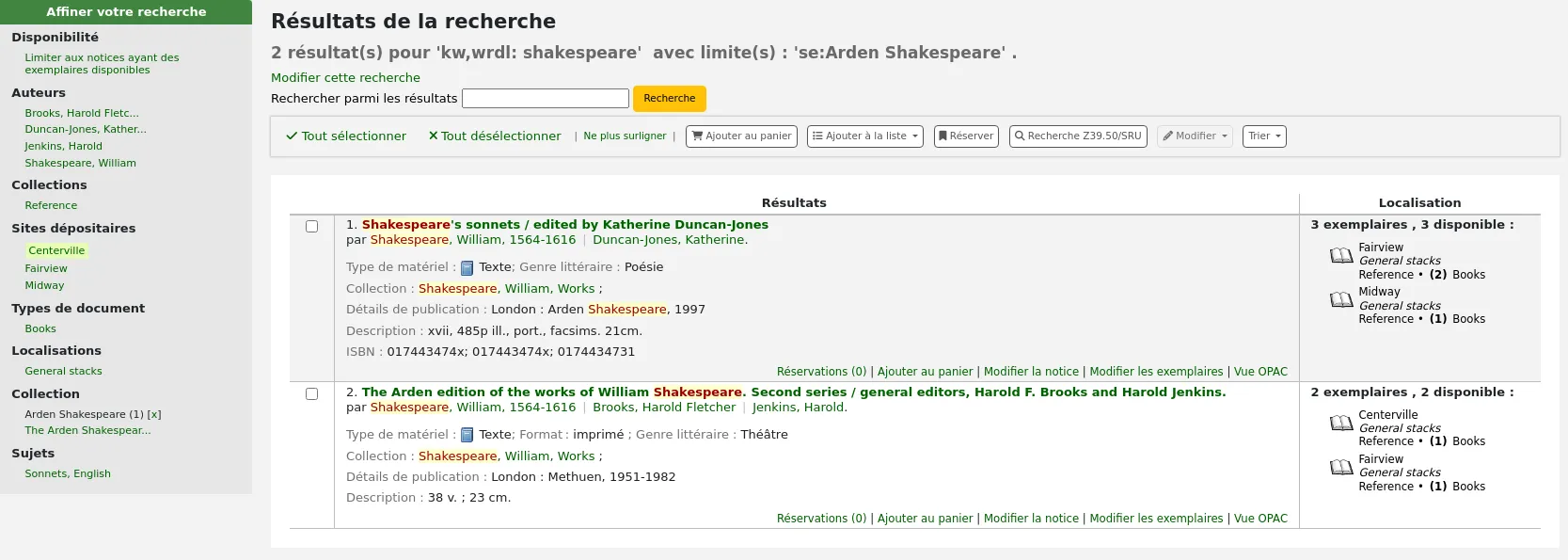
Si StaffHighlightedWords est paramétrée sur “Surligner”, le(s) terme(s) recherché(s) sera(seront) surlignés en jaune et le texte mis en rouge dans chaque notice. Vous pouvez retirer le surlignage en cliquant sur le lien “Ne plus surligner” en haut de la page.
Note
Le surlignage ne représente pas l’endroit où le terme recherché se trouve dans la notice, il souligne simplement la chaîne de caractères partout où elle est trouvée sur la page.
Par défaut, les résultats de votre recherche seront triés selon les valeurs des préférences système OPACdefaultSortField and OPACdefaultSortOrder. Pour modifier ce fonctionnement, vous pouvez choisir une autre méthode de tri dans le menu déroulant sur la droite.
Note
If using Elasticsearch in searchengine, and the results are sorted by relevancy, you can use the ElasticsearchBoostFieldMatch system preference to automatically and transparently do a second “exact match” search to boost exact results to the top of the results list.
Chaque résultat de recherche est affiché dans un tableau avec les informations bibliographiques dans la colonne de gauche et les informations d’exemplaire dans la colonne de droite.
Sous chaque titre de votre liste de résultats, une série de valeurs issues de votre leader apparaîtra. Il est important de noter que cela n’a rien à voir avec les types de documents ou les codes de collection que vous avez appliqués à vos notices, cette donnée est récupérée de vos champs fixes. Cela peut être activé ou désactivé avec la préférence système DisplayIconsXSLT.
Dans la colonne de droite, la disponibilité et les informations des exemplaires attachés à la notice sont affichées.
Note
Même si vous avez limité vos recherches à un site, tous les sites possédant l’exemplaire recherché s’afficheront sur l’écran des résultats.
La disponibilité des exemplaires dépend de leur statut. L’exemplaire suivant apparaîtra comme disponible :
Disponible (pas prêté, pas de statut particulier)
Réservé
Le statut de réservation d’un exemplaire n’affecte sa « disponibilité » que s’il est « en attente ». Les exemplaires « réservés sur étagère » seront affichés disponibles jusqu’à ce qu’un bibliothécaire les retire des rayons et les passe en retour, ce qui les marquera « en attente ».
L’exemplaire suivant apparaîtra comme indisponible :
Prêté
Réservé, en attente de retrait
En transfert
The availability of items is displayed only for the first twenty items in the record. This number can be changed with the MaxSearchResultsItemsPerRecordStatusCheck system preference.
If records have a lot of items, only twenty items will be displayed in the search results by default. This number can be changed with the maxItemsInSearchResults system preference.
The library name displayed in the item information column can be either the current library or the home library. You can choose which using the StaffSearchResultsDisplayBranch system preference.
Si les préférences système relatives aux images de couverture du Contenu enrichi sont activées, les images de couverture apparaîtront à côté des résultats de recherche.
Facettes
A gauche, vous trouverez des filtres, ou facettes, pour affiner votre recherche.
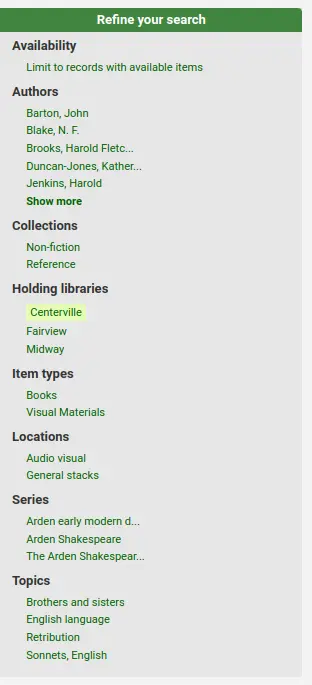
Les facettes actuellement disponibles incluent :
Disponibilité
Auteurs
Types de document
Localisations
Lieux (vedette de nom géographique)
Collection
Sujets (vedettes sujet)
Collections (codes de collection)
Site de rattachement, site dépositaire ou les deux
Note
Cela dépend du paramétrage de la préférence système DisplayLibraryFacets.
Titres (vedette de titre uniforme) (Zebra uniquement)
Langues (Elasticsearch uniquement)
Note
When using Elasticsearch, it is possible to remove facets and reorder them from the search engine configuration page.
By default, facets are constructed using the first twenty records. You can customize this with the maxRecordsForFacets system preference.
If you want to show the number of records that correspond to each facet next to it, you can make it appear with the displayFacetCount system preference. Note that this number is dependent on the maxRecordsForFacets system preference.
