Administración
Parámetros básicos
Ir a: Más > Administración
Importante
Configure todos los “parámetros” en el orden que aparecen.
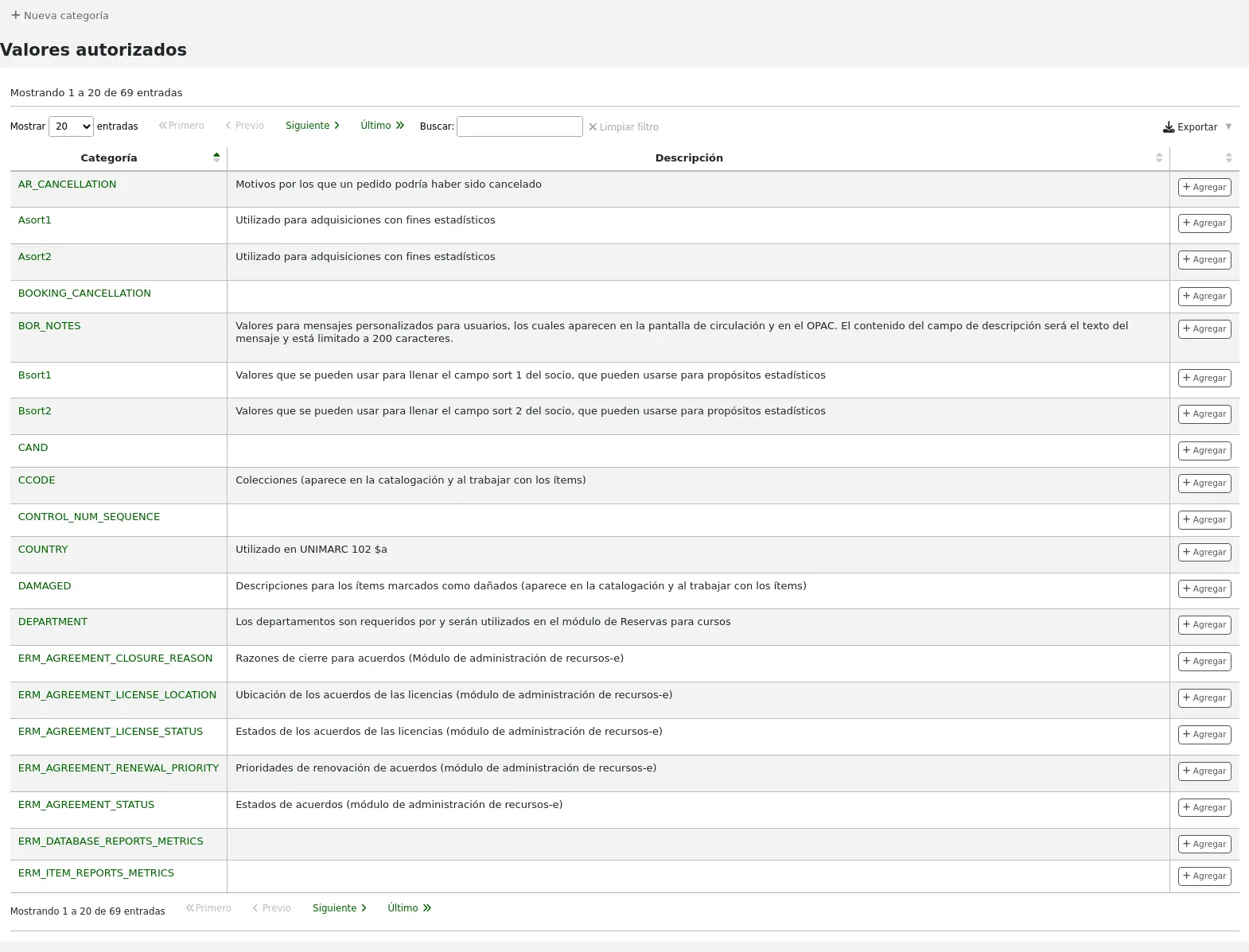
Bibliotecas
Al configurar su sistema Koha tendrá que completar la información para cada biblioteca que va a compartir su sistema. Estos datos son utilizados en diversas áreas de Koha.
Get there: More > Administration > Basic parameters > Libraries
Nota
Only staff with the manage_libraries permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
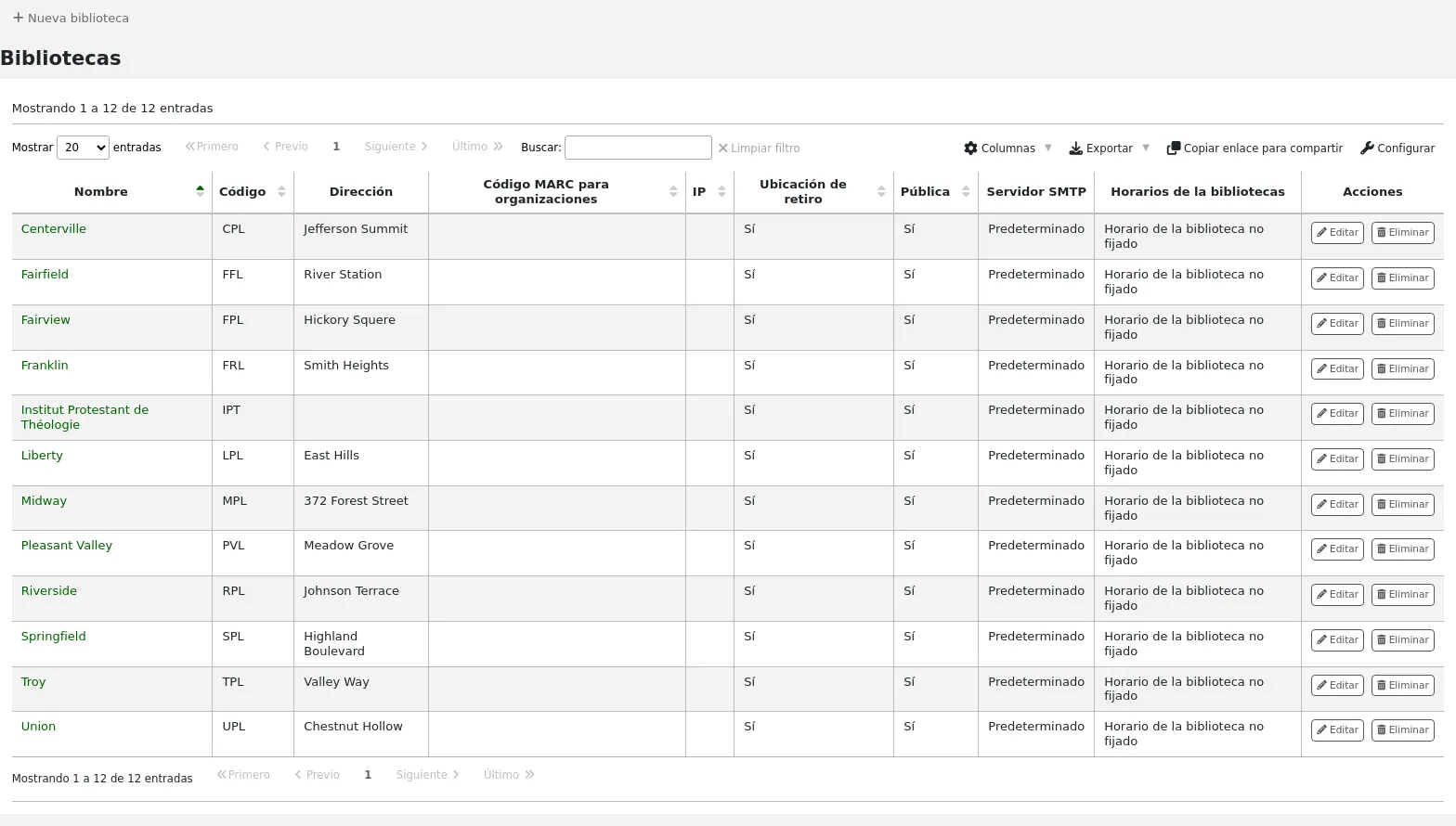
Al visitar esta página se presenta una lista de las bibliotecas que ya han sido añadidas al sistema.
Nota
You can customize the columns of this table in the Table settings section of the Administration module (table id: libraries).
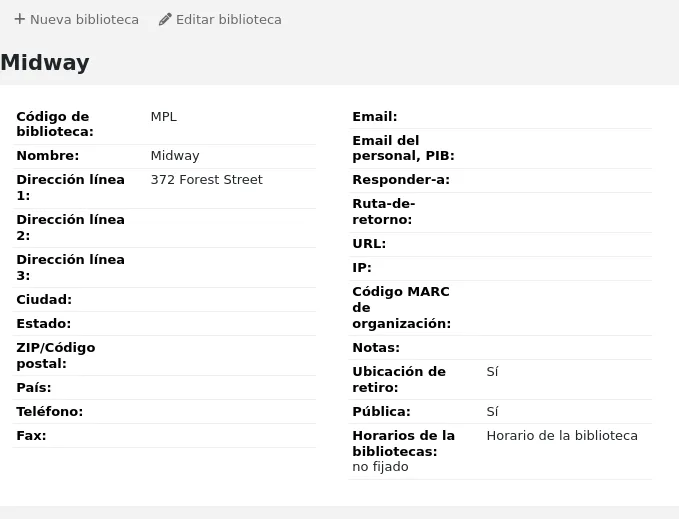
Clicking on the library’s name will bring you to a detailed view of the library’s information.
Agregando una biblioteca
Agregar una nueva biblioteca
Haga clic en “Nueva biblioteca”
Fill out the form
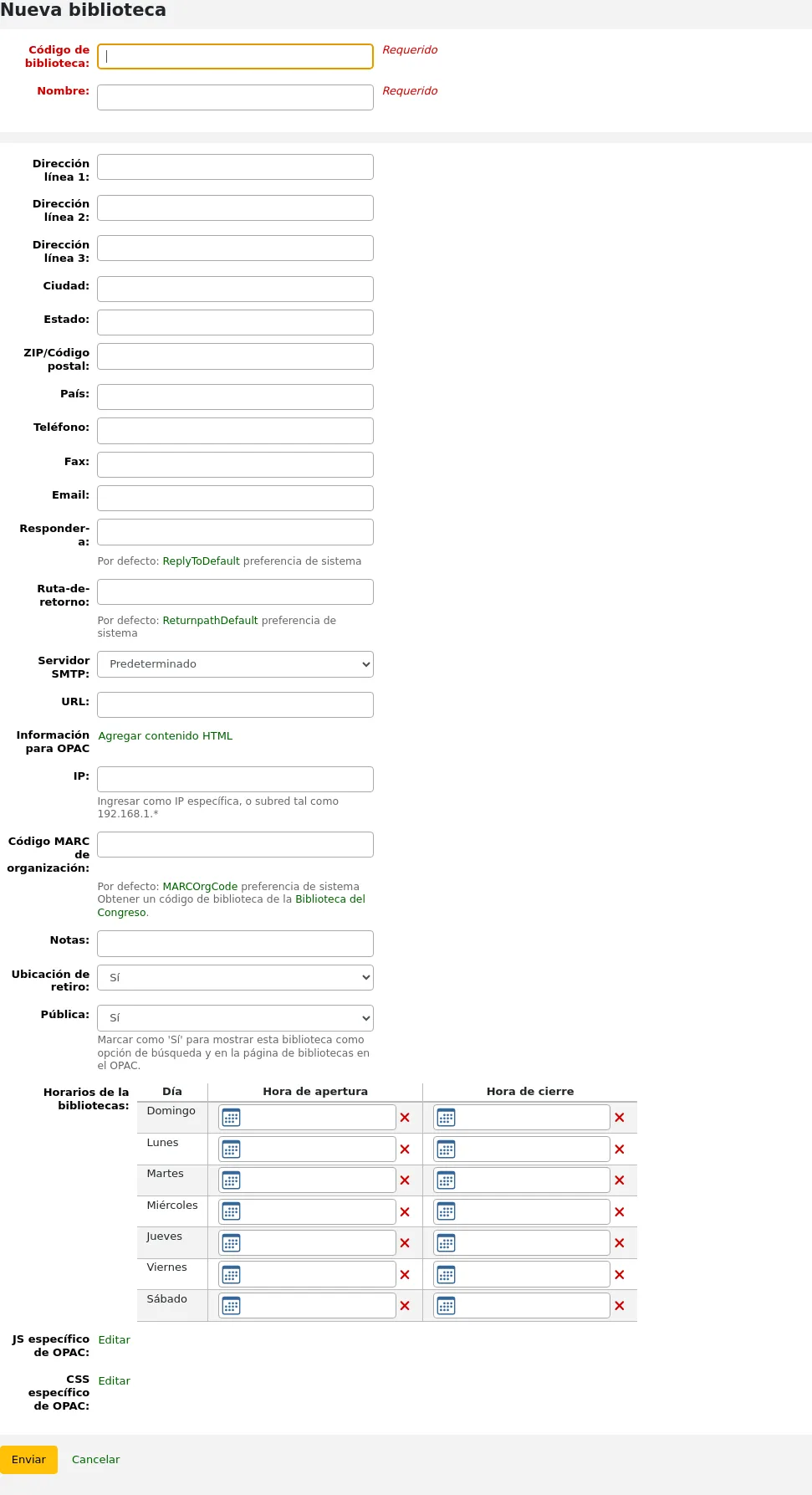
Library code (required): the code should not contain any spaces or hyphens and be 10 or fewer characters. This code will be used as a unique identifier in the database.
Name (required): the name will be displayed on the OPAC and staff interface wherever the library name displays, and should be a name that makes sense to your patrons and staff.
Address, city, state, zip/postal code, country, phone, fax: the address and contact fields can be used to make notices custom for each library, they will also be displayed in the “Libraries” page of the OPAC, if this library is set as “Public”
Email: the email address field is not required, but it should be filled for every library in your system
Nota
Asegúrese de ingresar la dirección de email de la biblioteca para asegurarse que los avisos se envían hacia y desde la dirección correcta
Nota
If no email address is entered here, the address in the KohaAdminEmailAddress system preference will be used to send notices from this library
ILL staff email: if this library uses a specific email address for interlibrary loan management, enter it here
Nota
If no email address is entered here, the address in the ILLDefaultStaffEmail system preference will be used to receive ILL requests to this library
Reply-To: you can enter a different “Reply-To” email address. This is the email address that all replies will go to.
Nota
If no email address is entered here, the address in the ReplytoDefault system preference will be used to receive replies to this library
Return-Path: you can enter a different “Return-Path” email address. This is the email address that all bounced messages will go to.
Nota
If no email address is entered here, the address in the ReturnpathDefault system preference will be used to receive bounced messages from this library.
SMTP server: if this library uses a different SMTP server from the default, specify it here.
URL: if this field is populated, the library name will be linked in the holdings table on the OPAC
OPAC info: this leads to the HTML customization tool, so that you can add additional information about the library. This information will appear in the “Libraries” page in the OPAC, as well as in the holdings table in the OPAC.
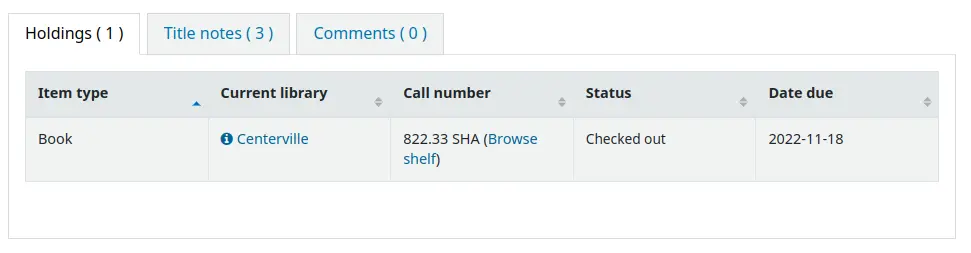
Clicking on the library name that has a small “i” icon next to it will open a pop-up with the information.
IP: this field does not have be filled in unless you plan on limiting access to the staff interface to a specific IP address or range of IP addresses.
Nota
Library IP addresses and ranges are used by the StaffLoginLibraryBasedOnIP and the StaffLoginRestrictLibraryByIP system preferences.
MARC organization code: if this library has a specific MARC organization code, you can enter it here.
Nota
If left blank, the code entered in the MARCOrgCode system preference will be used for this library.
Notes: if you have any notes you can put them here. These will not show in the OPAC.
Pickup location: choose whether this library will display as an available pickup location for holds.
Public: choose whether this library will appear in the “Libraries” page on the OPAC, as well as as a limit option in the OPAC advanced search.
Opening hours: if you do hourly loans, fill out the library’s opening hours for each day of the week. You can then set the ConsiderLibraryHoursInCirculation system preference according to your policies.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 24.05.
UserJS: use this field to add custom JavaScript to the OPAC of this library (when patrons are logged in, or if there is a
SetEnv OPAC_BRANCH_DEFAULTentry in the Apache configuration file)Version
This feature was added in Koha version 23.11.
Nota
General modifications applicable to all libraries can be put in the OPACUserJS system preference.
UserCSS: use this field to add custom CSS to the OPAC of this library (when patrons are logged in, or if there is a
SetEnv OPAC_BRANCH_DEFAULTentry in the Apache configuration file)Version
This feature was added in Koha version 23.11.