When there are more than five facets in a category, a “Show more” link will appear. By default, this link will show up to twenty facets. You can change the maximum number of facets shown with the FacetMaxCount system preference.
By default, when facets are longer than twenty characters, will be truncated. You can change the number of character after which a facet is truncated with the FacetLabelTruncationLength system preference.
Note
When using Elasticsearch, facets are never truncated. This is only for Zebra users.
By default, facets in each category are ordered alphabetically. You can change the order with the FacetOrder system preference. If the alphabetical order is incorrectly sorting the diacritics, you can use the FacetSortingLocale system preference to set your locale and ensure facets are in the correct order.
When using UNIMARC, the default separator for authors” last and first names in the facets is a comma, but you can change this using the UNIMARCAuthorsFacetsSeparator system preference, if necessary.
Note
If you have any search filters, they will appear above the facets.
Actions on search results
En haut, sous le nombre de résultats, il y a des boutons pour opérer différentes actions sur les notices sélectionnées.
Select all: selects all the records on the page.
Clear all: unselects all the records that were selected.
Ne plus surligner : retire le surlignage rouge/jaune du(des) terme(s) recherché(s).
Si StaffHighlightedWords est paramétrée sur “Surligner”, le(s) terme(s) recherché(s) sera(seront) surlignés en jaune et le texte mis en rouge dans chaque notice. Le lien “Ne plus surligner” retire ce surlignage.
« Ajouter au panier » : ajoute la(les) notice(s) sélectionnée(s) au panier.
Note
La préférence système intranetbookbag doit être paramétrée sur “Afficher” pour que ce bouton apparaisse.
Add to list: adds selected record(s) to the chosen list.
Place hold: places a hold on the selected record(s).
Browse selected records: goes to the detailed record page of the selected record(s). Clicking on “Next” or “Previous” from the detailed record will bring you to the next selected record.
Note
La préférence système BrowseResultSelection doit être activée pour que ce bouton apparaisse.
Z39.50/SRU search: opens the Z39.50/SRU search popup window with the fields prefilled with the search terms.
Edit: batch edit, batch delete or merge selected records.
Sort: changes the sorting field and order. The options are the same as the ones described in the sorting section above.
Note
By default, search results will be sorted based on the defaultSortField and defaultSortOrder system preferences values.
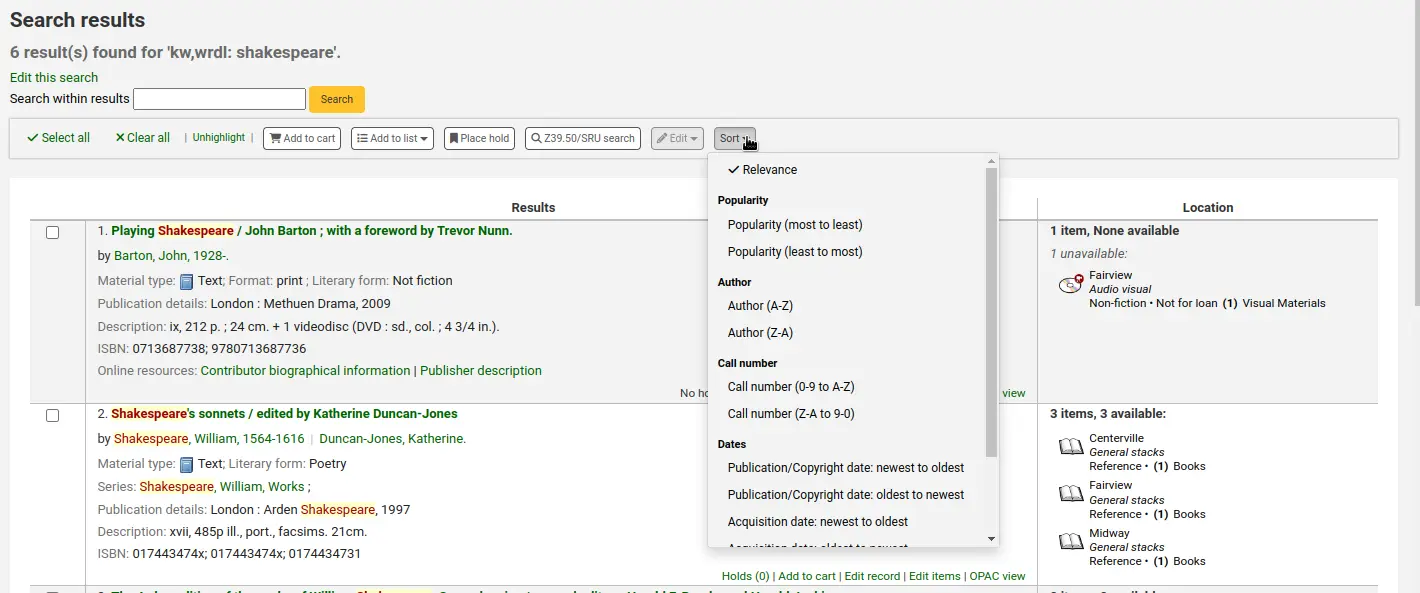
If the FilterSearchResultsByLoggedInBranch system preference is set to “Do”, a button will appear at the top of the “Location” column to allow the user to toggle the view of items and only show availability for the items from the library where they are logged in. The items from other libraries will show as unavailable.
Under each record, at the bottom, there are more action links:
“Réservations” : vous renvoie à l’onglet Réservations.
Recalls: links to that record’s “Recalls” tab.
« Ajouter au panier » : ajoute cette notice au panier.
Note
La préférence système intranetbookbag doit être paramétrée sur “Afficher” pour que ce lien apparaisse.
Demande d’article : vous renvoie à l’onglet Demande d’article de cette notice.
Edit record: links to that record’s MARC framework for editing.
Edit items: links to that record’s item list for editing.
OPAC view: links to that record’s detail page in the OPAC.
Note
L’option “Vue OPAC” nécessite que la préférence système OPACBaseURL soit bien paramétrée.
Search filters
Search filters are custom searches or filters that can be applied to search results.
Cette fonctionnalité est activée en utilisant la préférence système SavedSearchFilters.
Adding search filters
Once the SavedSearchFilters system preference is enabled, there will be a new option on the search results page to create a new search filter from this search.
To create a new search filter:
Search the catalog from the staff interface basic search or advanced search.
Click “Save search as filter” at the top of the results.
A form will pop up.
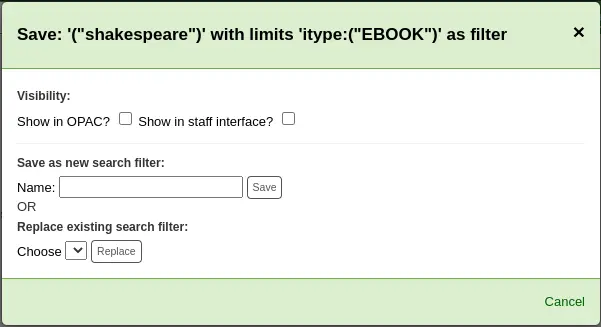
Visibility
Show on OPAC: If checked, this search filter will be available on the OPAC.
Show in staff interface: If checked, this search filter will be available in the staff interface.
Name: Enter the name of the search filter. This name will appear to staff and OPAC user, depending on where this search filter is available.
Click “Save” next to the name field.
Search filters will be displayed before the facets in the search results page, in the staff interface or OPAC, depending on visibility.
All search filters can be managed in the search filter administration section.
Editing existing search filters
Once you have existing search filters, the way to edit them is basically the same as adding a new one, but you are replacing instead of adding
Search the catalog from the staff interface basic search or advanced search.
Click “Save search as filter” at the top of the results.
The form will pop up.
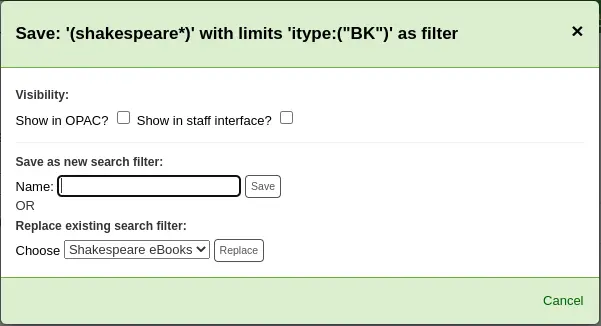
Choose which search filter to replace from the “Replace existing search filter” drop-down menu.
Click “Replace” next to the drop-down menu.
To further edit search filters, visit the search filter administration page.
Historique de recherche
Si vous avez paramétré la préférence système EnableSearchHistory pour conserver votre historique de recherche, alors vous pouvez accéder à cette information en cliquant sur votre nom d’utilisateur situé en haut à droite de l’interface professionnelle et choisissant “Historique de recherche”.
Vous verrez sur cette page votre historique de recherche bibliographique
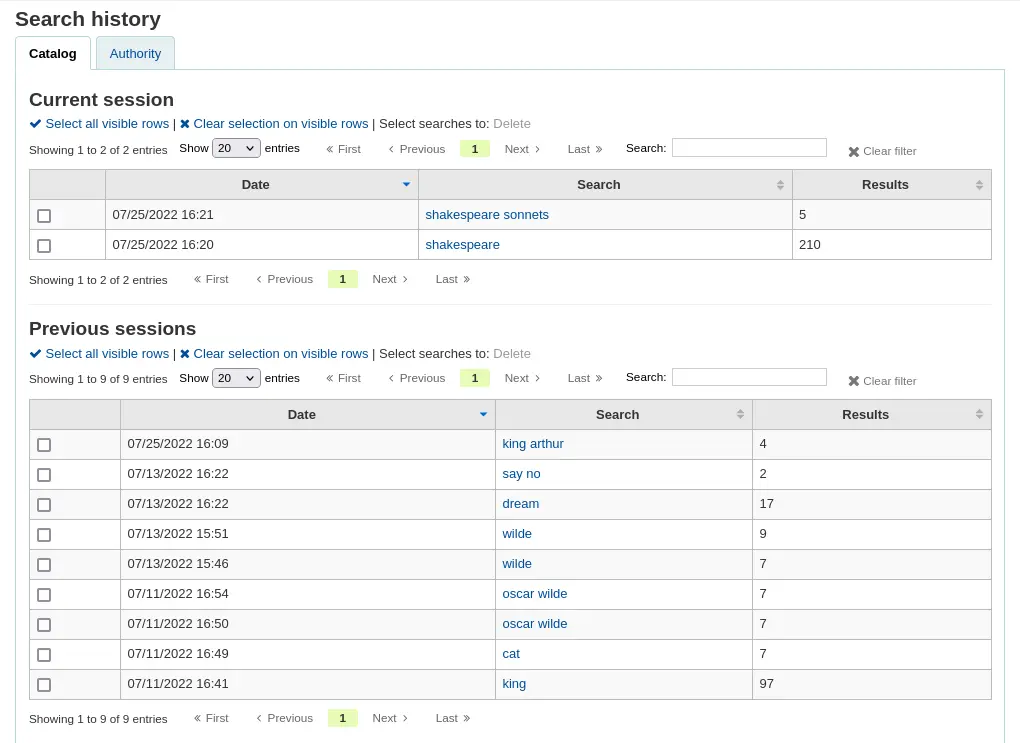
Et votre historique de recherche d’autorités.
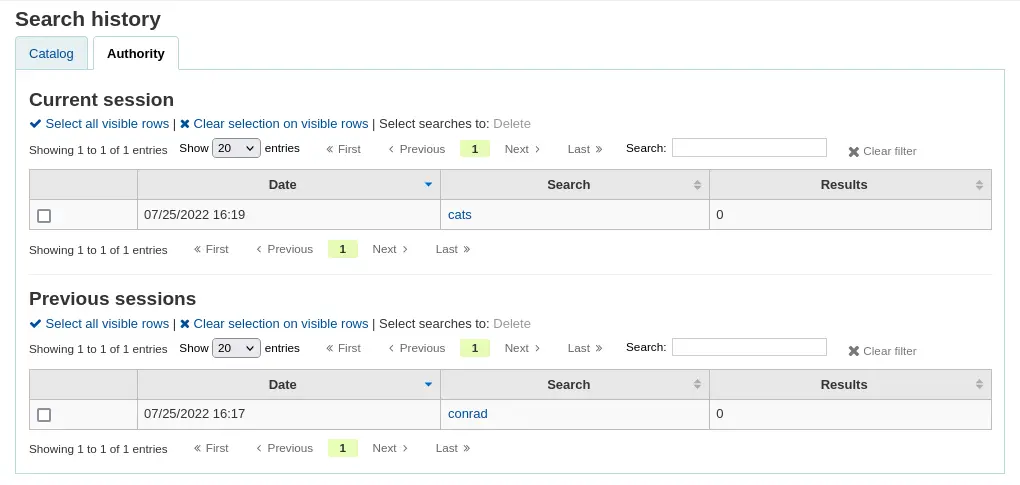
From the search history page, it is possible to relaunch a search by clicking on the search terms.
It is also possible to delete previous searches by selecting them and clicking on the “Delete” link at the top of the table.
Advanced search prefixes
Les préfixes suivants peuvent être ajoutés pour rechercher des termes dans la barre de recherche de mot-clé et ainsi limiter les résultats
ti: recherche titre
ex. ti:hamlet
su: recherche sujet
ex. su:cooking
pb: recherche éditeur
ex. pb:pingouin
au: recherche auteur
ex. au:rowling
su-geo: sujets géographiques
ex. su-geo:galles et kw:description et kw:voyage
bc: code à barres
ex. bc:502326000912
lex: lexile
niveaux lex:510
Guide to searching
Ce bref guide vous expliquera comment configurer une base de données MARC21 et comment fonctionne la recherche. Les champs MARC cités concernent l’indexation des données bibliographiques et non l’indexation de la base de données d’autorités.
Zebra indexing
Les bases de données Koha sont indexées par le logiciel open-source Zebra. La documentation décrit Zebra comme :
« …Zebra is a high-performance, general-purpose structured text indexing and retrieval engine. It reads records in a variety of input formats (for example email, XML, MARC) and provides access to them through a powerful combination of Boolean search expressions and relevance-ranked free-text queries.