Nota
General modifications applicable to all libraries can be put in the OPACUserCSS system preference.
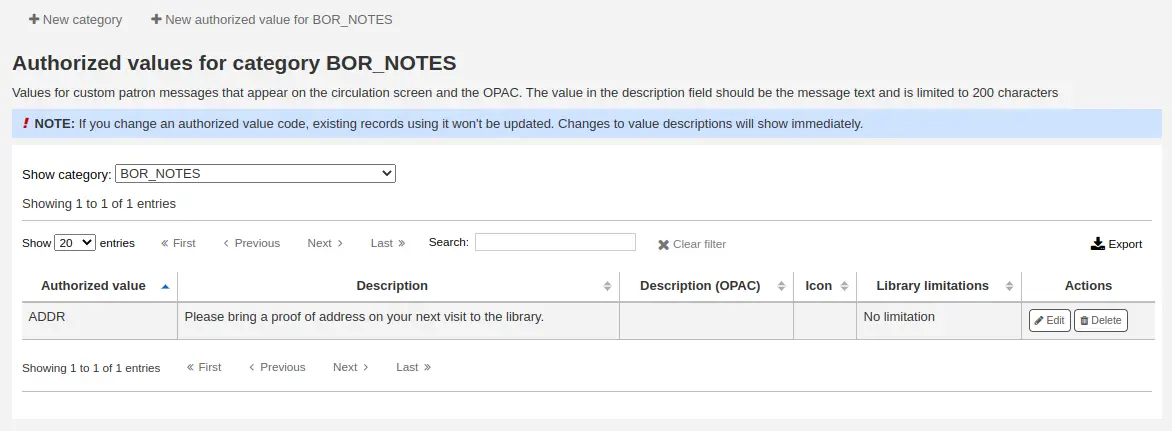
If you have any additional fields for libraries (branches), they will be displayed at the bottom of the form.
Click “Submit” to save the new library.
Editando/eliminando una biblioteca
From the libraries table, click “Edit” or “Delete” to edit or delete a library.

Advertencia
You will be unable to edit the “Library code”.
Advertencia
Usted no podrá borrar bibliotecas que tengan usuarios o ítems asociados a ellas.

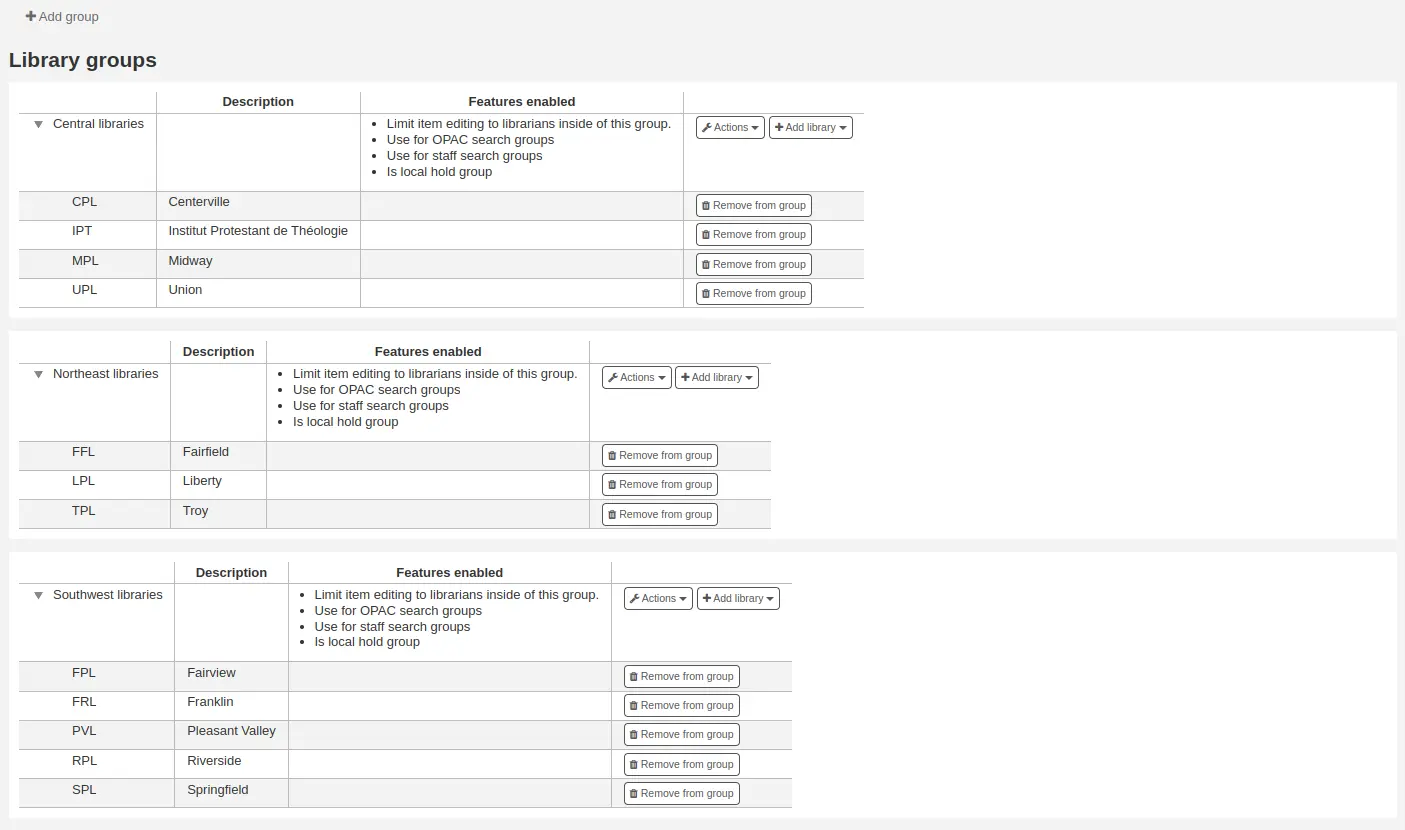
Grupos de bibliotecas
Library groups can serve various purposes: to limit access to patron data, to limit item modification, to limit OPAC or staff interface searches, or to define holds behavior.
Get there: More > Administration > Basic parameters > Library groups
Nota
Only staff with the manage_libraries permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Al visitar esta página se le presentará una lista de los grupos que ya han sido agregados al sistema.
Agregando un grupo
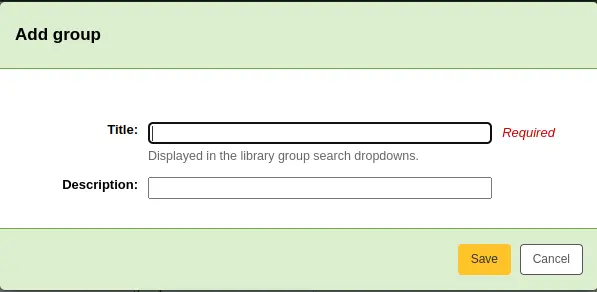
To create a new library group,
Click the “Add group” button at the top of the screen.
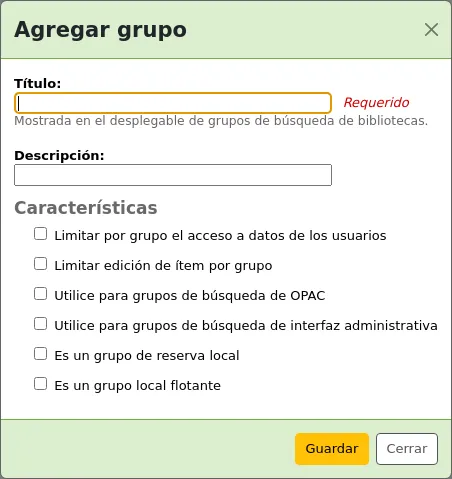
Title (required): give the group a title. This title will be displayed in the advanced search limit dropdown.
Description: optionally, enter a description for this group. The description is only used in this page to give an idea of what the group is used for.
Features: check the use of this group
Limit patron data access by group: this will limit staff members from seeing other groups” patrons.
Nota
This can be overridden with the view_borrower_infos_from_any_libraries permission (or the superlibrarian permission).
Limit item editing by group: this will limit staff members from editing items from other groups” libraries.
Nota
This can be overridden with the edit_any_item permission (or the superlibrarian permission).
Use for OPAC search groups: this will make the group visible in the library dropdown menu at the top of the OPAC (when the OpacAddMastheadLibraryPulldown system preference is set to “Add”) and on the advanced search page.
Use for staff search groups: this will make the group visible in the library dropdown menu in the staff interface advanced search.
Is local hold group: this will make this group a local hold group, which can be used to add hold policies in the circulation rules to limit patrons to placing holds on items within the group only.
Is local float group: this will make this group a local float group, which can be used in a return policy or in a hold policy in circulation rules to determine if an item “floats” (stays at the check-in library) or is transferred back to its home library.
Click “Save” to create the group.
Agregando una biblioteca al grupo
Haga clic en el botón “Agregar biblioteca” al lado del grupo para agregar una biblioteca a este grupo. Se le presentará con una lista de bibliotecas que no están en el grupo.
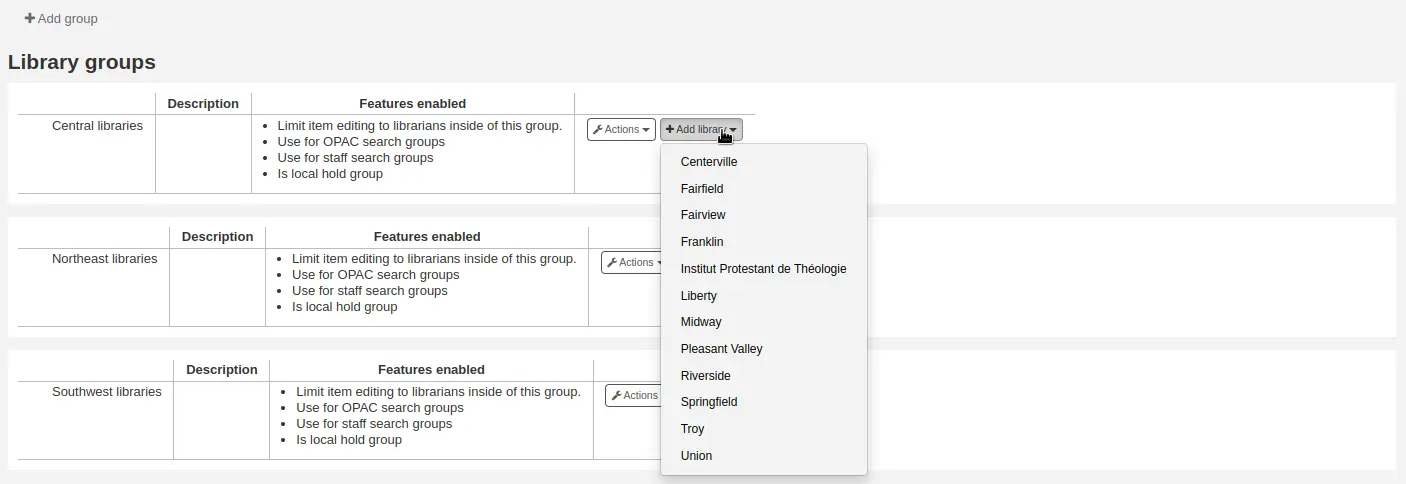
Agregando un sub-grupo
If your system is very large, you can create sub-groups. Click on the “Actions” button next to the group and select the “Add a sub-group” option.
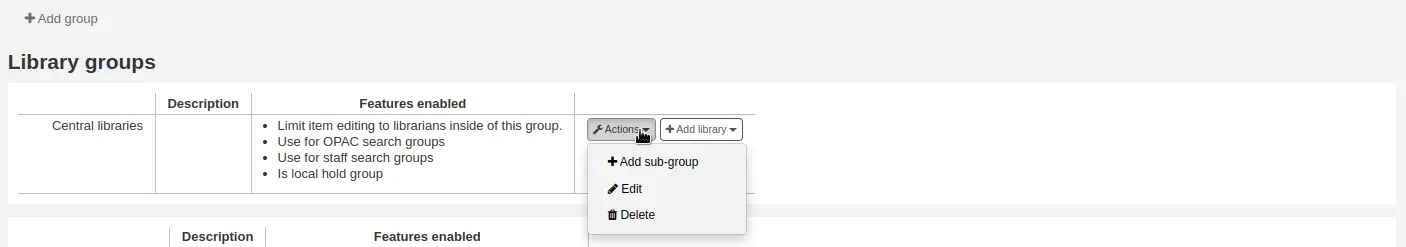
Fill in the title and the description (optional) of the sub-group. The features will be inherited from the parent group.
Eliminar un grupo
Para borrar un grupo, haga clic en el botón “Acciones” al lado del grupo y seleccione la opcion “Borrar”.

The system will ask to confirm the deletion.
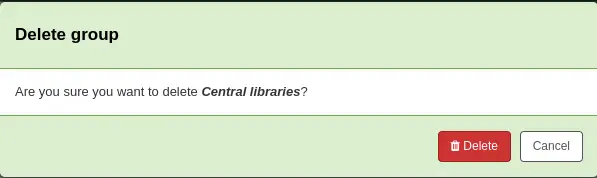
Click “Delete” to confirm and delete the group.
Circulation desks
Koha allows you to define several circulation desks within a single library. For example, if you have an adult circulation desk and a children’s circulation desk, or if you have a different desk for each floor or each department.
Make sure to enable the UseCirculationDesks system preference to use this functionality.
Get there: More > Administration > Patrons and circulation > Circulation desks
Adding circulation desks
To add a new circulation desk, click on the “New desk” button at the top of the page.
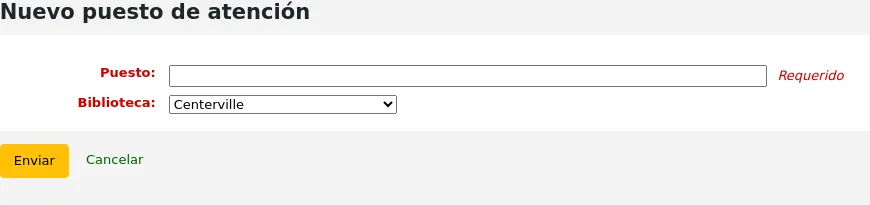
In the “Desk” field, enter a name for your desk.
Choose the library in which this desk is.
Click “Submit”.
Editing a circulation desk
To edit an existing circulation desk, click on the “Edit” button to the right of the desk to modify.
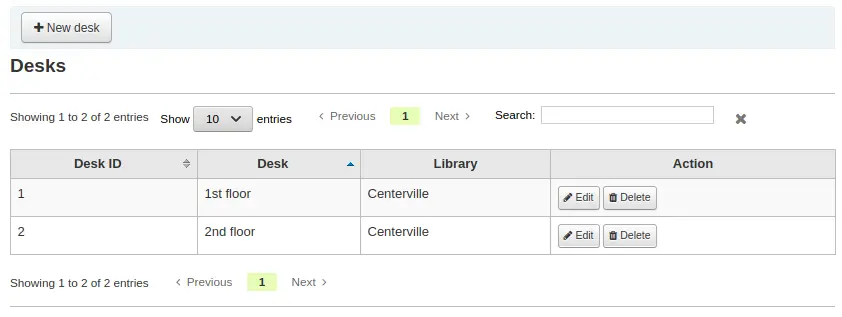
From there, you can change the name and/or the library of the desk.
Deleting a circulation desk
To delete an existing circulation desk, click on the “Delete” button to the right of the desk to remove.