Zebra supporte d’importantes bases de données (dix millions de notices, dix gigabytes de données). Il permet de faire de manière sécurisée des mises à jour incrémentales de base de données en direct dans des systèmes. Du fait que Zebra soutienne le protocole de recherche d’information standard-industriel, Z39.50, vous pouvez chercher dans les bases de données Zebra grâce à une variété de programmes et outils , libres mais aussi commerciaux, qui interagissent avec ce protocole… « Zebra - Guide utilisateur et Référence, p. 1, http://www.indexdata.dk/zebra/doc/zebra.pdf
Ce bref guide vous expliquera comment configurer une base de données MARC21 et comment fonctionne la recherche. Les champs MARC cités concernent l’indexation des données bibliographiques et non l’indexation de la base de données d’autorités.
Note
L’indexation décrite ici est définie et utilisée par l’Université du Sud-Est des Etats-Unis. Votre indexation peut varier.
Indexing configuration
Koha utilise trois fichiers de configuration durant l’indexation.
The first configuration file (etc/zebradb/biblios/etc/bib1.att) contains the Z39.50 bib-1 attribute list, plus the Koha local use attributes for Biblio Indexes, Items Index, and Fixed Fields and other special indexes. The Z39.50 Bib-1 profile is made up of several different types of attributes: Use, Relation, Position, Structure, Truncation, and Completeness. The bib-1 “Use” attribute is represented on the chart; the other attributes are used primarily when doing searches. While there are over 150+ use attributes that could be used to define your indexing set, it’s unlikely that you will choose to use them all. The attributes you elect to use are those that become the indexing rules for your database. The other five attribute sets define the various ways that a search can be further defined, and will not specifically be addressed in this document. For a complete list of the standard Bib-1 attributes, go to https://www.loc.gov/z3950/agency/defns/bib1.html.
Le second fichier est etc/zebradb/marc_defs/[marc21|unimarc]/biblios/record.abs, si vous utilisez l’indexation grs1 [par défaut jusqu’à la 3.16] ou etc/zebradb/marc_defs/[marc21|unimarc]/biblios/biblio-koha-indexdefs.xml si vous utilisez l’indexation dom [par défaut depuis la 3.18]. Chaque fichier contient la syntaxe abstraite qui fait correspondre les champs MARC21 à l’ensemble des Attributs d’utilisation que vous avez choisi d’utiliser. Pour être plus précis, le fichier xml à activer doit être transformé en biblio-zebra-indexdefs.xsl. Lisez le début de biblio-zebra-indexdefs.xsl pour en savoir plus sur le sujet. Les règles définies dans ce fichier fournissent un service Bath de niveau 0 et 1 acceptable , qui inclut auteur, sujet, mot-clé et services exacts tels que les identificateurs (LCCN, ISBN, ISSN, etc.)
Le troisième fichier (etc/zebradb/ccl.properties) est tout ce qui concerne les critères de champs du Common Command Language (CCL). Ce fichier combine le dossier des attributs bib-1, le résumé du dossier et ajoute des classificateurs,généralement connus sous le nom d’indexes. Les classificateurs ou indexes, pour cette base de données, sont les suivants: pn, cpn, cfn, ti, se, ut, nb, ns, sn, lcn, callnum, su, su-to, su-geo, su-ut, yr,pubdate, acqdate, ln, pl, ab, nt, rtype, mc-rtype, mus, au, su-na, kw, pb, ctype, and an.
Le Tableau d’indexation de Koha résume le contenu de ces trois fichiers dans un format plus lisible. Les deux premières colonnes identifiées comme Attribut Z39.50 et Nom Z39.50 correspondent avec le fichier des attributs Z39.50 bib-1. La troisième colonne nommée Champs MARC indexés est là où vous trouverez les correspondances entre les champs MARC et les attributs. La quatrième colonne nommée Qualificateurs identifie les abréviations de recherche utilisées dans la requête interne CCL. La description suivante fournit une définition du mot “qualificateurs”.
Les qualificateurs sont utilisés pour diriger la recherche vers un index précis de recherche, comme le titre (ti) et l’auteur (au). La norme CCL elle-même ne précise pas d’ensemble particulier de qualificateurs mais suggère quelques notations abrégées. Vous pouvez personnaliser l’analyseur syntaxique CCL pour supporter un ensemble particulier de qualificateurs à refléter le profil courant de la cible. Généralement, un qualificateur correspond à un attribut Usage particulier au sein de l’ensemble de l’attribut BIB-1. Il est aussi possible de définir d’autres attributs, comme les attributs de structure.
Dans la colonne des « Etiquettes MARC indexées », des conventions d’écriture sont utilisées et ont un sens précis. Ces conventions sont :
Une étiquette de 3 chiffres (par exemple 100) signifie que tous les sous-champs de l’étiquette peuvent être utilisés dans une requête de recherche. Ainsi, si vous recherchez par exemple “Jackson” comme auteur, vous récupérerez les notices où Jackson apparaît comme le nom ou le prénom de l’auteur.
Une étiquette de 3 chiffres qui possède un “$” suivi d’une lettre (par exemple 600$a) signifie que la requête de recherche ne portera que sur le sous-champ “a” de cette étiquette.
Une étiquette de 3 chiffres suivie d’un “:” et d’une lettre (par exemple 240:w) signifie que la requête de recherche peut être encore plus précise et qualifiée. La lettre qui suit les “:” identifie comment la recherche doit être réalisée. Les valeurs les plus communes sont :”w” (mot), “p” (phrase), “s” (type), and “n” (numerique).
Le contenu des étiquettes, sous-champs MARC, et/ou des éléments fixes des champs listés dans ce tableau sont tous indexés. Vous verrez que chaque ligne d’attribut ne correspond pas toujours à un qualificatif spécifique (index). LC numéro de carte, ligne 9 est un exemple. Cependant, tous les mots indexés (une chaîne de caractères précédée ou suivie d’un espace) peuvent être recherchés en utilisant le mot clé “kw”. Ainsi, bien que l’index spécifique “LC numéro de carte” n’existe pas, vous pouvez toujours rechercher par le LCNN puisque l’étiquette 010 est assignée à l’attribut LC-numéro de carte. Pour le vérifier, vous pouvez entrer 72180055 dans le champ de recherche simple. Vous devriez retrouver “The gods themselves” d’Isaac Asimov.
Exemples d’éléments de champs fixes indexés qui peuvent être vus dans le graphique entre l’Attribut 8822 et l’Attribut 8703. Ces attributs sont utilisées habituellement comme limitation. Les attributs des champs fixes représentent actuellement les codes BK. D’autres codes de format, s’ils sont nécessaires, peuvent être définis.
Common command language searching
Koha utilise le Langage Commun de Commande (LCC) (ISO 8777) comme protocole de recherche interne. Les recherches lancées dans l’interface graphique utilisent ce protocole, bien que la personne qui fait une recherche ne sache pas quels indexes, opérateurs et limiteurs sont disponibles et sont utilisés pour effectuer la recherche. La personne qui fait la recherche peut utiliser la “Recherche Avancée” et accéder à certains des indexes utilisés et ainsi obtenir des résultats plus précis. Cependant, quelques usagers de la bibliothèque et membres du personnel préfèrent utiliser une commande de langage pour effectuer une recherche. Cette partie du manuel présente et explique l’utilisation d’une commande de langage pour une faire une recherche. Les indexes, opérateurs et limiteurs utilisés sont identiques à ceux utilisés dans l’interface graphique.