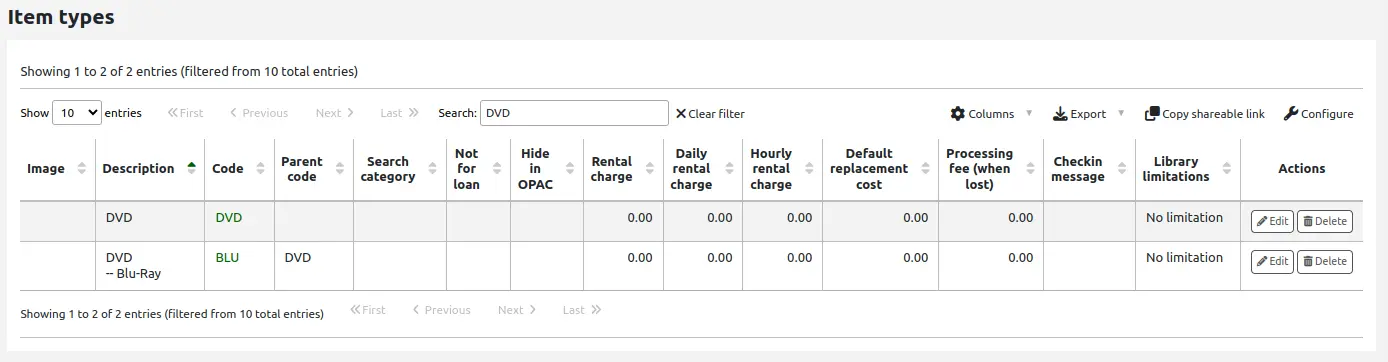
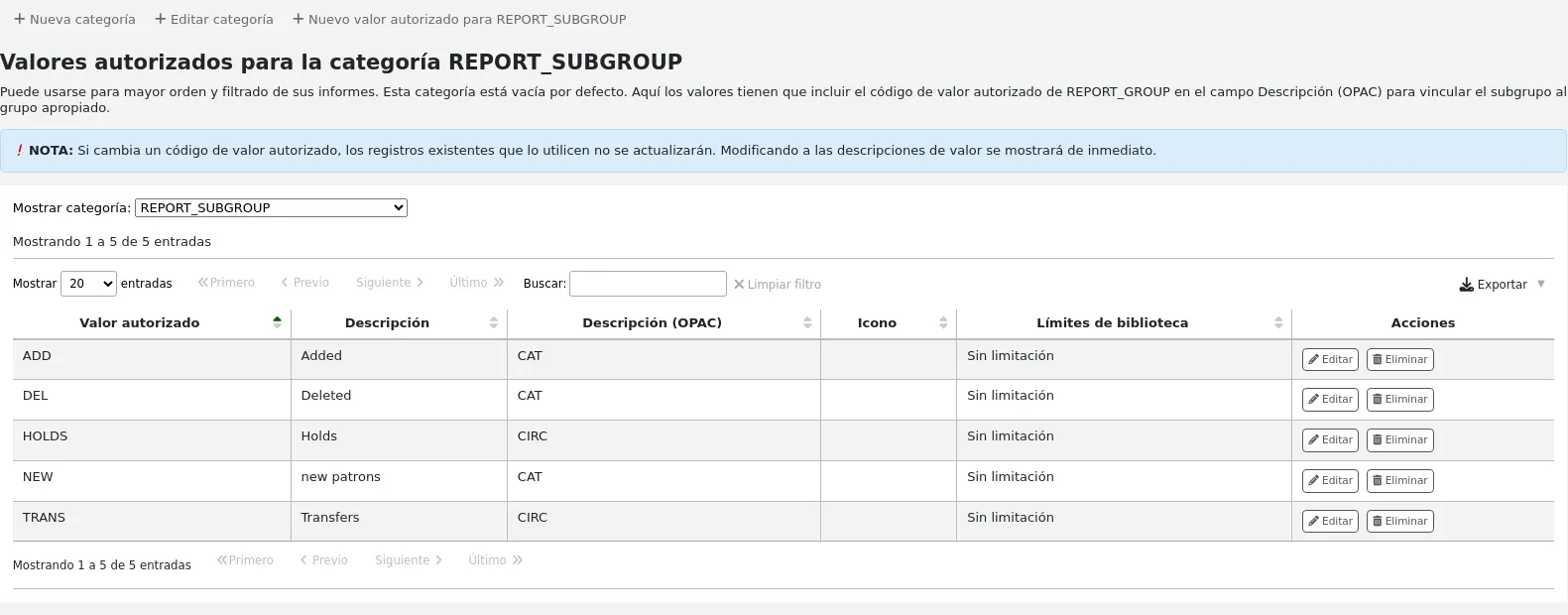
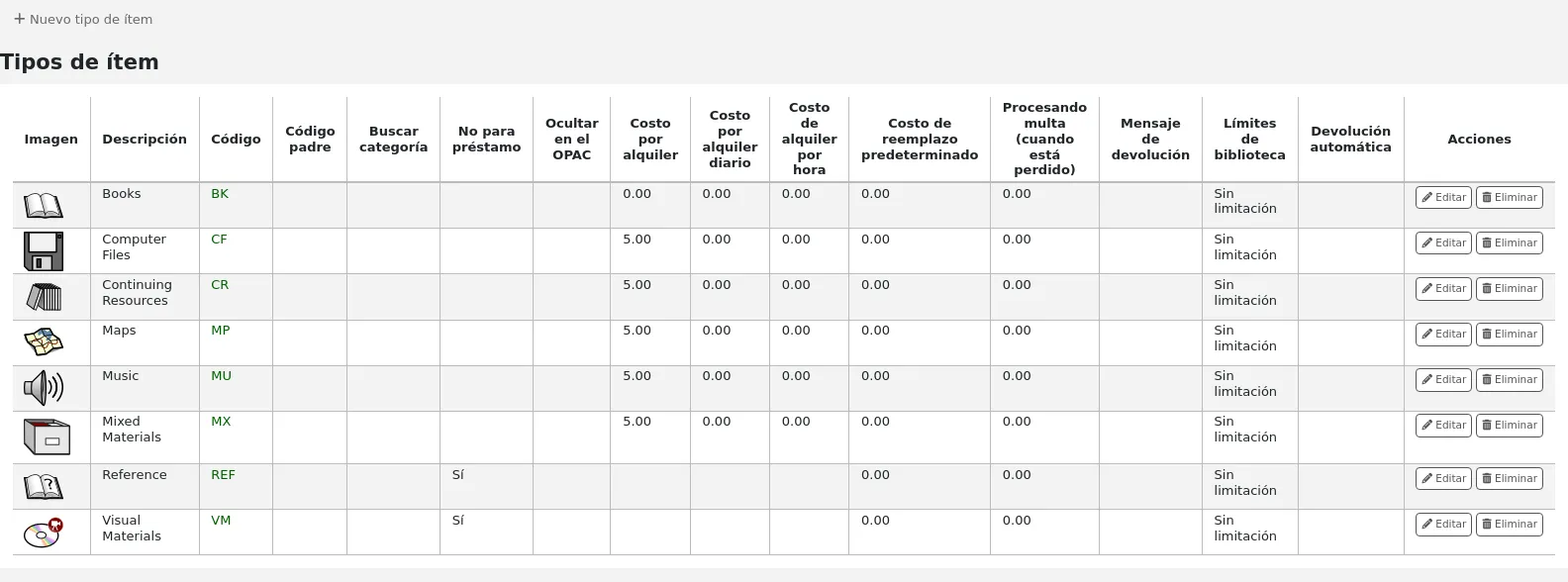
Tipos de ítem
Llegar allí: Más > Administración > Parámetros básicos > Tipos de ejemplares
Nota
Only staff with the manage_itemtypes permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Koha allows you to organize your collection by item types and collection codes. Along with libraries and patron categories, item types are used to control circulation rules.
Los tipos de ítems normalmente se refieren al tipo de material (libros, CD, DVD, etc.), pero se pueden utilizar en la forma más conveniente para su biblioteca.
Nota
You can customize the columns of this table in the Table settings section of the Administration module (table id: table_item_type).
Agregando tipos de ejemplares
To add a new item type,
Click the “New item type” button at the top of the item types page.
Fill out the form:
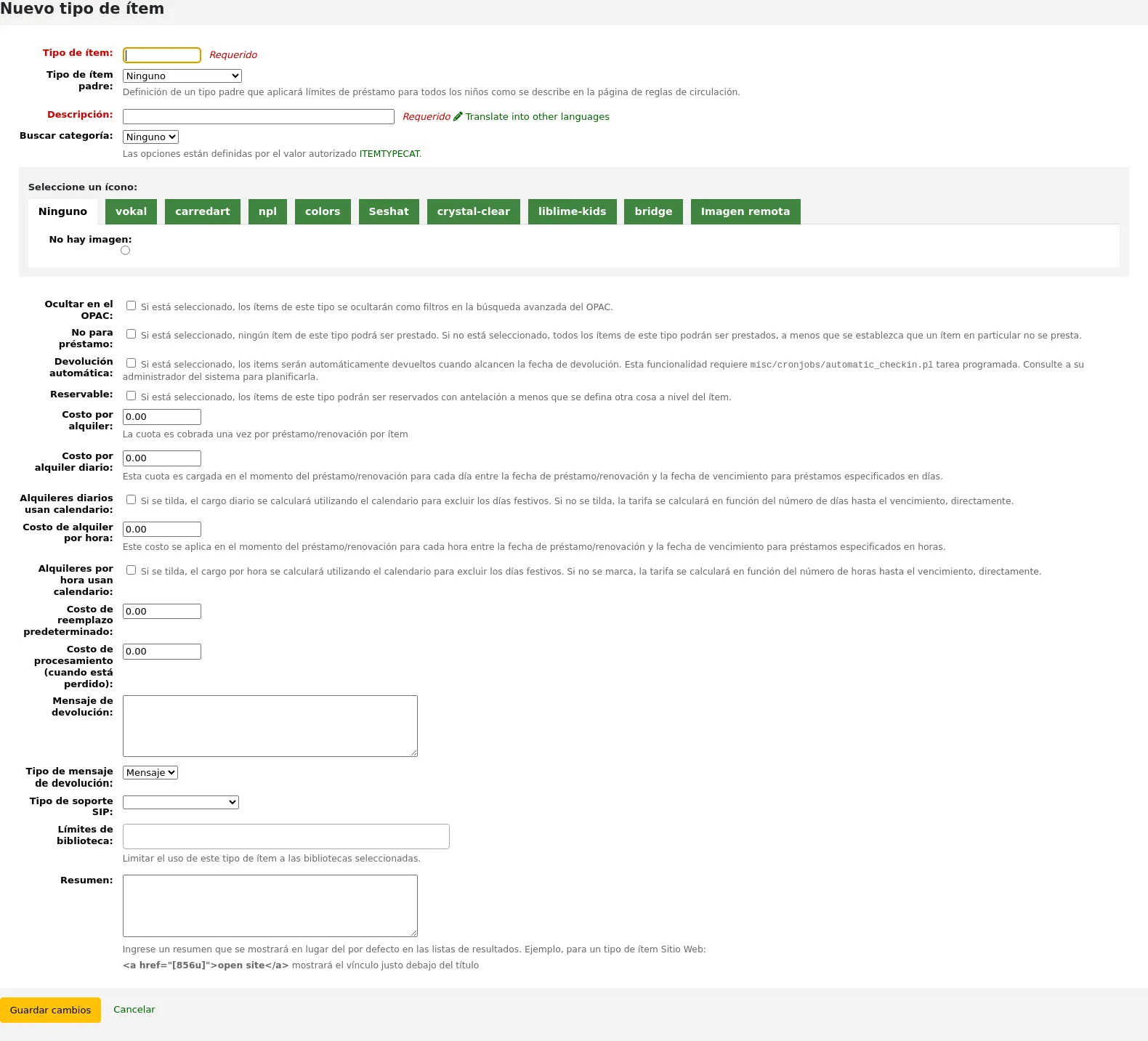
Item type: enter a short code for your item type (maximum of 10 characters)
Parent item type: you can choose an item type that will act as a parent category for this item type. You can then define circulation rules based on that parent item type.
por ejemplo, podría tener tipos de artículos DVD y Blu-ray, y el DVD sería el padre del tipo de artículo Blu-ray.
A continuación, puede crear una regla de circulación para Blu-ray solamente o DVD y Blu-ray (DVD)
Description: enter the plain text definition of the item type
In systems with multiple languages installed, you can translate the item type description in to all of those languages using the “Translate into other languages” link.
Search category: item types can be grouped together for searching at the same time in the OPAC advanced search. For example, you can put DVDs and Blu-rays in a group called “Movies” and then patrons can search them together. These groups are defined in the ITEMTYPECAT authorized value category.
Nota
Search categories are used in the OPAC only. Staff can search for individual item types in the staff interface advanced search.
Choose an icon: you can choose to have an image associated with your item type. These images will appear in the staff interface and the OPAC, in the advanced search and in the holdings table, or the bibliographic record if the item-level_itypes system preference is set to record-level. You can choose an icon from a series of image collections, or you can link to a remote image.
Advertencia
If this option is not enabled, you can change the setting of the noItemTypeImages or OPACNoItemTypeImages.
Nota
To have your item type images appear in the OPAC you need to set OPACnoItemTypeImages to “Show”.
Hide in OPAC: for items that you are suppressing from the OPAC, you can hide their item type from being searched in the OPAC.
Importante
This will not prevent those items to appear in search results, it will simply remove the item type from the advanced search form.
If you want to completely hide items from a certain item type, let’s say that you have a professional library with books reserved for staff and you don’t want those to appear in the OPAC, use the OpacHiddenItems system preference.
Not for loan: check this option for item types that should not circulate. Items marked “Not for loan” will appear in the catalog, but cannot be checked out to patrons.
Automatic check-in: you can check this option for items that are not physical, but for which you still have circulation rules, such as museum passes or ebooks.
Nota
This option requires the cronjob misc/cronjobs/automatic_checkin.pl. Ask your system administrator to schedule it.
Bookable: check this option to allow bookings for all items of this item type.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 24.11.
Rental charge: if you charge a flat rental fee for checking out items of this type, enter the fee here. This fee will be charged to the patron upon checkout and renewal.
Importante
Do not enter symbols in this field, only numbers and decimal points (ex. $5.00 should be entered as 5 or 5.00).
Daily rental charge: if a rental charge should be charged by the number of days the item is checked out for, enter the daily fee here. This fee will be charged to the patron upon checkout multiplied by the number of days this item is checked out. For example, for an item checked out for 7 days with a daily rental charge of 1$, the patron will be charged 7$ upon checkout. This daily rental charge will also be applied for renewals.
Importante
Do not enter symbols in this field, only numbers and decimal points (ex. $5.00 should be entered as 5 or 5.00).
Daily rentals use calendar: check this option to exclude holidays from the daily rental fee calculation.
Nota
Make sure to enter the closed days in the calendar to exclude them from the daily rental charge.
Hourly rental charge: if items are loaned out hourly, enter the cost per hour here. Again, the total (hourly cost * number of hours loaned) will be charged to the patron upon checkout and renewal.
Importante
Do not enter symbols in this field, only numbers and decimal points (ex. $5.00 should be entered as 5 or 5.00).
Hourly rentals use calendar: check this option to exclude holidays from the hourly rental fee calculation.
Nota
Make sure to enter the closed days in the calendar to exclude them from the daily rental charge.
Default replacement cost: this is the amount that will be charged to the patron when an item of this type is lost AND the item doesn’t have a replacement cost. If the item has a replacement cost, that is the amount that will be charged to the patron.
Importante
Do not enter symbols in this field, only numbers and decimal points (ex. $5.00 should be entered as 5 or 5.00).
Processing fee (when lost): this processing fee will be added to the replacement cost if a patron loses an item of this type.
Importante
Do not enter symbols in this field, only numbers and decimal points (ex. $5.00 should be entered as 5 or 5.00).
Checkin message: if you would like a message or alert to appear when items of this type are checked in, enter the message here.
Checkin message type: the checkin message can be a “message” or an “alert”. The only difference between these two is the styling. A message is blue
and an alert is yellow.
SIP media type: some SIP devices need you to use a SIP-specific media type instead of Koha’s item type (usually lockers and sorters need this media type). If you use a device like this choose the SIP media type for this item type.
Library limitation: if this item type is only to be used in specific libraries, you can select them here. Select “All libraries” if this item type is used across the library system.
Nota
Si se deja en blanco, se asume “Todas las bibliotecas”.
Truco
Para seleccionar más de una biblioteca, sostenga la tecla “Ctrl” mientras selecciona las bibliotecas.
Summary: this summary is used in non-XSLT displays only.
Check for previous checkouts: this setting only appears if the CheckPrevCheckout system preference is set to either “Unless overridden by patron category or by item type, do” or “Unless overridden by patron category or by item type, do not”. This allows libraries to customize whether Koha should warn staff when a patron has already checked out the same title, on a per-item type basis.
Inherit from system preferences: use the setting from the CheckPrevCheckout system preference.
Yes and override system preferences: always check the patron’s circulation history for this item type, regardless of the setting of the CheckPrevCheckout system preference.
No and override system preferences: never check the patron’s circulation history for this item type, regardless of the setting of the CheckPrevCheckout system preference.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 25.11.
When finished, click “Save changes”.
Nota
All fields, with the exception of the “Item type” will be editable from the item types list.
Your new item type will now appear on the list.
Editando tipos de ejemplares
To edit an item type, click the “Edit” button next to it, or click the item type code.
See the Adding item types section for a description of each field.
Importante
No podrá editar el código que asignó como “Tipo de ejemplar” pero podrá editar la descripción del ejemplar.
Eliminando tipos de ejemplares
To delete an item type, click the “Delete” button next to it.
Importante
You will not be able to delete item types that are being used by items or bibliographic records within your system. If that is the case, a message will alert you that the item type is in use.

Usuarios y circulación
Ajustes para el control de la circulación y la información del usuario.
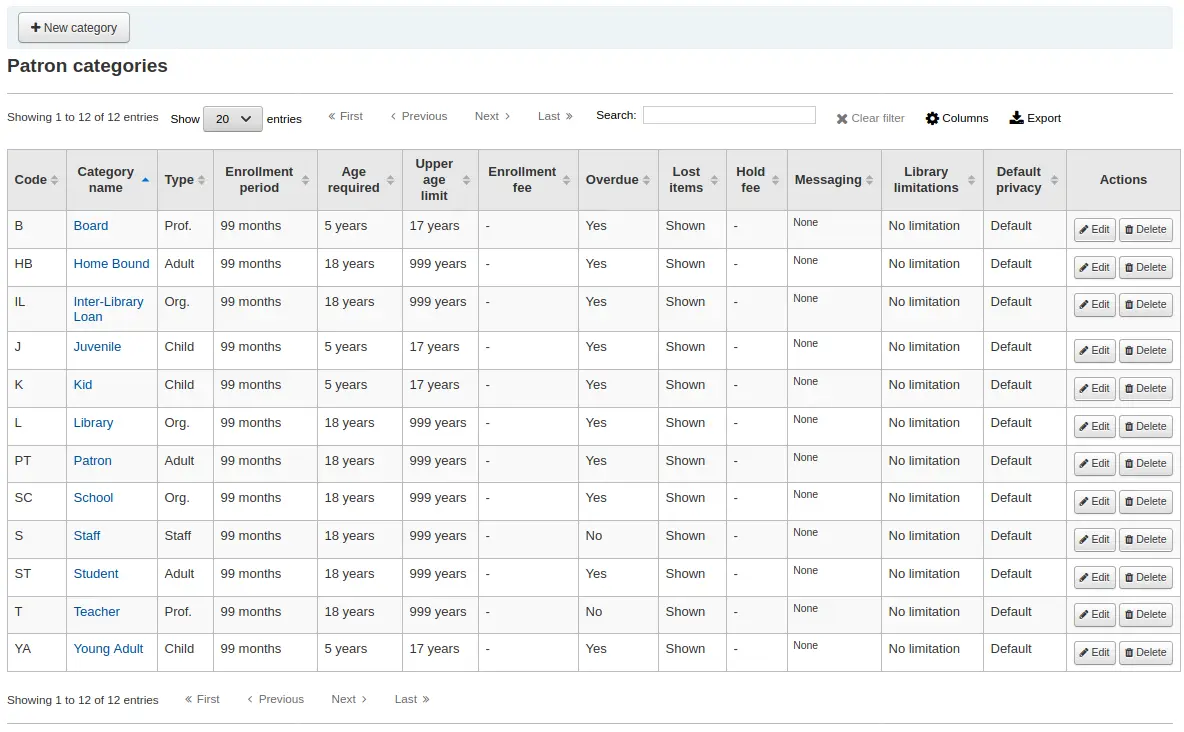
Categorías de usuario
Las categorías de usuarios le permiten organizar sus usuarios según diferentes roles, grupos de edad y los tipos de usuario.
Llegar allí: Más > Administración > Usuarios y circulación > categorías de Usuario
Nota
You can customize the columns of this table in the Table settings section of the Administration module (table id: patron_categories).
Nota
Only staff with the manage_patron_categories permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
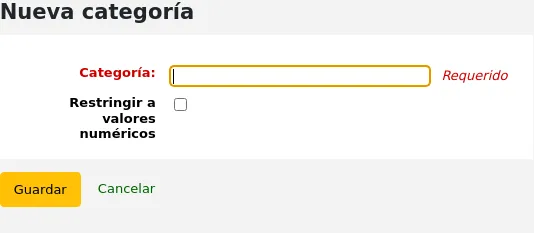
Agregando una categoría de usuario
Para agregar una nueva categoría de usuario haga clic en “Nueva Categoría” en la parte superior de la página

Category code: an identifier for your new category.
El código de la categoría está limitada a 10 caracteres (números y letras) y debe ser único.
Este campo es obligatorio para guardar la categoría de usuario. Si se deja en blanco se mostrará un mensaje de error.
Description: a plain text version of the category.
The description will be visible throughout Koha.
Este campo es obligatorio para guardar la categoría de usuario. Si se deja en blanco se mostrará un mensaje de error.
Enrollment period:
In months: should be filled in if you have a limited enrollment period for your patrons. For example, student cards expire after 9 months
Until date: you can choose a date when the cards will expire
Este campo es obligatorio para guardar la categoría de usuario. Si se deja en blanco se mostrará un mensaje de error.
Advertencia
You cannot enter both a month limit and a date until for one category. Choose to enter either one or the other.
Password expiration: enter the number of days after which a patron has to change their password.
Age required: minimum age (in years) requirement associated with the category. For example, an “Adult” patron category could have a minimum age of 18 years; this means patrons must be at least 18 to be in the patron category.
When creating or updating a patron, a warning will appear if the patron is too young for this category.

This value is used by the update_patrons_category.pl cron job to change the category of patrons who are too young.
Upper age limit: maximum age (in years) associated with the category. For example, a “Children” patron category could have an upper age limit of 18, meaning patrons can have children cards until they turn 18.
When creating or updating a patron, a warning will appear if the patron is too old for this category.

This value is used by the update_patrons_category.pl cron job to change the category of patrons who are too old.
Enrollment fee: enter the amount if you charge a membership fee for your patrons (such as those who live in another region).
Advertencia
Only enter numbers and decimals in this field.
Nota
Depending on your value for the FeeOnChangePatronCategory system preference, this fee will be charged on patron renewal as well as when they are first enrolled.
Aviso de vencimiento requerido: seleccione “Sí” en caso de desear que los usuarios de esta categoría reciban avisos de retraso. Esto le permitirá configurar los disparadores de avisos por vencimiento en el módulo Herramientas.
Lost items in staff interface: decide on a patron category basis if lost items are shown in the staff interface.
Shown: lost items are shown in the staff interface.
Ocultos por defecto: los items pedidos son ocultados, pero el personal puede hacer clic en “Mostrar todos los items” y verlos.
Nota
This is only applicable in the staff interface, so changing this value on patron categories who do not have access to the staff interface won’t make any difference.
Hold fee: enter the fee amount if you charge patrons from this category a fee for placing holds on items.
Advertencia
Only enter numbers and decimals in this field.
Category type: choose one of the six main parent categories
Adult: most common patron type, usually used for a general “Patron” category.
Child: another common patron type.
Staff: library staff
Organizational: organizations can be used as guarantors for Professional patrons.
Professional: professional patrons can be linked to Organizational patrons.
Statistical: this patron type is used strictly for statistical purposes, such as in-house use of items.
Este campo es obligatorio para guardar la categoría de usuario. Si se deja en blanco se mostrará un mensaje de error.
Can be guarantee: if the patrons of this category can have guarantors, choose yes. This will make the “Patron guarantor” and “Non-patron guarantor” sections appear in the patron form.
Library limitations: if necessary, limit this patron category to only some libraries in your library system. Select “All libraries” if any library should to be able to use this category.
Truco
To select more than one library, hold the “Ctrl” key while making your selection.
Password reset in OPAC: decide whether patrons of this category are allowed to reset their password through the OPAC’s “Forgotten password” function. By default, it will follow the rule set in the OpacResetPassword system preference.
Follow system preference OpacResetPassword.
Allowed: patrons of this category will be able to reset their password through the OPAC regardless of the setting in OpacResetPassword.
Not allowed: patrons of this category will not be able to reset their password through the OPAC regardless of the setting in OpacResetPassword.
Password change in OPAC: decide whether patrons of this category are allowed to change their password through the OPAC. By default, it will follow the rule set in the OpacPasswordChange system preference.
Follow system preference OpacPasswordChange.
Allowed: patrons of this category will be able to change their password through the OPAC regardless of the setting in OpacPasswordChange.
Not allowed: patrons of this category will be not able to change their password through the OPAC regardless of the setting in OpacPasswordChange.
Minimum password length: enter the minimum password length for patrons of this category. Leave blank to use the default length set in the minPasswordLength system preference.
Require strong password: decide whether to enforce a strong password policy (at least one uppercase letter, one lowercase letter and one digit) for patrons of this category. By default, it will follow the rule set in the RequireStrongPassword system preference.
Follow the system preference RequireStrongPassword.
Yes: patrons of this category will be required to have a strong password regardless of the setting in RequireStrongPassword.
No: patrons of this category will not be required to have a strong password regardless of the setting in RequireStrongPassword.
Force new patron password reset: choose whether staff-created patrons of this category are forced to change their password after their first OPAC login.
Follow system preference ForcePasswordResetWhenSetByStaff
Force: patrons of this category will be forced to change their password when they log into the OPAC for the first time, regardless of the setting in ForcePasswordResetWhenSetByStaff
Don’t force: patrons of this category will not be forced to change their password when they log into the OPAC for the first time, regardless of the setting in ForcePasswordResetWhenSetByStaff
Nota
This only applies to patrons whose account was manually created by staff members (as opposed to self-registered patrons).
Version
This setting was added to Koha in version 24.11.
Block expired patrons OPAC actions: decide if patrons from this category are blocked from performing actions in the OPAC if their account is expired. By default, it will follow the rule set in the BlockExpiredPatronOpacActions system preference.
Follow the system preference BlockExpiredPatronOpacActions.
Block specific actions:
Nota
This setting overrides what is in the BlockExpiredPatronOpacActions system preference.
Advertencia
Prior to Koha version 24.11, this setting is a simple on/off choice, and all actions are blocked if it is turned on.
Check for previous checkouts: if the CheckPrevCheckout system preference is set to either “Unless overridden by patron category” options, you will be able to set the value for this particular patron category here.
Yes and try to override system preferences: Koha will check if the patron already checked out this item, unless the patron’s personal settings prevent it.
No and try to override system preferences: Koha will not check in the patron already checked out this item, unless the patron’s personal settings permit it.
Inherit from system preferences: the setting of the CheckPrevCheckout system preference will be followed.
Can place ILL in OPAC: if the ILLModule system preference is enabled, this setting determines if patrons of this category can place ILL requests from the OPAC.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 23.11. In previous versions, all patrons can place ILL requests from the OPAC.
Default privacy: choose the default privacy settings for patrons of this category.
Default: checkout history will be kept indefinitely, until either the batch_anonymize.pl script is run or there is a manual batch anonymization which is performed.
Never: checkout history is anonymized upon return. Statistics are kept, but the link between the checkout, the item and the patron is removed.
Forever: checkout history is never anonymized for patrons of this category, regardless of the cron job or manual anonymization.
This setting can be edited by the patron via the OPAC if you allow it with the OPACPrivacy system preference.
Exclude from local holds priority: choose whether holds for patrons of this category are given a priority.
Yes: holds for patrons of this category are not given special priority, regardless of the setting in LocalHoldsPriority.
No: holds for patrons of this category are subjected to the setting in LocalHoldsPriority.
Checkout charge limit: prevent patrons from this category from checking out items if they owe more than the specified amount.
If this field is left empty, or is at 0, the value in the noissuescharge system preference will be used for patrons from this category.
If this field has a value, it will override the value in the noissuescharge system preference for patrons from this category.
Version
This setting was added to Koha in version 24.11.
Guarantees checkout charge limit: prevent patrons from this category from checking out items if their guarantees collectively owe more than the specified amount.
If this field is left empty, or is at 0, the value in the NoIssuesChargeGuarantees system preference will be used for patrons from this category.
If this field has a value, it will override the value in the NoIssuesChargeGuarantees system preference for patrons from this category.
Version
This setting was added to Koha in version 24.11.
Guarantors with guarantees checkout charge limit: prevent patrons from this category from checking out items if the patron has guarantors and those guarantors” guarantees collectively owe more than the specified amount.
If this field is left empty, or is at 0, the value in the NoIssuesChargeGuarantorsWithGuarantees system preference will be used for patrons from this category.
If this field has a value, it will override the value in the NoIssuesChargeGuarantorsWithGuarantees system preference for patrons from this category.
Version
This setting was added to Koha in version 24.11.
Default messaging preferences for this patron category: assign advanced messaging preferences by default to the patron category
These default preferences can be changed on an individual basis for each patron. This setting is just a default to make it easier to set up messages when creating new patrons.
Nota
This requires that you have EnhancedMessagingPreferences system preference set to “Allow”.
Advertencia
These defaults will only be applied to new patrons that are added to the system. They will not edit the preferences of the existing patrons.
If you need to apply the default preferences to existing patrons, you can force those changes by running the borrowers-force-messaging-defaults script found in the misc/maintenance folder. Ask your system administrator for assistance with this script.
Circulation and fine rules
These rules define how your items are circulated, how and when fines are calculated and how holds are handled.
Get there: More > Administration > Patrons and circulation > Circulation and fine rules
Nota
Only staff with the manage_circ_rules permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Las normas se aplicarán de la más específica a la menos específica, utilizando la primera encontrada en este orden:
misma biblioteca, misma categoría de usuario, mismo tipo de ítem
misma biblioteca, misma categoría de usuario, todos los tipos de ítem
misma biblioteca, todas las categorías de usuario, mismo tipo de ítem
misma biblioteca, todas las categorías de usuario, todos los tipos de ítem
predeterminado (todas las bibliotecas), misma categoría usuario, mismo tipo de ítem
predeterminado (todas la bibliotecas), misma categoría de usuario, todos los tipos de ítem
predeterminado (todas las bibliotecas), todas las categorías de usuarios, mismo tipo de ítem
predeterminado (todas las bibliotecas), todas las categorías de usuarios, todos los tipos de ítems
The CircControl and HomeOrHoldingBranch also come in to play when figuring out which circulation rule to follow.
If CircControl is set to «the library you are logged in at» circulation rules will be selected based on the library you are logged in at
If CircControl is set to «the library the patron is from» circulation rules will be selected based on the patron’s library
If CircControl is set to «the library the item is from» circulation rules will be selected based on the item’s library where HomeOrHoldingBranch chooses if the item’s home library or its holding library is used.
If IndependentBranches is set to “Yes” then the value of HomeOrHoldingBranch is used in figuring out if the item can be checked out. If the item’s home library does not match the logged in library, the item cannot be checked out unless you have the superlibrarian permission.
Importante
Como mínimo usted tendrá que establecer por defecto una regla de circulación. Esta regla debe ser fijada para todos los tipos de ejemplares, todas las bibliotecas y todas las categorías de usuario. Eso permitirá atrapar todos los casos que no coincidan con una regla específica. En el momento del préstamo si usted no tiene una regla para todas las bibliotecas todos los tipos de ejemplares y todas las categorías de usuario, entonces puede ver a los usuarios con sus reservas siendo bloqueadas.
Definiendo reglas de circulación
Using the issuing rules matrix you can define rules that depend on patron category/item type combos.
Nota
The matrix being very wide, you can export the existing rules in Microsoft Excel or CSV format, to look at them, using the “Export” button at the top of the table.
To set your rules, choose a library from the pull down (or “Standard rules for all libraries” if you want to apply these rules to all branches):
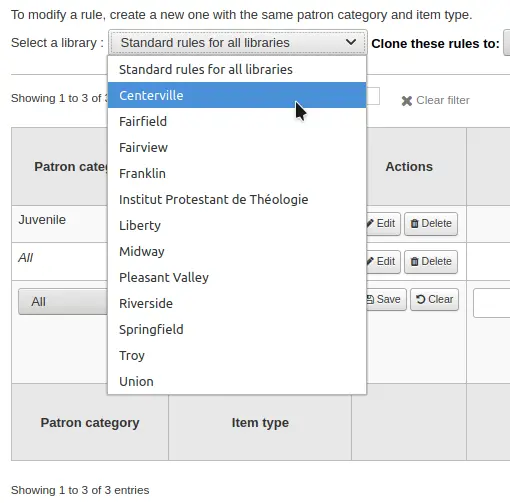
De la matriz usted puede seleccionar cualquier combinación de categorías de usuarios y tipos de ítem a los cuales aplicar la regla
Primero seleccione a cual categoría de usuario aplicará esta regla. Si deja esto en “Todas” se le aplicará a todas las categorías.
Choose the item type you would like this rule to apply to. If you leave this to “All” it will apply to all item types for this patron category
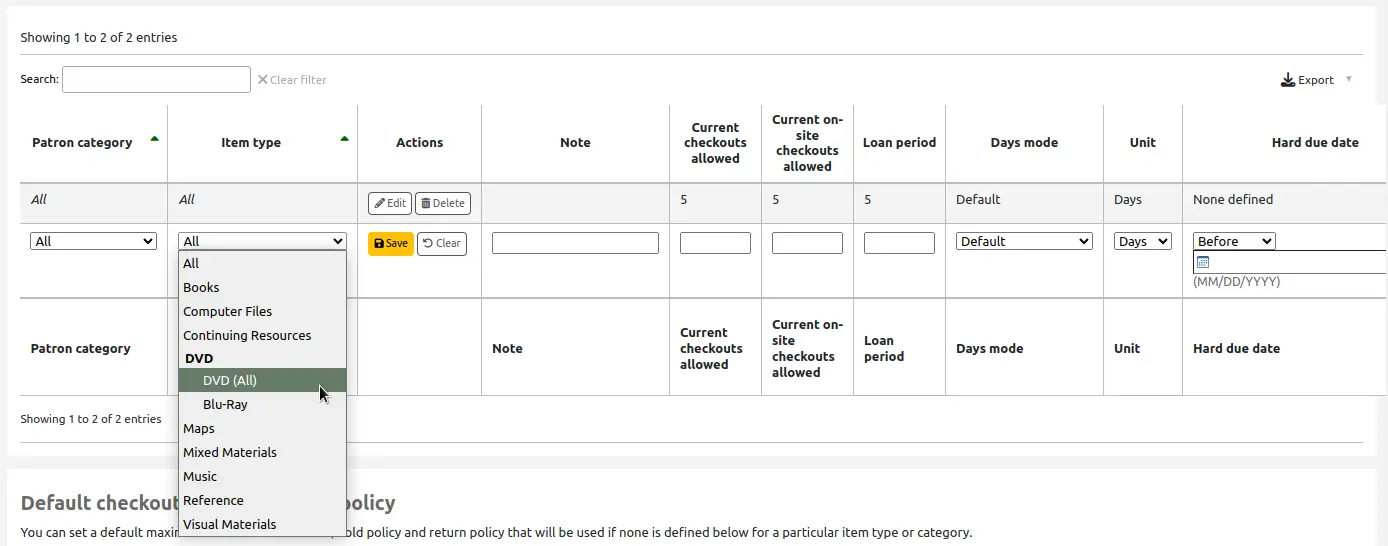
If an item type has a parent item type, the rule will be displayed as Parent -> Child. The number of current checkouts will be limited to either the maximum for the parent (including sibling types) or the specific type’s rule, whichever is less.