Index
The CCL standard itself doesn’t specify a particular set of qualifiers (indexes), but it does suggest a few short-hand notations such as “ti”, “au”, and “su”. Koha has a default set of indexes; it’s possible to customize that set by adding needed indexes based on local requirements. A qualifier (index) maps to a particular use-attribute within the Z39.50 BIB-1 attribute set. The complete Z39.50 Bib-1 Attribute can be viewed at https://www.loc.gov/z3950/agency/defns/bib1.html.
L’ensemble d’indexes standard de Koha est un exemple assez commun des règles d’indexation MARC21. Les indexes définis dans Koha sont des indexes utilisés habituellement par d’autres SIGBs. Les attributs définis Z39.50 Bib-1 correspondant aux indexes incluent :
Attribut Bib-1 |
Qualificateur (index) |
|---|---|
Nom de personne |
pn |
Raison sociale |
cpn |
Nom de congrès |
cfn |
Titre |
ti |
Title-series |
se |
Titre-uniforme |
ut |
ISBN |
nb |
ISSN |
ns |
Local number |
sn |
Local-classification |
lcn and callnum |
Sujet |
su, su-to, su-geo, su-ut |
Pubdate |
yr,pubdate |
Date d’Acquisition |
acqdate |
Langue |
ln |
Place-of-publication |
pl |
Abstract |
ab |
Notes |
nt |
Record-type |
rtype, mc-rtype, mus |
Auteur |
au, aut |
Subject-person-name |
su-na |
Any (keyword) |
kw |
Editeur |
pb |
Content-type |
ctype |
Koha-Auth-Number |
an |
Author-personal-bibliography |
aub |
Author-in-order |
auo |
Table:Attributs
Pour les tags MARC21 correspondant à chaque Attribut Bib-1 et à la combinaison d’index, consultez le Graphique d’indexation de Koha.
Audience examples
aud:a Préscolaire
aud:b Primaire
aud:c Pré-adolescent
aud:d Adolescent
aud:e Adulte
aud:f Spécialisé
aud:g Général
aud:j Jeunesse
Contents examples
fic:1 Fiction
fic:0 Non Fiction
bio:b Biographie
mus:j Enregistrement musical
mus:I Pas d’enregistrement musical
Search syntax
Dans la barre de recherche, un mot seul récupère généralement des ensembles de grande taille. Pour restreindre une recherche, vous pouvez utiliser plusieurs mots. Koha utilise automatiquement l’opérateur Booléen « et » pour créer un ensemble de notices correspondant à vos données. Lorsque vous souhaitez restreindre la recherche à un auteur, un titre, un sujet ou d’autres champs spécifiques, ou bien utiliser un opérateur Booléen, il n’y a pas d’autre moyen pour obtenir un résultat plus précis. L’usager peut bien sûr aller sur la page « Recherche avancée »; cependant si vous savez construire une recherche LCC, vous pouvez obtenir un résultat plus précis en utilisant la barre de recherche sur n’importe quelle page.
Il y a un ordre spécifique pour la syntaxe de recherche LCC. Bien qu’elle puisse être utilisée pour des recherches simples, c’est une manière efficace de réaliser des recherches complexes. Cela vous permet d’avoir un meilleur contrôle sur vos résultats de recherche. Pour construire une recherche LCC, saisissez d’abord le code d’index désiré, puis le signe égal, suivi du/des mots de recherche . Voir ci-dessus des exemples de recherche simple LCC.
ti=principes de comptabilité
au=brown joseph
su=poésie
su-na=Shakespeare
kw=marlin
Vous pouvez affiner votre recherche en combinant les termes de recherche avec les opérateurs Booléens “et”, “ou” ou “sauf”. Voir les exemples de recherche suivants utilisant les opérateurs Booléens.
ti=principes de comptabilité et au=brown joseph
su=poésie sauf su-na=Shakespeare
kw=communication et su=débat
Vous pouvez également choisir de rechercher des choses qui commencent par un caractère ou une série de caractères
ti,first-in-subfield=C (affichera tous les titres qui commencent par la lettre “C”)
D’autres recherches de localisation de chaînes peuvent être réalisées avec les mots-clés suivants :
rtrn : troncature à droite
ltrn : troncature à gauche
lrtrn : troncature à gauche et droite
st-date : type de date
st-numeric : type de numéro (entier)
ext : recherche exacte dans tout le sous-champ (ne fonctionne pas avec icu)
phr : recherche d’expression dans n’importe quel sous-champ
startswithnt : sous-champ commence avec
Using specific indexes and Boolean operators are not the only way a search can be refined. You can also refine your search as a phrase when looking for a title, author, or subject. The syntax for this search is index,phr=search words.
Voici les résultats de plusieurs types de recherche, pour la recherche des mots “Cour suprême”. Les résultats montrent que l’index de recherche et l’ordre des mots font une différence dans les résultats de recherche. Dans ces exemples s’affichent la quantité des résultats et la recherche elle-même. La recherche effectuée sera toujours affichée entre de simples guillemets.









Vous pouvez aussi choisir d’utiliser des limiteurs dans votre recherche. Quelques limiteurs basiques incluent les dates, langues, types de notices et types de documents. Dans la Recherche Avancée, vous pouvez cliquer sur la case ou saisir des données pour limiter la recherche. Vous pouvez aussi appliquer les mêmes limites avec LCC en utilisant la syntaxe des exemples suivants:
Par Date : su=cour suprême et yr,st-numeric=>2000

Lorsque vous limitez par date, vous pouvez utiliser les symboles « > » (plus que), « < » (moins que), « = » (égal), ou « aaaa-aaaa; » (intervalle).
Par Type de document : su=allaitement et itype:BK

Chaque bibliothèque a différents types de documents définis dans leur configuration de circulation. Lorsque vous paramétrez les types de documents, vous définissez un code et un nom pour chacun. Le nom s’affichera sur la page de la Recherche Avancée. Le code que vous avez saisi est utilisé comme une limite de recherche LCC, formaté comme « itype:x », ou « x » est son code assigné. L’ensemble initial de types de documents de Koha sera modifié en conséquence pour refléter vos collections, ainsi les limiteurs de vos types de documents peuvent être différents des initiaux. Voilà les limiteurs initiaux de types de documents.
itype:BKS Livres, Livrets, Livres d’exercices
itype:SR Cassettes Audio, CDs
itype:IR Classeurs
itype:CF CD-ROMs, DVD-ROMs, Ressources générales en ligne
itype:VR DVDs, VHS
itype:KT Kit
itype:AR Maquettes
itype:SER Périodiques
Par format : su=cour suprême not l-format:sr

Les limiteurs de format sont un dérivé d’une combinaison des positions LDR, 006 et 007. Les formats sont généralement définis comme ce qui suit.
l-format:ta a- Impression normale
l-format:tb b- Gros caractères
l-format:fk c- Braille
I-format:sd CD audio
l-format:ss Cassette audio
l-format:vf cassette vidéo
l-format:vd DVD video
l-format:co CD logiciel
I-format:cr Site web
Par type de contenu : su=cour suprême not ctype:l

Les types de contenu sont pris des étiquettes 008 MARC, positions 24-27.