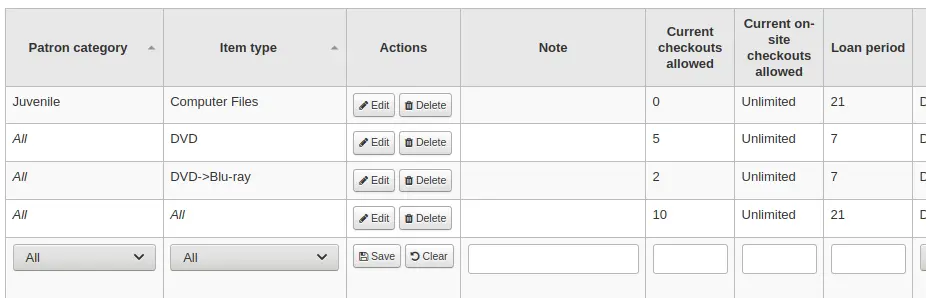
In the example above, there is a rule for the DVD item type with a maximum of 5 checkouts and a rule for Blu-ray, a child of DVD, with a maximum of 2 checkouts. A patron at this library will be able to check out a maximum of 2 Blu-rays in a total of 5 items of either DVD or Blu-ray types.
To summarize, a patron at this library would be able to take either : - 0 Blu-ray and a maximum of 5 DVDs - 1 Blu-ray and a maximum of 4 DVDs - 2 Blu-ray and a maximum of 3 DVDs
Agregar notas acerca de sus reglas de circulacion en el campo de notas. Esto puede ayudar a recordar el porqué y el cuándo algo fué cambiado por última vez.
Limit the number of items of this type a patron of this category can have checked out at the same time by entering a number in the “Current checkouts allowed” field.
If you’re allowing on-site checkouts then you may also want to set a limit on the number of items of this type patrons of this category can have on-site.
Nota
This setting also depends on the ConsiderOnSiteCheckoutsAsNormalCheckouts preference
Define the period of time an item of this type can be checked out to a patron of this category by entering the number of units (days or hours) in the “Loan period” box.
Define if the loan period should include closed days or not in the “Days mode” column. The option chosen here will override the useDaysMode system preference for this particular rule.
The “Default” option will take the option defined in the useDaysMode system preference
Choose the “Calendar” option if you want to use the calendar to skip the days when the library is closed
Choose the “Datedue” option if you want to push the due date to the next open day
Choose the “Days” option if you want to ignore the calendar and calculate the due date directly
Choose the “Dayweek” option if you want to use the calendar to push the due date to the next open matching weekday for weekly loan periods, or the next open day otherwise
Elija en qué unidad de tiempo, días u horas, se calculará el período de préstamo y las multas en la columna «Unidad»
Nota
If using “hours”, you can set library opening hours for each library and determine how the due time is calculated should it fall outside of opening hours.
También puede definir una fecha de devolución estricta para un tipo de usuario específico o tipo de ejemplar. Una fecha de vencimiento estricta ofrece tres opciones:
Exactamente: Con esta regla la fecha de vencimiento de cualquier ejemplar en préstamo será establecida a una fecha estricta.
Antes: Koha calcularia el período normal del préstamo. Si la fecha calculada de vencimiento fúera después o en la fecha estricta, se usará en lugar la fecha estricta de vencimiento.
Después: Koha calcularía el período normal de préstamo. Sí la fecha calculada de vencimiento fuerá antes de la fecha estricta, se usará en lugar la fecha estricta de vencimiento.
“Cantidad de multa” debe tener la cantidad que quiere cobrar por ejemplares retrasados,
Importante
Introducir sólo números enteros y decimales (no símbolos de monedas).
Enter the “Fine charging interval” in the unit you set (ex. charge fines every 1 day, or every 2 hours). The finesCalendar system preference controls whether the days the library is closed will be taken into account or not.
“Cuando cobrar” es muy útil en bibliotecas que tienen un intervalo en los cargos de multas de más de 1 día.
Fin de intervalo: Dado un período de gracia de 2 días y un intervalo de cargos de 7 días, el primer cargo aparecerá 7 días después de la fecha de vencimiento, siempre escogerá un intervalo de cargo (7 días), antes de que el primer cargo se cobre.
Comienzo de intervalo: Dado un período de gracia de 2 días y un intervalo de cargos de 7 días, el primer cargo aparecerá 2 días después de la fecha de vencimiento y el segundo cargo aparecerá 7 días después de la fecha de vencimiento.
The “Fine grace period” is the period of time an item can be overdue before you start charging fines. The FinesIncludeGracePeriod system preference controls if the grace period will be included when calculating the fine or not.
Importante
This can only be set for the “Day” unit, not in “Hours”
El “Máximo de multas por retrasos” es la multa máxima por ejemplar para este usuario y la combinación de tipo de ejemplar.
Importante
If this field is left blank then Koha will not put a limit on the fines this item will accrue. A maximum fine amount for all overdues can be set using the MaxFine system preference.
Si usted quiere prevenir el sobrecargo a los usuarios por ejemplares perdidos, puede marcar la casilla debajo de “Tope de multa por cargo de reemplazo”. Esto previene que las multas de los usuarios vayan por encima del precio del cargo de reemplazo del ejemplar.
Nota
Si tambien se establece el “Tope de multas por tardanza” la multa será la menor de las dos, si las dos se aplican a la tardanza del préstamo.
If you charge patrons a fine when they don’t come to pick up their waiting holds in time (see below the number of days set in “Holds pickup period (day)”), enter the amount of the fine in “Expired hold charge”.
If this field is left empty, the value in the ExpireReservesMaxPickUpDelayCharge system preference is used.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 25.05.
Si su biblioteca “multa” a socios, suspendiendo su cuenta, usted puede ingresar el número de días que deben ser suspendidos en el campo “Suspensión en días”
Importante
This can only be set for the “Day” unit, not in “Hours”
You can also define the maximum number of days a patron will be suspended in the “Max suspension duration” setting
The “Suspension charging interval” option is just like the “Fin charging interval”. For example, you could “fine” a patron one day suspension for every two days overdue.
A continuación decida si el usuario puede renovar este tipo de ejemplar y si es así, ingrese el número de veces que podrá renovarlo en la casilla “Renovaciones permitidas”
If you allow unseen renewals (see UnseenRenewals), enter how many “unseen” renewals patrons can make. This is not in addition to the regular renewals, but rather how many “unseen” renewals can be made among the total number of renewals.
Si está permitiendo renovaciones puede controlar cuan largo es el período de renovación (en las unidades que haya elegido) en la casilla de “Período de renovación”.
Si usted está permitiendo renovaciones, puede controlar con qué antelación a la fecha de vencimiento los usuarios pueden renovar sus materiales con la casilla “No renovable antes de”.
Los ejemplares pueden ser renovados en cualquier momento si este valor se deja en blanco. De otra forma los ejemplares sólo podrán ser renovados si el ejemplar se vence antes del número en unidades (días/horas) ingresada en esta casilla.
To control this value on a more granular level please set the NoRenewalBeforePrecision preference.
If you enable automatic renewals (see below), enter how much time before the due date the automatic renewal takes place.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 23.11.
In previous versions, automatic renewals use the “no renewals before” value, which applies to both regular and automatic renewals.
Usted puede habilitar las renovaciones automáticas para ciertos ejemplares/usuarios si lo desea. Esto renovará automáticamente siguiendo sus reglas de circulación, a menos que exista una reserva en el ejemplar.
Importante
Necesitará habilitar la tarea programada para la renovación automática para que esto funcione.
Importante
This feature needs to have the «no automatic renewal before» column filled in or it will auto renew every day after the due date.
If you are using automatic renewals, you can use the “No automatic renewals after” to limit the time a patron can have the item. For example: don’t allow automatic renewals after a checkout period of 80 days.
Similar to the hard due date setting, you can also stop automatic renewals after a specific date using the “No automatic renewal after (hard limit)” setting.
If patrons of this category can place holds on items of this type, enter the total numbers of items (of this type) that can be put on hold in the “Holds allowed” field.
Leave empty to have unlimited holds.
If you’d rather put a hold limit per patron category, independent of the item type, see the default checkout and hold policy by patron category section below.
If you want to have a hard hold limit, independent of patron category and item type, for this particular library, see the Default checkout, hold, and return policy section below.
If you want to have a hard hold limit, independent of patron category, item type, and across all libraries, see the maxreserves system preference.
También puede establecer un límite diario en el número de reservas que un usuario pueda poner.
While the two settings before limit the holds that can be placed across various records, the next setting is used to limit the number of holds that can be placed on one record at the same time. For example, for fiction books you might want to allow only one item to be placed on hold at the same time by the same user. But for serials where items represent different issues more than one hold at the same time is fine.
Nota
If this is set to a number that is greater than 1, but not Unlimited, then staff will have the option of placing multiple holds at once when placing a hold on the next available item in the staff interface
Siguiente puede decidir como la disponibilidad de los ejemplares puede influir en la habilidad de poner una reservación. La opción «Se permite la reservación en la estantería» tiene tres opciones:
Sí: Esto permitirá poner reservas en ejemplares en todo tiempo. No importa si están disponibles o en préstamo.
Si no hay ninguno disponible: Esto permitirá poner uno o más ejemplares del registro en reserva tan pronto cómo se den en préstamo. No importando si hay uno o más ejemplares disponibles en la estantería.
Sí todos no están disponibles: Esto permitirá poner una reserva tan pronto cómo todos los ejemplares en el registro se den en préstamo, que puedan llenar una reserva. Esto es especialmente útil para bibliotecas que no ofrecen el servicio de dar los ejemplares en reserva a los usuarios desde la estantería.
Under “OPAC item level hold” you can decide if patrons are allowed to place item specific holds on the item type in question. The options are:
Permitir: Permitirá a los usuarios la opción de elegir el próximo disponible o un ejemplar específico.
No permitir: Sólo permitirá a los usuarios elegir el próximo ejemplar disponible.
Forzar: Solo permitirá a los usuarios elegir un ejemplar específico.
You can set the number of days patrons have to come pick up their holds in the “Holds pickup period (day)” column. This value will set the hold’s “expiration date”. After that period, holds will be marked as problematic and will appear in the “Holds waiting past their expiration date” tab in the Holds awaiting pickup report.
The default period is set in the ReservesMaxPickUpDelay system preference, but this column allows to have more granular rules for various library, patron category, and item type combinations.
Version
This circulation rule option was added to Koha in version 23.11.
If you want to allow patrons of this category to be able to place article requests on items of this type, choose an option in the “Article requests” column
No: patrons of this category will not be able to place article requests on items of this type
Yes: patrons of this category will be able to place article requests on items of this type, either on specific items (for example in the case of serial issues) or on entire records (for example in the case of monographs)
Record only: patrons of this category will be able to place article requests on records of this type, but not on specific items
Item only: patrons of this category will be able to place article requests on items of this type, but not on entire records
Advertencia
This column will only appear if the ArticleRequests system preference is enabled.
If you want to use the article request functionality you need to enable it using the ArticleRequests system preference and configure the form using the other related preferences.
If you charge a rental fee for the item type and want to give this specific patron category a discount on that fee, enter the percentage discount (without the % symbol) in the “Rental discount” field
Nota
Enter the discount percentage using a decimal point.
Discounts must be a positive number with no more than two digits after the decimal. Whole numbers are also allowed. For example:
5,10,0.50,3.25,99.99.Values like
0.5,25.123, or-10are not accepted.If the UseRecalls system preference is enabled, you will have several options to control recalls.
Recalls allowed (total): enter the number of current recalls a patron of this category can have on items or records of this item type.
Recalls per record (count): enter the number of current recalls a patron of this category can have on any one record of this item type.
On shelf recalls allowed: choose if patrons can recall items on records that have available items
If any unavailable: if a record has more than one item and at least one is unavailable, the patron will be able to recall items from this record
If all unavailable: all items of a record must be unavailable in order for a patron to recall an item from this record
Recall due date interval (day): enter the number of days a patron has to return an item that has been recalled
Recall overdue fine amount: enter the fine amount a patron will be charged if they don’t return the recalled item by the due date
Recall pickup period: enter the number of days a patron has to come pick up the item they have recalled, once it has been marked as awaiting pickup.
Nota
This value supersedes the value in the RecallsMaxPickUpDelay system preference.
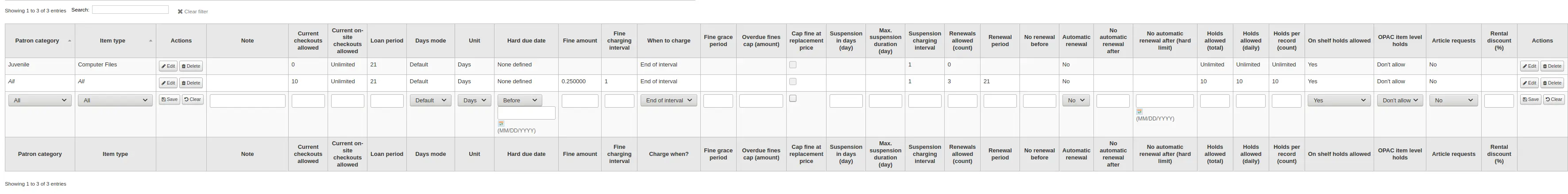
When finished, click “Save” to save your changes. To modify a rule, simply click the “Edit” button either at the beginning or at the end of the row. The row of the rule being edited will be highlighted in yellow and the values will appear filled in at the bottom of the table. Edit the values at the bottom and click save.
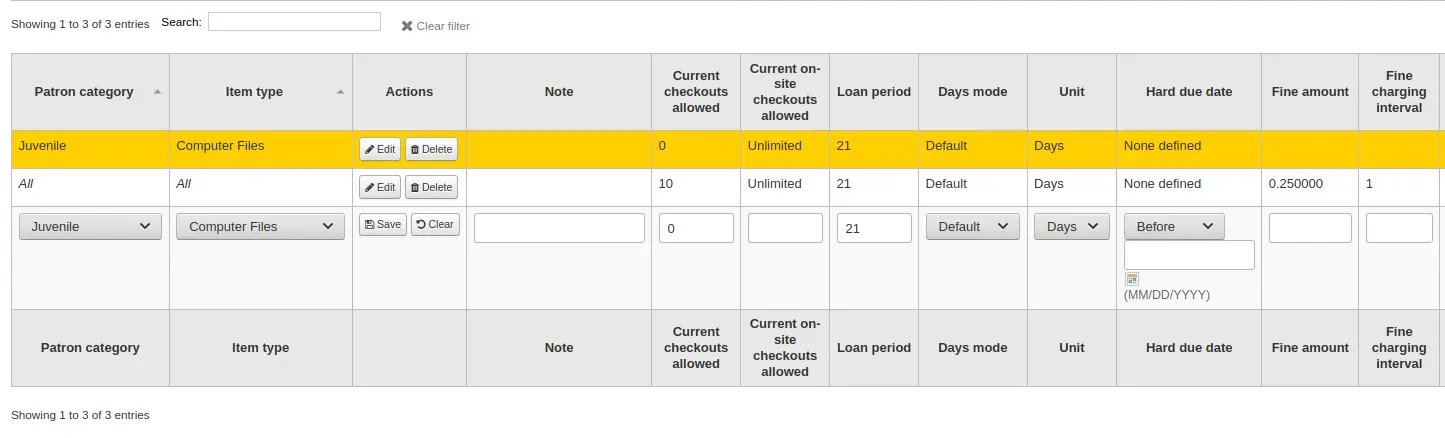
Nota
If, while editing a rule, you change either the patron category or the item type, it will create a new rule. You can do this to duplicate rules instead of creating new ones if the values are similar.
Alternatively, you can create a rule with the same patron category and item type and it will edit the existing one, as there can only be one rule per library- patron category-item type combination.
If you would like to delete your rule, click the “Delete” button at the beginning or at the end of the rule row.
Para ahorrar tiempo puede clonar las reglas de una biblioteca a otra, eligiendo la opción de clonar arriba de las reglas de la matriz. Por favor note que esto modifica todas las reglas ya configuradas por esa biblioteca.

Luego de elegir clonar, se le presentará un mensaje de confirmación.
Políticas predeterminadas de préstamo, reserva y devolución
Usted puede establecer un número máximo predeterminado de préstamos y reservas y una póliza de reservas que se utilizará si no se definen debajo para un tipo de ejemplar o categoría. Este es la regla de retroceso para todos los defectos.