Il y a deux types de limiteur qui ne sont pas décrits dans ce document. Ce sont: Public et Contenu. La seule différence dans la syntaxe du LCC est le limiteur réel. Ils sont reproduits ici au cas où vous voudriez utiliser ces limiteurs.
Koha search indexes
Zebra
Les champs ne sont pas tous indexés par défaut dans le moteur de recherche Zebra. Dessous, s’affichent les champs MARC21 indexés dans Zebra.
Champ |
Description |
|---|---|
Leader/06 |
Record-type, rtype |
Leader/07 |
Niveau bibliographique |
Leader/06-07 |
Material-type |
001 |
Control-number |
005 |
Date/temps-dernière-modification, dtml, date-temps-dernière-modification |
007 |
Microform-generation:n:range(data,11,1), Material-type,ff7-00:w:range(data,0,1), ff7-01:w:range(data,1,1), ff7-02:w:range(data,2,1), ff7-01-02:w:range(data,0,2) |
008 |
date-entered-on-file:n:range(data,0,5), date-entered-on-file:s:range(data,0,5), pubdate:w:range(data,7,4), pubdate:n:range(data,7,4), pubdate:y:range(data,7,4), pubdate:s:range(data,7,4), pl:w:range(data,15,3), ta:w:range(data,22,1), ff8-23:w:range(data,23,1), ff8-29:w:range(data,29,1), lf:w:range(data,33,1), bio:w:range(data,34,1), ln:n:range(data,35,3), ctype:w:range(data,24,4), Record-source:w:range(data,39,0) |
010 |
LC-card-number, Identifier-standard |
011 |
LC-card-number, Identifier-standard |
015 |
BNB-card-number, BGF-number, Number-db, Number-natl-biblio, Identifier-standard |
017 |
Number-legal-deposit, Identifier-standard |
018 |
Identifier-standard |
020$a |
ISBN:w, Identifier-standard:w |
020 |
Identifier-standard |
022$a |
ISSN:w, Identifier-standard:w |
022 |
Identifier-standard |
023 |
Identifier-standard |
024$a |
Identifier-other |
024 |
Identifier-standard |
025 |
Identifier-standard |
027 |
Report-number, Identifier-standard |
028 |
Number-music-publisher, Identifier-standard |
030 |
CODEN, Identifier-standard |
034 |
Map-scale |
035 |
Other-control-number |
037 |
Identifier-standard, Stock-number |
040 |
Code-institution, Record-source |
041$a |
ln-audio |
041$h |
language-original |
041$j |
In-soustitre |
041 |
ln |
043 |
Code-geographic |
050$b |
LC-call-number:w, LC-call-number:p, LC-call-number:s |
050 |
LC-call-number:w, LC-call-number:p, LC-call-number:s |
052 |
Geographic-class |
060 |
NLM-cote |
070 |
NAL-cote |
080 |
UDC-classification |
082 |
Dewey-classification:w, Dewey-classification:s |
086 |
Number-govt-pub |
100$9 |
Cross-Reference:w, Koha-Auth-Number |
100$a |
Author,Author:p, Author:s, Editor, Author-personal-bibliography, Author-personal-bibliography:p, Author-personal-bibliography:s |
100 |
Author, Author-title, Author-name-personal, Name, Name-and-title, Personal-name |
110$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
110 |
Author, Author-title, Author-name-corporate, Name, Name-and-title, Corporate-name |
111$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
111 |
Author, Author-title, Author-name-corporate, Name, Name-and-title, Conference-name |
130$n |
Thematic-number |
130$r |
Music-key |
130$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
130 |
Titre, Titre-uniforme |
210 |
Title, Title-abbreviated |
211 |
Title, Title-abbreviated |
212 |
Title, Title-other-variant |
214 |
Title, Title-expanded |
222 |
Title, Title-key |
240$r |
Music-key |
240$n |
Thematic-number |
240 |
Title:w, Title:p, Title-uniform |
243$n |
Thematic-number |
243$r |
Music-key |
243 |
Title:w, Title:p, Title-collective |
245$a |
Title-cover:w, Title-cover:p, Title-cover:s, Title:w, Title:p, Title:s |
245$c |
Author, Author-in-order:w, Author-in-order:p, Author-in-order:s |
245$9 |
Cross-Reference:w, Koha-Auth-Number |
245 |
Title:w, Title:p |
246 |
Title, Title:p, Title-abbreviated, Title-expanded, Title-former |
247 |
Title, Title:p, Title-former, Title-other-variant, Related-periodical |
260$a |
pl:w, pl:p |
260$b |
Publisher:w, Publisher:p |
260$c |
copydate, copydate:s |
260 |
Fournisseur, pl |
264 |
Fournisseur |
300 |
Extent:w, Extent:p |
400$a |
Name-and-title |
400$t |
Author-title, Name-and-title, Title, Title-series |
400$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
400 |
Author, Author-name-personal, Name, Personal-name |
410 |
Author, Corporate-name |
410$a |
Name-and-title |
410$t |
Author-title, Title, Title-series |
410$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
410 |
Author-name-corporate, Name |
411 |
Author, Conference-name |
411$a |
Name-and-title |
411$t |
Author-title, Title-series |
411 |
Author-name-corporate, Name |
440$a |
Title-series:w, Title-series:p |
440$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
440 |
Title-series:w, Title-series:p, Title, Title-series |
490$a |
Title-series:w, Title-series:p |
490 |
Title, Title-series |
490$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
500 |
Note:w, Note:p |
502 |
Material-type |
505$r |
Auteur |
505$t |
Titre |
505 |
Note:w, Note:p |
510 |
Indexed-by |
520 |
Abstract:w, Abstract:p |
521$a |
lex:n |
526$c |
arl, arl:n |
526$d |
arp, arp:n |
590 |
Note:w, Note:p |
600$a |
Name-and-title, Name, Personal-name, Subject-name-personal, Subject |
600$t |
Name-and-title, Title, Subject |
600$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
600 |
Name, Personal-name, Subject-name-personal, Subject |
610$a |
Name-and-title |
610$t |
Name-and-title, Title |
610$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
610 |
Name, Subject, Corporate-name |
611 |
Nom de congrès |
611$a |
Name-and-title |
611$t |
Name-and-title, Title |
611$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
611 |
Name, Subject |
630$n |
Thematic-number |
630$r |
Music-key |
630$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
630 |
Sujet |
650$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
650 |
Subject, Subject:p |
651$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