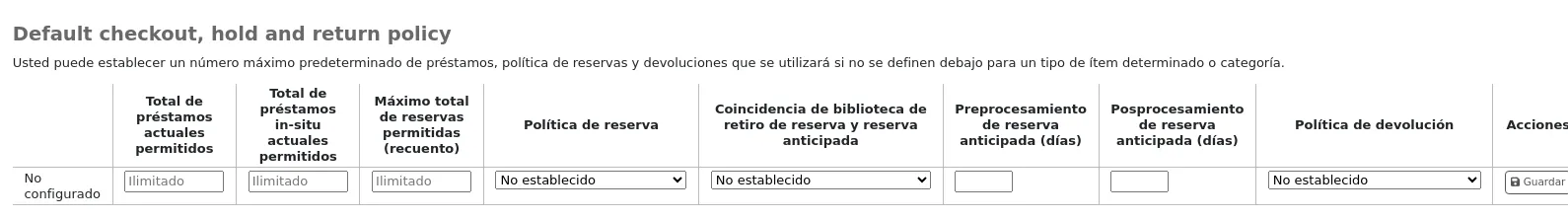
De este menú usted puede establecer un valor predeterminado para todos los tipos de ítems y usuarios de la biblioteca.
Total current checkouts allowed: enter the total number of items patrons can have checked out at one time
Total current on-site checkouts allowed: enter the total number of items patrons can have checked out on site at a time (OnSiteCheckouts needs to be set to “Enable”)
Maximum total holds allowed (count): enter the total number of pending holds patrons can have at the same time.
Hold policy: control where patrons can place holds from
From any library: patrons from any library may put items on hold (default if none is defined)
From local hold group: only patrons from a library in the item home library’s local hold group may put this book on hold
From home library: only patrons from the item’s home library may put items on hold.
No holds allowed: no patron may put items on hold.
Hold and booking pickup library match: control where patron can pick up holds and bookings
a cualquier biblioteca.
grupo de reserva del ejemplar
grupo de reserva del usuario
biblioteca de origen del ítem.
biblioteca de la reserva
Booking pre-processing (days): enter a number of days to prevent a new booking from starting too soon after an existing booking ends. This gives staff time to prepare the item between two bookings.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 24.11.
Booking post-processing (days): enter a number of days to prevent a new booking from ending too close to the start of an existing booking. This gives staff time to receive and process the item between two bookings.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 24.11.
Return policy: control where the item returns to once it is checked in
Sede de devolución de ítem
El ítem regresa a sede de préstamo
Item floats: when an item floats, it stays where it was checked in and does not ever return “home”
Item floats by library group: The item will not be transferred and will stay at the library it was checked in at, if the check-in library is within the same “float group” in library groups as the item’s home library. If the library is not in the same float group, the item will be transferred back to its home library.
Once your policy is set, you can unset it by clicking the “Unset” button to the right of the rule.
Default checkout and hold policy by patron category
Para esta biblioteca, puede especificar el número máximo de préstamos locales que un usuario de una determinada categoría puede tener, independientemente del tipo de ejemplar.
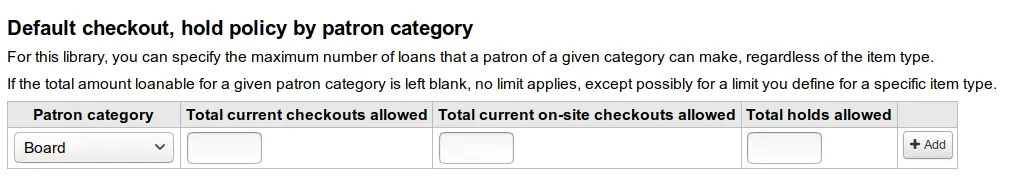
Nota
Si la cantidad total de préstamos, préstamos y reservas locales a una catagoría dada de usuario se deja en blanco, no se aplicarán límites, excepto posiblemente que se defina un límite en las reglas de circulacion en la parte superior.
Por ejemplo, si usted tiene una regla en la matriz que dice que los usuarios Junta se les permiten 10 libros y 5 DVDs, pero desea hacerlo de modo que los usuarios Junta tengan solo un total de 12 ítems prestados a la vez. Si introduce 12 aquí y el usuario tiene 10 libros prestados entonces solo se le permitirán 2 DVDs que equivalen a los 12 permitidos en total.
Default waiting hold cancellation policy
For this library, you can specify if patrons can cancel holds that are already awaiting pickup.
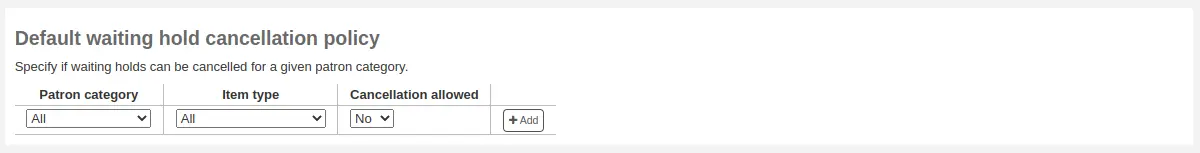
For each patron category and item type combination, choose if these patrons can cancel holds that are already waiting for pickup.
Just like the circulation rules, the more specific rules will apply before the more generic rules (i.e. the «all» patron categories / «all» item types rule will apply only if no other rule exists for this combination).
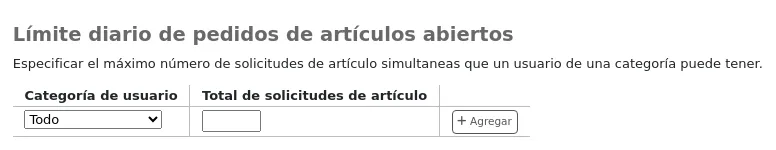
Default open article requests limit
If ArticleRequests is enabled, you can set a maximum number of open article requests a patron of a category can have at one time.
Nota
This will only appear if the ArticleRequests system preference is enabled.
Choose the patron category you want to limit.
Enter the number of open article requests a patron of this category can have at one given time
Click “Add”
Cargo predeterminado para solicitud de artículo
If ArticleRequests is enabled, you can set the fee a patron from a given category (or any category) needs to pay in order to request the article.

Nota
This will only appear if the ArticleRequests system preference is enabled.
Choose the patron category for which you want to add a fee, or choose “All” to set an overall fee for all patrons
Nota
The fee specific to a patron category will supersede the fee for all categories.
For example, if you set a fee for all categories to 2$ and a fee for Faculty to 3$, Faculty members will be charged 3$ and any other patron will be charged 2$.
Enter the fee amount (use a period as the decimal and don’t enter any symbols, e.g. enter 5.00 for 5$)
Click “Add”
The fee is charged to the patron when the request is placed.
When placing the request, either through the staff interface or the OPAC, a message appears to inform the staff member or the patron that the patron will be charged for every request and the amount of the fee.
Política predeterminada de reembolso de costo por ítem perdido y devolución
Here, you can specify the default policy for lost item fees on return.

Refund lost item replacement fee: choose whether or not the item’s replacement cost is refunded when the lost item is returned.
Refund lost item charge: the replacement cost is refunded. This might create a credit to be paid out to the patron if they had already paid the fee.
Refund lost item charge (only if unpaid): the replacement cost is refunded only if it hasn’t yet been paid.
Refund lost item charge and charge new overdue fine: the replacement cost is refunded and overdue fines are calculated as of today.
Refund lost item charge and restore overdue fine: the replacement cost is refunded and fines are restored as of the day the item was declared lost.
Leave lost item charge: the replacement cost stays in the patron’s account.
Refund lost item processing fee: choose whether or not the item’s processing fee is refunded when the lost item is returned.
Refund lost item processing charge: the processing fee is refunded. This might create a credit to be paid out to the patron if they had already paid the fee.
Refund lost item processing charge (only if unpaid): the processing fee is refunded only if it hasn’t yet been paid.
Leave lost item processing charge: the processing fee stays in the patron’s account.
This policy will apply to this library. This rule is to be used with the RefundLostOnReturnControl system preference.
Nota
You can limit refunds based on age:
use the NoRefundOnLostReturnedItemsAge system preference to limit refunds based on when the item was marked lost;
use the NoRefundOnLostFinesPaidAge system preference to limit refunds based on when the fee was paid.
Default holds and bookings policies by item type
You can set and edit holds and bookings policies for a given item type, regardless of the patron’s category.
Select the item type from the dropdown menu.
Set policies as explained below.
Click “Add” to save this rule.
Add as many rules as you need.
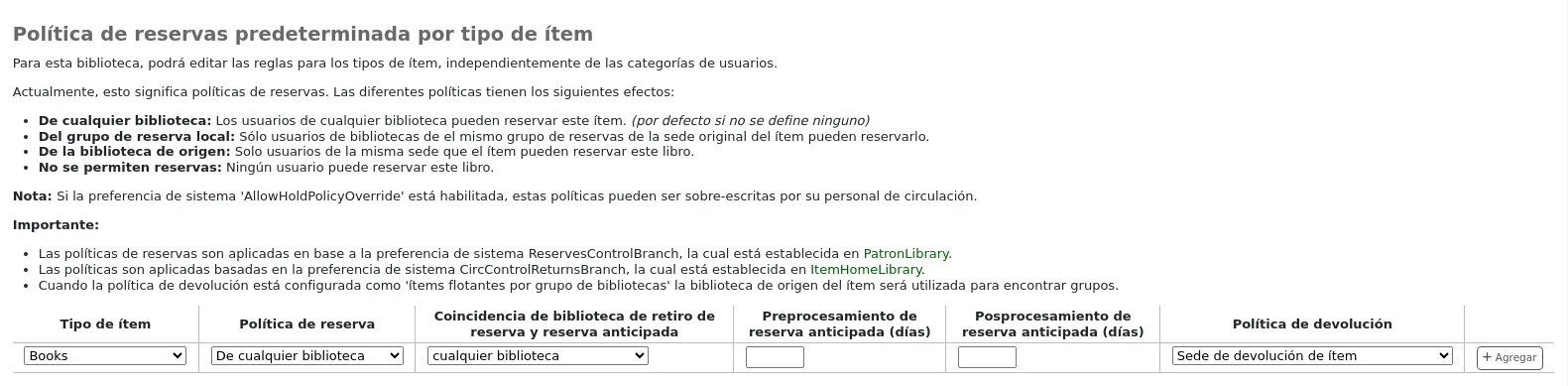
Hold policy: the various hold policies have the following effects.
From any library: patrons from any library may put this item on hold. (default if none is defined)
From local hold group: only patrons from libraries in the same item’s home library hold groups may put this book on hold.
From home library: only patrons from the item’s home library may put this book on hold.
No holds allowed: no patron may put this book on hold.
If the system preference AllowHoldPolicyOverride is set to “allow”, these hold policies can be overridden by staff.
Nota
The hold policies are applied based on the ReservesControlBranch system preference.
Hold and booking pickup library match: control where a patron can collect holds and bookings of the specified item type.
a cualquier biblioteca.
grupo de reserva del ejemplar
grupo de reserva del usuario
biblioteca de origen del ítem.
biblioteca de la reserva
Booking pre-processing (days): add a buffer period before a new booking, to give staff time to prepare the item in-between two bookings.
Enter a number of days. This will prevent a new booking from starting too soon after an existing booking ends.
Booking post-processing (days): add a buffer period after a new booking, to give staff time to receive the item in-between two bookings.
Enter a number of days. This will prevent a new booking from ending too close to the start of an existing booking.
Return policy: the various return policies have the following effects.
Item returns home: on check-in at another library, the librarian will be prompted to transfer the item to its home library.
Item returns to issuing branch: on check-in, the librarian will be prompted to transfer the item to the library where it was checked out.
Item floats: the item will not be transferred from the library it was checked in at. It will remain at the check-in library until transferred manually or checked in at another library.
Item floats by library group: the item will not be transferred and will stay at the library it was checked in at, if the check-in library is within the same “float group” in library groups as the item’s home library. If the library is not in the same float group, the item will be transferred back to its home library.
When return policy is set to “item floats by library group” the item’s homebranch will be used to find groups.
Nota
The library whose return policy is used is determined by the CircControlReturnsBranch system preference.
Example
You may allow holds in your library service generally. However, you do not want brand new stock in the “New items” item type to be reserved by patrons at libraries other than the one to which the new stock belongs.
For the “New items” item type, you will set the “Hold policy” to “From home library” so that those items can only be placed on hold if the items” owning library and the patron’s home library are the same. You can set “Hold and booking pickup library match” to “item’s home library” to ensure the items on hold can only be collected from their home library. You should also set “Return policy” to “item returns home”.
Tipos de atributo de usuario
Get there: More > Administration > Patrons and circulation > Patron attribute types
Nota
Only staff with the manage_patron_attributes permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Patron attributes can be used to define custom fields to associate with your patron records. In order to enable the use of custom fields you need to set the ExtendedPatronAttributes system preference.
Un uso común para este campo sería el de contener el número de documento (ID) de un usuario/estudiante o el número de su Licencia de conducir.
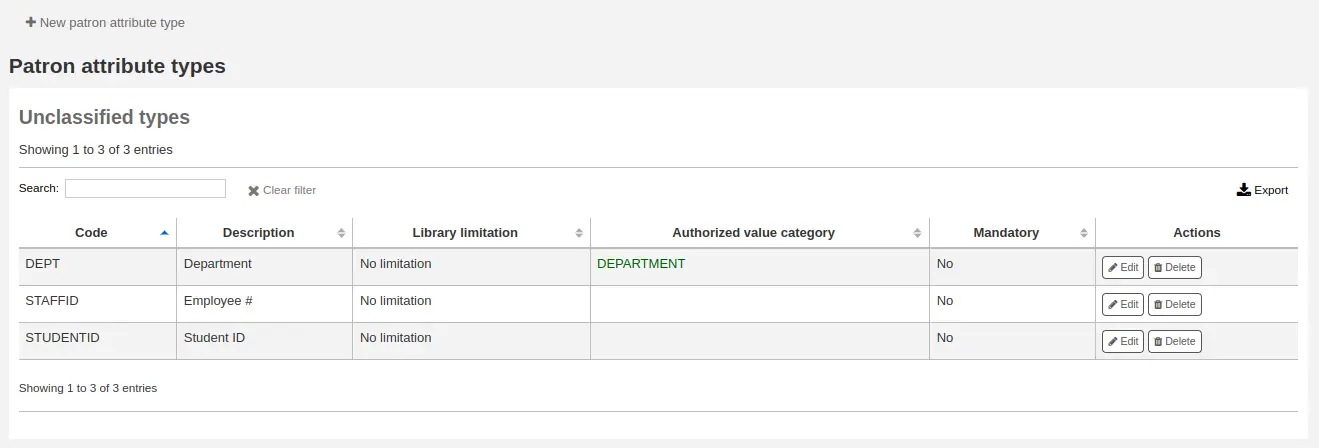
Adding patron attribute types
To add a new patron attribute type, click the “New patron attribute type” button at the top of the page
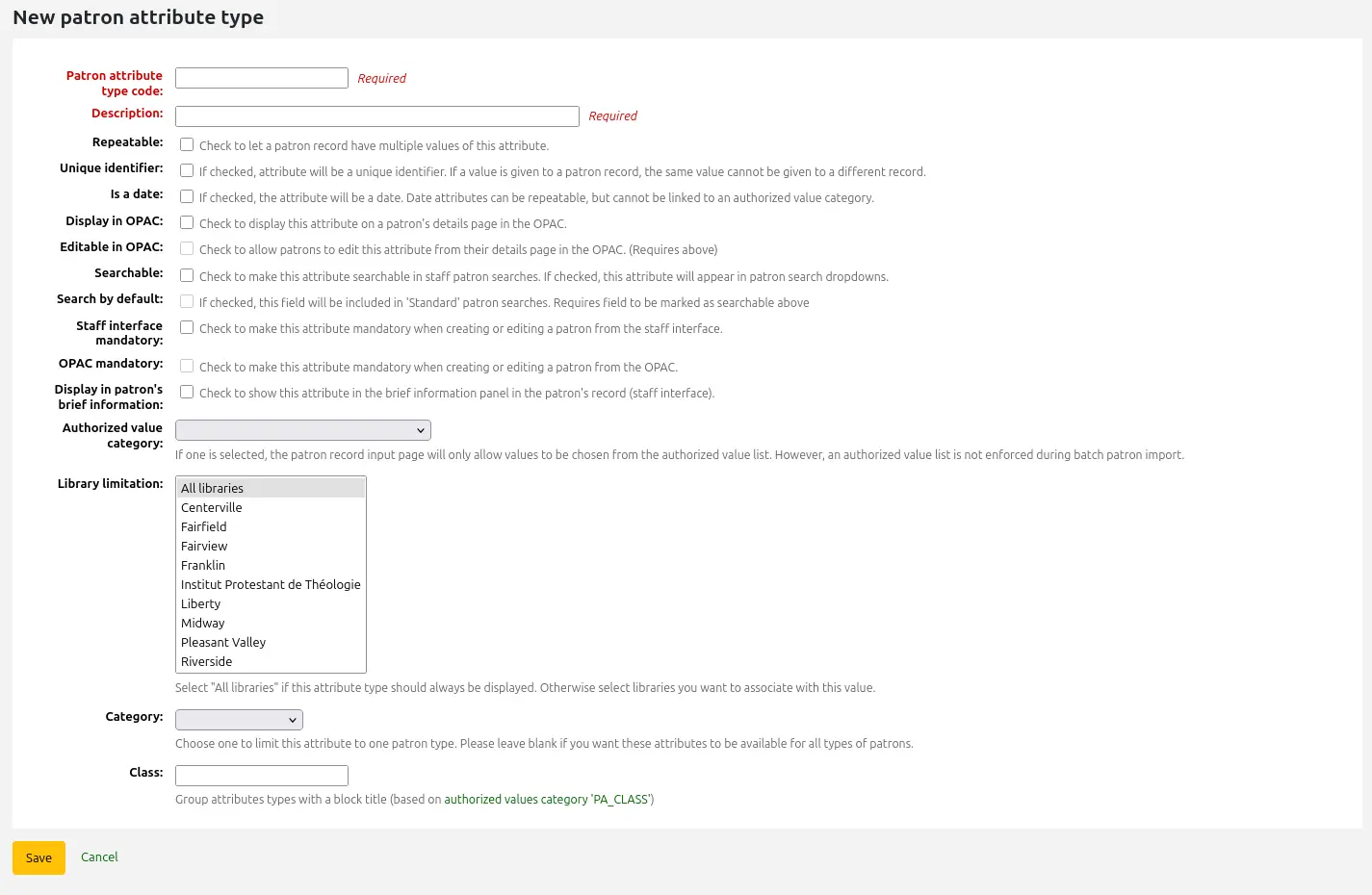
Patron attribute type code: enter a short code to identify this field
Advertencia
Este valor no puede ser cambiado después de que se define un atributo
Description: enter a longer (plain text) explanation of what this field will contain
Repeatable: check this box if a patron record can have multiple values of this attribute.