651 |
Name-geographic, Subject,Subject:p |
652$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
653$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
653 |
Subject, Subject:p |
654$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
654 |
Sujet |
655$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
655 |
Sujet |
656$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
656 |
Sujet |
657$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
657 |
Sujet |
690$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
690 |
Subject, Subject:p |
700$9 |
Cross-Reference, Koha-Auth-Number |
700$a |
Author, Author:p |
700$n |
Thematic-number |
700$r |
Music-key |
700$t |
Author-title, Name-and-title, Title, Title-uniform |
700 |
Author, Author-name-corporate, Author-name-personal, Name, Editor, Personal-name |
710 |
Author, Corporate-name |
710$t |
Author-title, Name-and-title, Title, Title-uniform |
710$a |
Name-and-title |
710$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
710 |
Author, Name |
711$a |
Name-and-title |
711$t |
Author-title, Title, Title-uniform |
711$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
711 |
Author-name-corporate, Name, Conference-name |
730$n |
Thematic-number |
730$r |
Music-key |
730$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
730 |
Titre, Titre-uniforme |
740 |
Title, Title-other-variant |
773$t |
Host-item |
780$t |
Titre |
780$w |
Numéro-contrôle-notice |
780 |
Title, Title-former, Related-periodical |
785$w |
Numéro-contrôle-notice |
785 |
Related-periodical |
787$w |
Numéro-contrôle-notice |
800$a |
Name-and-title |
800$t |
Author-title, Name-and-title, Title, Title-series |
800$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
800 |
Author, Author-name-personal, Name, Personal-name |
810$a |
Name-and-title |
810$t |
Author-title, Name-and-title, Title, Title-series |
810$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
810 |
Author, Corporate-name, Author-name-corporate, Name |
811$a |
Name-and-title |
811$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
811$t |
Author-title, Name-and-title, Title, Title-series |
811 |
Author, Author-name-corporate, Name, Conference-name |
830$9 |
Koha-Auth-Number |
830 |
Title, Title-series |
840 |
Title, Title-series |
942$0 |
totalissues:n, totalissues:s |
942$2 |
cn-bib-source |
942$6 |
cn-bib-sort:n, cn-bib-sort:s |
942$c |
itemtype:w |
942$n |
Suppress:w, Suppress:n |
942$h |
cn-class |
942$i |
cn-item |
942$k |
cn-prefix |
942$m |
cn-suffix |
952$0 |
withdrawn:n, withdrawn:w |
952$1 |
lost, lost:n |
952$2 |
classification-source |
952$3 |
materials-specified |
952$4 |
damaged:n, damaged:w |
952$5 |
restricted:n, restricted:w |
952$6 |
cn-sort:n, cn-sort:s |
952$7 |
notforloan:n, notforloan:w |
952$8 |
ccode |
952$9 |
itemnumber:n, itemnumber:s |
952$a |
homebranch |
952$b |
holdingbranch |
952$c |
location |
952$d |
Date-of-acquisition, Date-of-acquisition:d, Date-of-acquisition:s |
952$e |
acqsource |
952$f |
coded-location-qualifier |
952$g |
price |
952$j |
stack:n, stack:w |
952$l |
issues:n, issues:w, issues:s |
952$m |
renewals:n, renewals:w |
952$n |
reserves:n, reserves:w |
952$o |
Local-classification:w, Local-classification:p, Local-classification:s |
952$p |
barcode, barcode:n |
952$q |
onloan:n, onloan:w |
952$r |
datelastseen |
952$s |
datelastborrowed |
952$t |
copynumber |
952$u |
uri:u |
952$v |
replacementprice |
952$w |
replacementpricedate |
952$y |
itype:w |
952$z |
Note:w, Note:p |
999$c |
Local-Number:n, Local-Number:w, Local-Number:s |
999$d |
biblioitemnumber:n, biblioitemnumber:w, biblioitemnumber:s |
Table : Indexes
Index Elasticsearch
The Elasticsearch indexes are available in
admin/searchengine/elasticsearch/mappings.yaml
Ils sont copiés ici pour vous y référer plus facilement.
Index de notices bibliographiques
Index bibliographiques MARC21
Nom de l’index |
Champs MARC |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
résumé |
520 |
|
acqsource |
952$e |
|
arl |
526$c |
|
arp |
526$d |
|
auteur |
100$a |
|
110$a |
||
111$a |
||
245$c |
||
700$a |
||
author-in-order |
245$c |
|
author-name-corporate |
110 |
|
111 |
||
711 |
||
810 |
||
811 |
||
author-name-personal |
100 |
|
400 |
||
700 |
||
800 |
||
author-personal-bibliography |
100$a |
|
author-title |
100 |
|
110 |
||
111 |
||
400$t |
||
410$t |
||
411$t |
||
700$t |
||
710$t |
||
711$t |
||
800$t |
||
810$t |
||
811$t |
||
code à barres |
952$p |
|
bgf-number |
015 |
|
niveau bibliographique |
leader/7 |
|
biblioitemnumber |
999$d |
|
bio |
008/34 |
|
bnb-card-number |
015 |
|
ccode |
952$8 |
|
classification-source |
952$2 |
|
cn-bib-sort |
942$6 |
|
cn-bib-source |
942$2 |
|
cn-class |
942$h |
|
cn-item |
942$i |
|
cn-prefix |
942$k |
|
cn-sort |
952$6 |
|
cn-suffix |
942$m |
|
code-geographic |
043 |
|
code-institution |
040 |
|
coded-location-qualifier |
952$f |
|
coden |
030 |
|
nom de congrès |
111 |
|
411 |
||
611 |
||
711 |
||
811 |
||
numéro de contrôle |
001 |
|
copydate |
260$c |
|
copynumber |
952$t |
|
raison sociale |
110 |
|
410 |
||
610 |
||
710 |
||
810 |
||
cross-reference |
100$9 |
|
245$9 |
||
700$9 |
||
ctype |
008/24-27 |
|
curriculum |
658$a $b $c |
|
endommagé |
952$4 |
|
date d’entrée dans le fichier |
008/00-05 |
|
date d’acquisition |
952$d |
|
date de plublication |
008/07-10 |
|
date de dernière modification |
005 |
|
datelastborrowed |
952$s |
|
datelastseen |
952$r |
|
classification dewey |
082 |
|
dissertation-information |
502 |
|
éditeur |
100$a |
|
700 |
||
extent |
300 |
|
ff7-00 |
007/00 |
|
ff7-01 |
007/01 |
|
ff7-01-02 |
007/00-01 |
|
ff7-02 |
007/02 |
|
ff8-23 |
008/23 |
|
ff8-29 |
008/29 |
|
geographic-class |
052 |
|
geolocation_lat |
034$s |
added in 24.05 |
geolocation_lon |
034$t |
added in 24.05 |
holdingbranch |
952$b |
|
homebranch |
952$a |
|