Advertencia
Este valor no puede ser cambiado después de que se define un atributo
Unique identifier: check this box if a value is given to a patron record, the same value cannot be given to a different record.
Los atributos únicos pueden ser utilizados como puntos de coincidencia en la herramienta de importación de usuarios
Advertencia
Este valor no puede ser cambiado después de que se define un atributo
Is a date: check this box if the attribute value should be a date. A date picker will be available.
Importante
Date attribute types cannot be linked to authorized value categories.
Version
The date option was added to Koha in version 24.05.
Display in OPAC: check this box to display this attribute on a patron’s details page in the OPAC.
Editable in OPAC: check this box to enable patrons to edit this information in the OPAC.
Searchable: check this box to make this attribute searchable in the staff interface’s patron search.
Search by default: check this box to make this attribute searchable in the staff interface’s “standard” patron search, i.e., not a search on a particular field.
This option requires that the attribute type be searchable (see previous option).
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 23.11.
Mandatory: check this box if the attribute must be filled for every patron
Display in patron’s brief information: check this box to make this attribute visible in the patron’s short detail display on the left of the checkout screen and other patron pages

Authorized value category: if one is selected, the patron record input page will only allow values to be chosen from the authorized value list.
You will first need to add an authorized value list for it to appear in this menu
Advertencia
An authorized value list is not enforced during batch patron import.
Library limitations: if you would like this attribute to only be used by specific branches you can choose those branches from this list. Choose “All branches” to show it for all libraries.
Advertencia
Patrons with attributes already set for them will not be altered. The branch limitation only limits the field based on the library at which the current staff is logged in.
If an attribute is set for a patron, it will be displayed in their file to all staff. However, only staff from the selected branches will be able to edit it.
Category: if you’d like to only show this attribute on patrons of one type choose that patron category here
Class: if you have a lot of attributes it might be handy to group them so that you can easily find them for editing. If you create an authorized value for PA_CLASS it will show in the “Class” drop-down menu and you can then change your attributes page to have sections of attributes
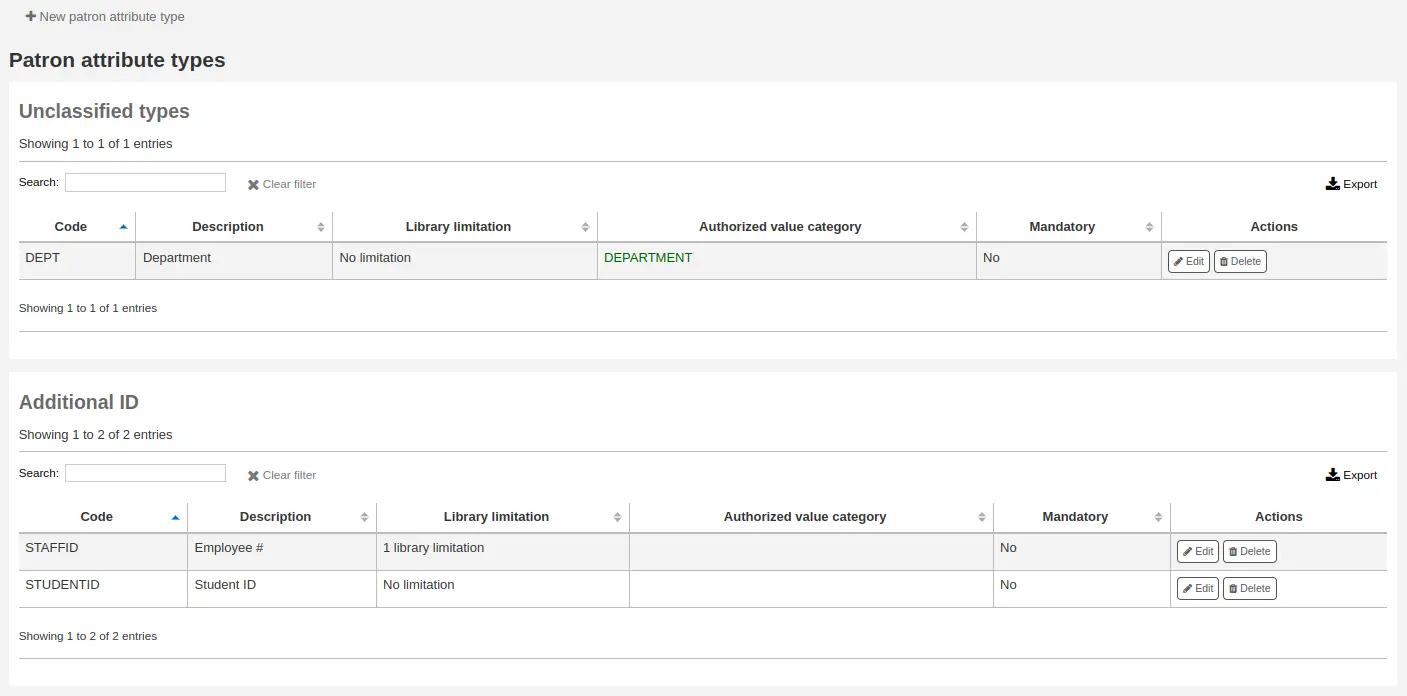
Click “Save” to save your new attribute.
Once added, your attribute will appear on the list of attributes and also on the patron record add/edit form
Editing/deleting patron attribute types
Each patron attribute has an edit and a delete button beside it on the list of attributes.

Algunos de los campos en el atributo no se puede editar una vez creados:
Código de tipo de atributo de usuario
Repetible
Identificador único
Usted no podrá eliminar un atributo si está en uso.

Límites de transferencia de la biblioteca
Limitar la capacidad de transferir ítems entre bibliotecas basado en la biblioteca de origen, la biblioteca receptora y código de colección en cuestión.
Get there: More > Administration > Patrons and circulation > Library transfer limits
Nota
Only staff with the manage_transfers permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Estas reglas sólo entrarán en vigor si la preferencia UseBranchTransferLimits se configura en “forzar”.
Antes de comenzar querrá seleccionar para cual biblioteca está definiendo estos límites.
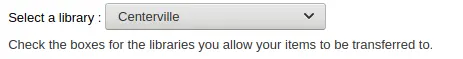
Transfer limits are set based on the collections codes you have applied via the Authorized values administration area.
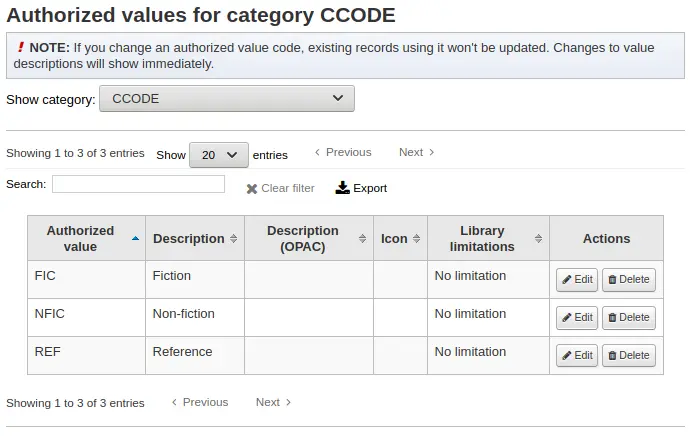
Los códigos de colección aparecerán como pestañas arriba de los recuadros de opciones:
Check the boxes for the libraries you allow your items to be transferred to for the collection code you have selected at the top (in the example below - FIC)
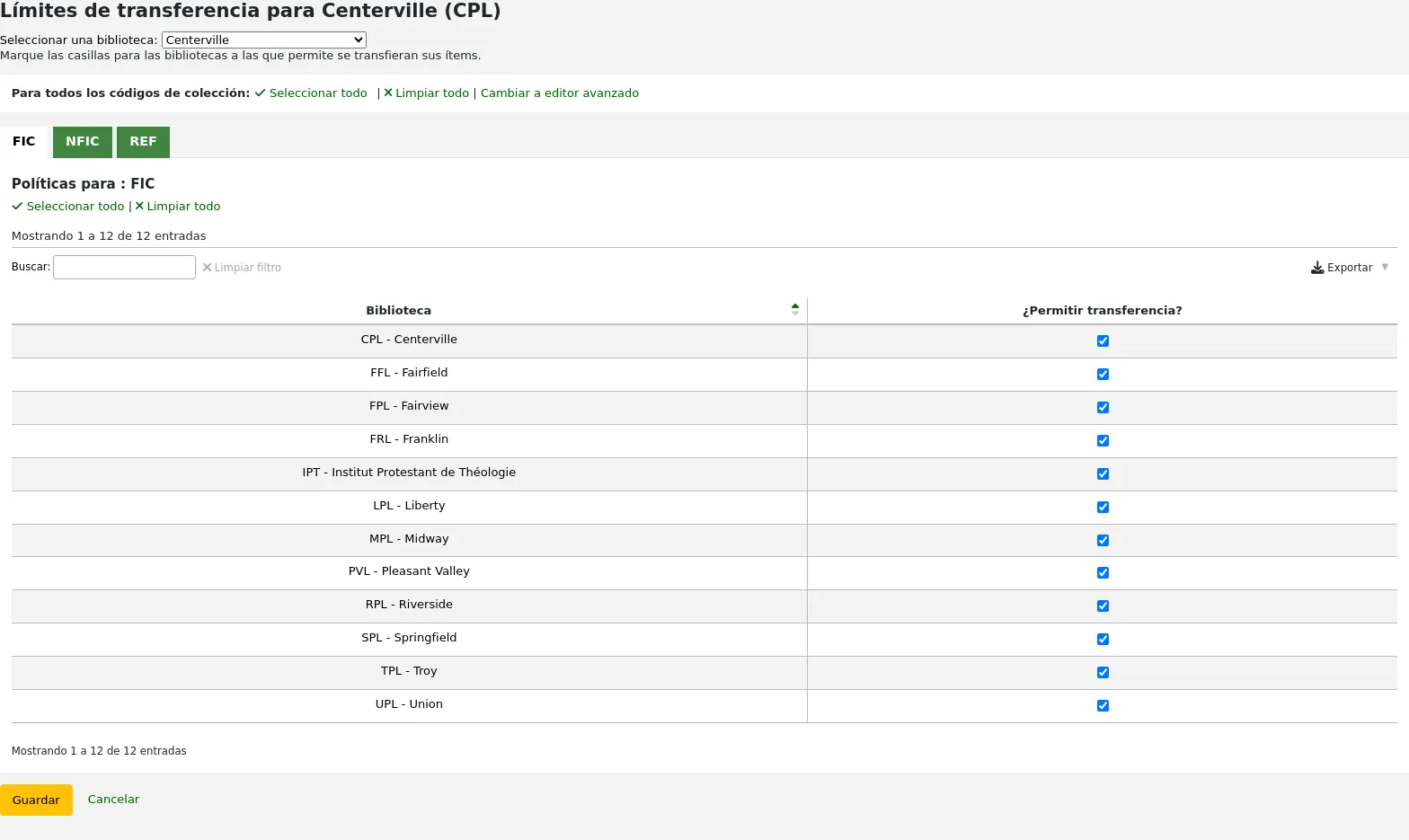
In the above example, Centerville library will allow patrons from all libraries except Liberty and Franklin to request items from their branch.
Matriz de costo de transporte
The transport cost matrix lets a library system define relative costs to transport books to one another.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_transfers permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
In order for the system to use this matrix you must first set the UseTransportCostMatrix preference to “Use”.
Importante
The transport cost matrix takes precedence in controlling where holds are filled from, if the matrix is not used then Koha checks the StaticHoldsQueueWeight.
Costos son valores decimales entre algún máximo arbitrario (ej. 1 o 100) y 0 el cual es el mínimo (sin) costo. Por ejemplo, puede utilizar la distancia entre cada biblioteca en kilómetros como su “costo”, si eso refleja adecuadamente el costo de transferencia. Tal vez oficinas postales sean una mejor medida. Bibliotecas que compartan una oficina postal pueden tener un costo 1, oficinas postales adyacentes un costo 2, etc.
Para ingresar costos de transporte simplemente haga clic en la celda que desea alterar, desmarque la casilla “Deshabilitar” e ingrese su “costo”
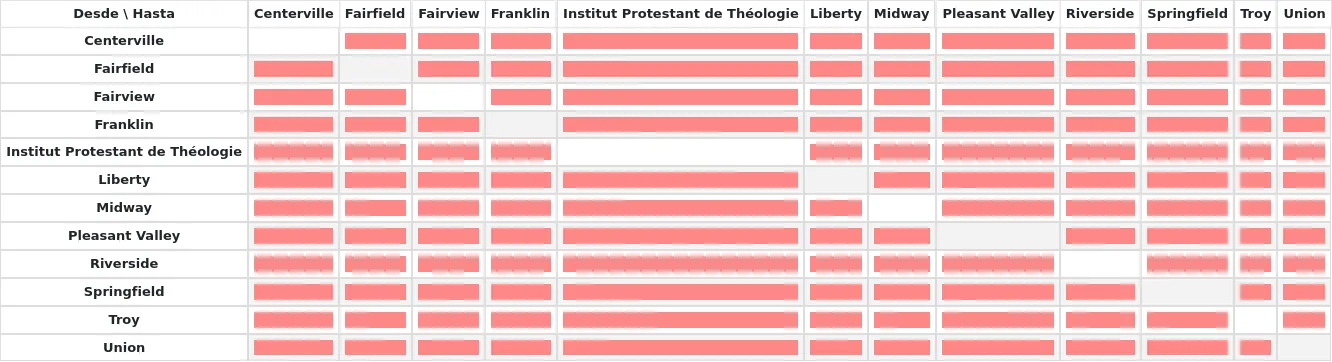
Luego de ingresar su costo, presione “Intro” en su teclado o haga clic en el botón “Guardar” al fondo de la matriz para guardar sus cambios.
Nota
Un valor inválido no hará diferencia donde las bibliotecas de «De» y «A» sean la misma biblioteca. Sin embargo, como mejor práctica, deberías poner un 0 ahí. Para todas las demás combinaciones de Desde/Hacia, un valor inválido hará que esa relación actúe como si hubiera sido desactivada. Así que, en resumen, no dejes ninguno de los valores vacío. Es mejor poner siempre un número ahí (incluso si eliges deshabilitar la opción dada de Hacia/Desde).
Alertas de circulación de ítems
Las bibliotecas pueden decidir si quieren tener a los usuarios automáticamente notificados de eventos de circulación (préstamos y devoluciones).
Get there: More > Administration > Patrons and circulation > Item circulation alerts
Nota
Only staff with the manage_item_circ_alerts permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Estas preferencias se establecen sobre la base de los tipos de usuario y los tipos de ítems.
Importante
Estas preferencias pueden ser anuladas cambiando las preferencias de mensajería individuales del usuario.
Para establecer alertas de circulación:
Elija su biblioteca desde el menú desplegable en la parte superior de la pantalla
Para establecer preferencias para todas las bibliotecas, mantenga el menú posicionado en “Predeterminado”
Por defecto, todos los tipos de ítems y usuarios se les informa de todos los préstamos y devoluciones. Para cambiar esto, haga clic sobre el tipo combinado ítem/usuario al cual quiere dejar de enviar avisos.
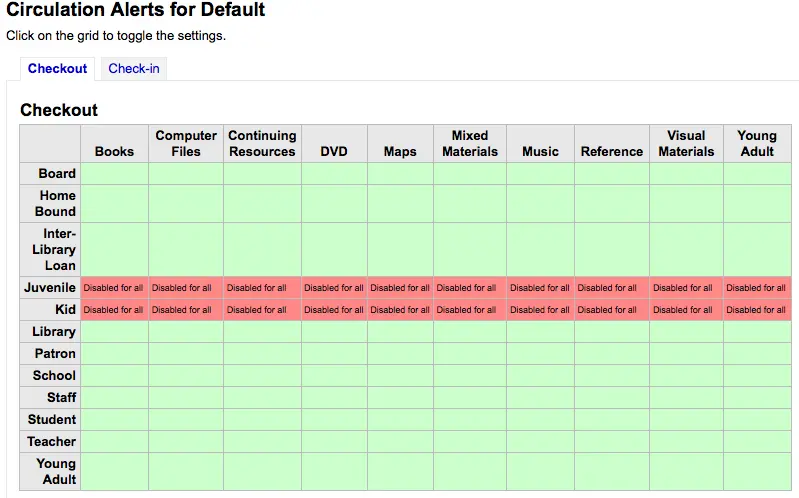
En el ejemplo anterior, los menores y de niños no recibirán avisos de circulación.