host-item |
773$a $t |
|
host-item-number |
773$9 |
|
identifier-other |
024$a |
|
identifier-publisher-for-music |
028 |
|
identifier-standard |
010 |
|
011 |
||
015 |
||
017 |
||
018 |
||
020$a |
||
022$a |
||
index-term-genre |
655$a |
|
index-term-uncontrolled |
653$a |
|
indexé par |
510 |
|
interest-age-level |
521$a |
|
interest-grade-level |
521$a |
|
isbn |
020$a |
|
issn |
022$a |
|
fascicules |
952$l |
|
itemnumber |
952$9 |
|
type de document |
942$c |
|
952$y |
||
koha-auth-number |
100$9 |
|
110$9 |
||
111$9 |
||
130$9 |
||
245$9 |
||
400$9 |
||
410$9 |
||
440$9 |
||
490$9 |
||
600$9 |
||
610$9 |
||
611$9 |
||
630$9 |
||
648$9 |
||
650$9 |
||
651$9 |
||
652$9 |
||
653$9 |
||
654$9 |
||
655$9 |
||
656$9 |
||
657$9 |
||
662$9 |
||
690$9 |
||
691$9 |
||
696$9 |
||
697$9 |
||
698$9 |
||
699$9 |
||
700$9 |
||
710$9 |
||
711$9 |
||
730$9 |
||
751$9 |
||
796$9 |
||
797$9 |
||
797$9 |
||
798$9 |
||
799$9 |
||
800$9 |
||
810$9 |
||
811$9 |
||
830$9 |
||
896$9 |
||
897$9 |
||
898$9 |
||
899$9 |
||
language-original |
041$h |
|
lc-call-number |
050$b |
|
lc-card-number |
010 |
|
011 |
||
lexile-number |
521$a |
|
lf |
008/33 |
|
llength |
leader/00-04 |
|
ln |
008/35-37 |
|
ln-audio |
041$a |
|
In-soustitre |
041$j |
|
classification locale |
952$o |
|
numéro local |
999$c |
|
location |
952$c |
|
perdu |
952$1 |
|
map-scale |
034 |
|
type de matériel |
007 |
|
materials-specified |
952$3 |
|
microform-generation |
007/11 |
|
music-key |
130$r |
|
240$r |
||
243$r |
||
630$r |
||
700$r |
||
730$r |
||
nal-call-number |
070 |
|
nom |
100 |
|
110 |
||
111 |
||
400 |
||
600$a |
||
610 |
||
611 |
||
700 |
||
710 |
||
711 |
||
800 |
||
810 |
||
811 |
||
nom et titre |
100 |
|
110 |
||
111 |
||
400$a $t |
||
410$a |
||
411$a |
||
600$a $t |
||
610$a $t |
||
611$a $t |
||
700$t |
||
710$a $t |
||
711$a |
||
800$a $t |
||
810$a $t |
||
811$a $t |
||
nom géographique |
651 |
|
751$a |
||
nlm-call-number |
060 |
|
not-onloan-count |
999$x |
|
note |
500 |
|
505 |
||
520 |
added in 24.05 |
|
561 |
added in 24.05 |
|
563 |
added in 24.05 |
|
590 |
||
952$z |
||
notforloan |
952$7 |
|
number-db |
015 |
|
number-govt-pub |
086 |
|
numéro de dépôt légal |
017 |
|
number-local-acquisition |
952$i |
|
number-natl-biblio |
015 |
|
onloan |
952$q |
|
autre numéro de contrôle |
035 |
|
nom de personne |
100 |
|
400 |
||
600$a |
||
700 |
||
800 |
||
pl (publisher-location) |
008/15-17 |
|
260a |
||
264a |
||
752ad |
added in 24.05 |
|
price |
952$g |
|
fournisseur |
260 |
|
264 |
||
éditeur |
260$b |
|
reading-grade-level |
521$a |
|
numéro-contrôle-notice |
770$w |
|
772$w |
||
773$w |
||
774$w |
||
775$w |
||
776$w |
||
777$w |
||
780$w |
||
785$w |
||
787$w |
||
800$w |
||
810$w |
||
811$w |
||
830$w |
||
record-source |
008/39 |
|
related-periodical |
247 |
|
780 |
||
785 |
||
renouvellements |
952$m |
|
replacementprice |
952$v |
|
replacementpricedate |
952$w |
|
numéro de rapport |
027 |
|
réservations |
952$n |
|
suspendu |
952$5 |
|
rtype |
leader/06 |
|
stack |
952$j |
|
numéro d’inventaire |
037 |
|
su-geo |
651$a |
|
sujet |
600$a |
|
600$t |
||
610$a |
||
611 |
||
630$n |
||
630$r |
||
650$a |
||
650$b |
||
650$c |
||
650$d |
||
650$v |
||
650$x |
||
650$y |
||
650$z |
||
651 |
||
653$a |
||
sujet nom de personne |
600$a |
|
suppression |
942$n |
|
ta |
008/22 |
|
thematic-number |
130$n |
|
240$n |
||
243$n |
||
630$n |
||
700$n |
||
730$n |
||
titre |
130 |
|
210 |
||
211 |
||
212 |
||
214 |
||
222 |
||
240 |
||
245$a |
||
246 |
||
247 |
||
490$a |
||
505$t |
||
700$t |
||
710$t |
||
711$t |
||
730 |
||
740 |
||
780 |
||
785 |
||
titre abrégé |
210 |
|
211 |
||
246 |
||
title-cover |
245$a |
|
title-expanded |
214 |
|
246 |
||
title-former |
246 |
|
247 |
||
780 |
||
title-key |
222 |
|
title-later |
785 |
|
title-other-variant |
212 |
|
247 |
||
740 |
||
title-series |
440$a |
|
490$a |
||
titre-uniforme |
130 |
|
240 |
||
700$t |
||
710$t |
||
711$t |
||
730 |
||
totalissues |
942$9 |
|
udc-classification |
080 |
|
uri |
952$u |
|
retiré des collections |
952$0 |
Index bibliographiques UNIMARC
Nom de l’index |
Champs MARC |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
auteur |
200$f |
|
200$g |
||
700$a |
||
701 |
||
700$a |
||
bio |
105$a/12 |
|
ccode |
995$8 |
|
ctype |
105$a/04-07 |
|
date d’entrée dans le fichier |
099$c |
|
date d’acquisition |
995$5 |
|
date de plublication |
100$a/09-12 |
|
date de dernière modification |
099$d |
|
ff8-29 |
105$a/08 |
|
holdingbranch |
995$c |
|
homebranch |
995$b |
|
host-item-number |
461$9 |
|
identifier-standard |
010$a $z |
|
011$a $y $z |
||
isbn |
010$a $z |
|
issn |
011$a $y $z |
|
itemnumber |
995$9 |
|
itype |
200$b |
|
995$r |
||
lc-card-number |
995$j |
|
lf |
105$a/11 |
|
ln |
101$a |
|
classification locale |
686 |
|
995$k |
||
numéro local |
001 |
|
location |
995$e |
|
not-onloan-count |
999$x |
|
notforloan |
995$o |
|
onloan |
995$n |
|
pl (publisher location) |
210$a |
added in 24.05 |
214$a |
added in 24.05 |
|
éditeur |
210$c |
|
su-geo |
607$a |
|
sujet |
600 |
|
600$a |
||
601 |
||
602 |
||
604 |
||
605 |
||
606 |
||
607 |
||
608 |
||
610 |
||
suppression |
955$n |
|
ta |
100$a/17 |
|
titre |
200$a |
|
200$c |
||
200$d |
||
200$e |
||
200$h |
||
200$i |
||
205 |
||
304$a |
||
327$a |
||
327$b |
||
327$c |
||
327$d |
||
327$e |
||
327$f |
||
327$g |
||
327$h |
||
327$i |
||
328$t |
||
410$t |
||
411$t |
||
412$t |
||
413$t |
||
421$t |
||
422$t |
||
423$t |
||
424$t |
||
425$t |
||
430$t |
||
431$t |
||
432$t |
||
433$t |
||
434$t |
||
435$t |
||
436$t |
||
437$t |
||
440$t |
||
441$t |
||
442$t |
||
443$t |
||
444$t |
||
445$t |
||
446$t |
||
447$t |
||
448$t |
||
451$t |
||
452$t |
||
453$t |
||
454$t |
||
455$t |
||
456$t |
||
461$t |
||
462$t |
||
463$t |
||
464$t |
||
470$t |
||
481$t |
||
482$t |
||
488$t |
||
title-series |
225$a |