Ciudades y pueblos
Para estandarizar el ingreso de usuarios, puede definir ciudades o pueblos dentro de su región, para que cuando los nuevos usuarios sean agregados, los bibliotecarios simplemente seleccionarán la ciudad de una lista en lugar de tener que tipear la ciudad y el código postal.
Get there: More > Administration > Patrons and circulation > Cities and towns
Nota
Only staff with the manage_cities permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Adding a city
To add a new city, click the “New city” button at the top of the page and enter the city name, state, zip/postal code and country.
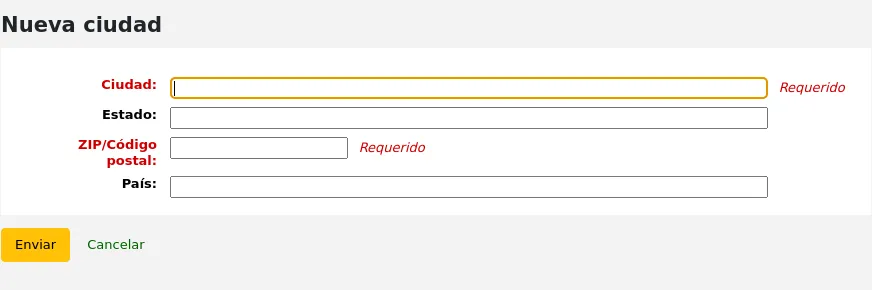
One you click Submit, your city will be saved and will be listed on the Cities and towns page
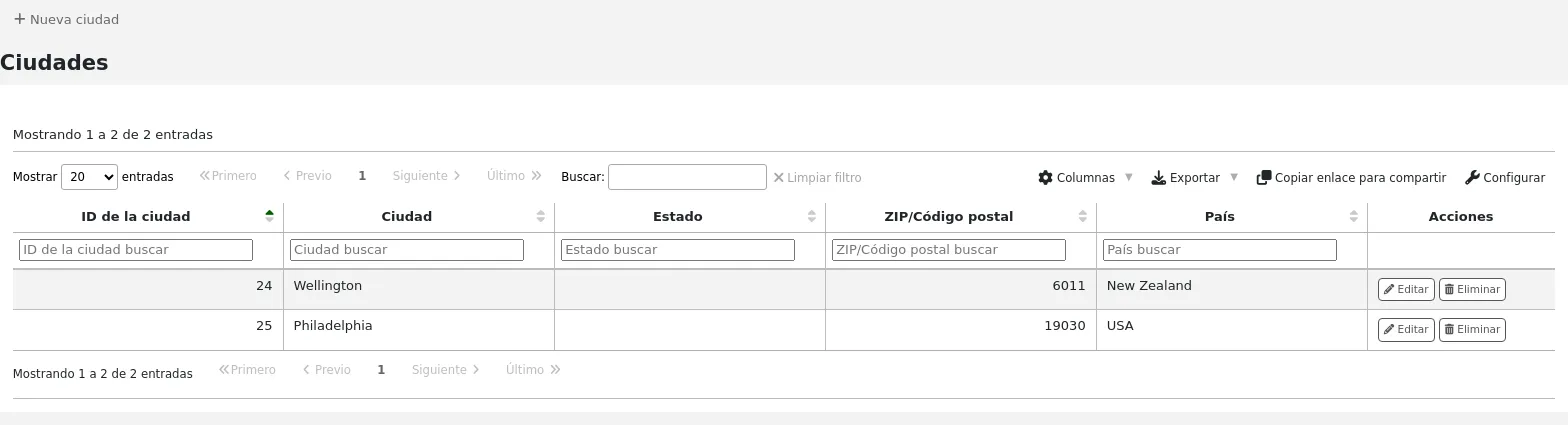
Las ciudades pueden ser modificadas o eliminadas en cualquier momento.
Viewing cities on patron add form
If you have defined local cities using the “New city” form, then when adding or editing a patron record you will see those cities in a pull down menu to make city selection easy.
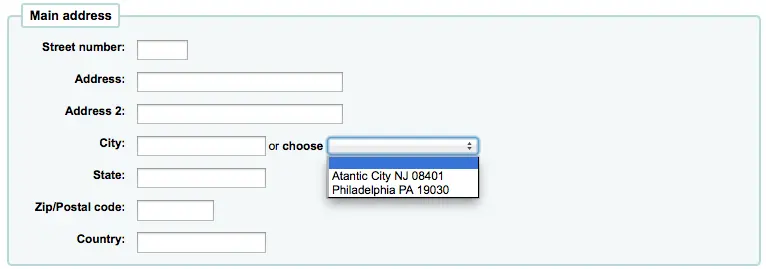
Esto permitirá facilitar la entrada de las ciudades en el registro de usuario sin correr el riesgo potencial de errores tipográficos o códigos postales equivocados.
Curbside pickup
The curbside pickup feature is used to set up appointments with patrons for them to pick up their holds. This section is used to configure the pickup windows
Get there: More > Administration > Patrons and circulation > Curbside pickup
Nota
In order to use this module, you must enable it with the CurbsidePickup system preference.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_curbside_pickups permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Setting up curbside pickup
From the configuration page, click the tab corresponding to the library for which you’re setting up curbside pickup
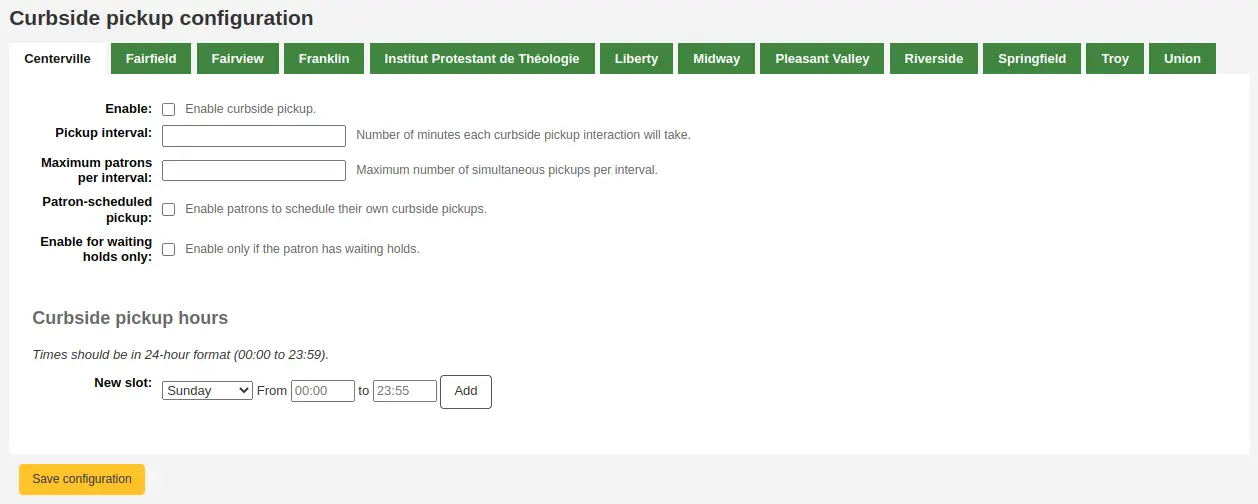
Fill out the form
Enable: check this box to enable curbside pickup at this library
Pickup interval: enter the number of minutes each curbside pickup interaction will take
Maximum patrons per interval: enter the number of patrons who can pickup in the same interval
Patron-scheduled pickup: check this box if you want to allow patrons to set up their own curbside pickup appointment through the OPAC
Enable for waiting holds only: check this box if curbside pickup should be limited to patrons who have holds awaiting pickup
Create curbside pickup slots
For each slot, enter the day of the week, the starting and ending hours of the time slot in which patrons can come
these can be your opening hours, if you allow curbside pickup throughout the day, or specific time slots in which you allow patrons to come by
For the hours, the format must be XX:XX (numbers with a colon) and it must be in 24-hour format (e.g. 1 PM is 13:00)
Click “Add”
Click “Save configuration”
Do this for every library that offers curbside pickup.
Patron restriction types
If you are using patron restriction types, you can manage the restriction types available from here.
Patron restriction types are enabled by the PatronRestrictionTypes system preference.
Get there: More > Administration > Patrons and circulation > Patron restriction types
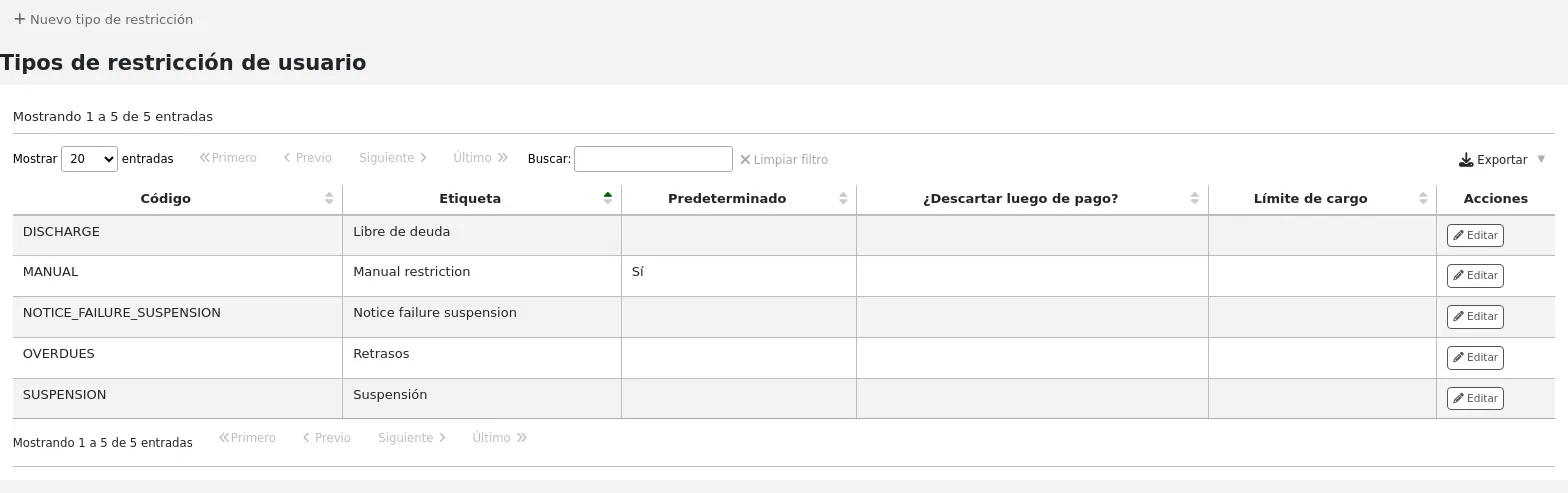
Nota
Only staff with the manage_patron_restrictions permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Adding a restriction type
To add a new restriction type, click the “New restriction type” button at the top of the page.
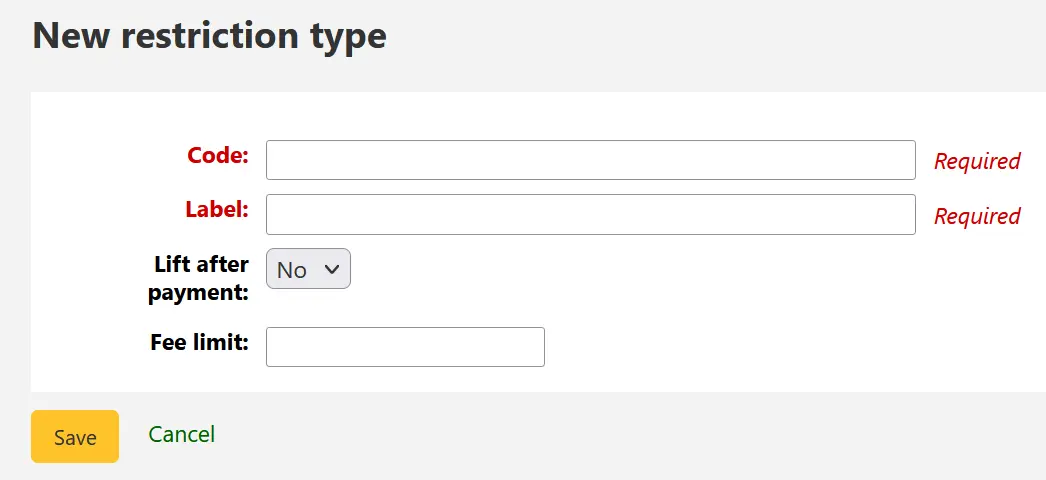
Code: enter a code for the restriction. Codes are limited to 50 characters and should not contain spaces, diacritics, or special characters.
Label: enter the label for the restriction. The label will be the one displayed throughout Koha.
Lift after payment: if set to “Yes”, restrictions using this type will be automatically lifted after payments equal to or exceeding the amount defined in “Fee Limit”.
Fee Limit: enter the amount that must be paid in order to lift a restriction of this type. This field is only used if “Lift after payment” is set to “Yes”.
Once you click “Save”, your restriction type will be saved and will be listed in the table of restriction types.
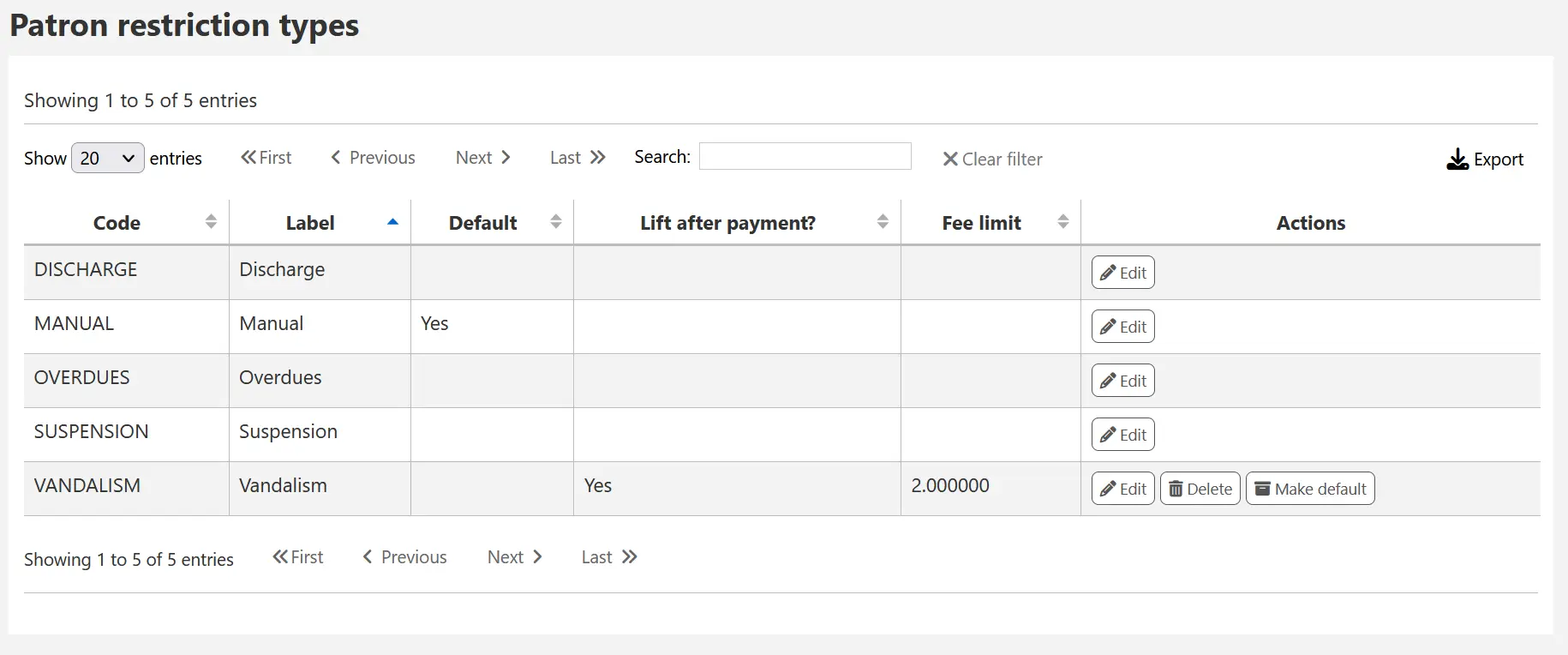
Locally created restriction types can be set to set as the default restriction type to use when manually adding a restriction to a patron account. This can be achieved using the “Make default” button.
You can also delete any locally created restriction types using the “Delete” so long as they have not been assigned as the default.
Contabilidad
Get there: More > Administration > Accounting
This section deals with the parameters used in managing the patron accounts.
Tipos de débito
Get there: More > Administration > Accounting > Debit types
Nota
Only staff with the manage_accounts permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
This is where you define the manual fees you can charge patrons.
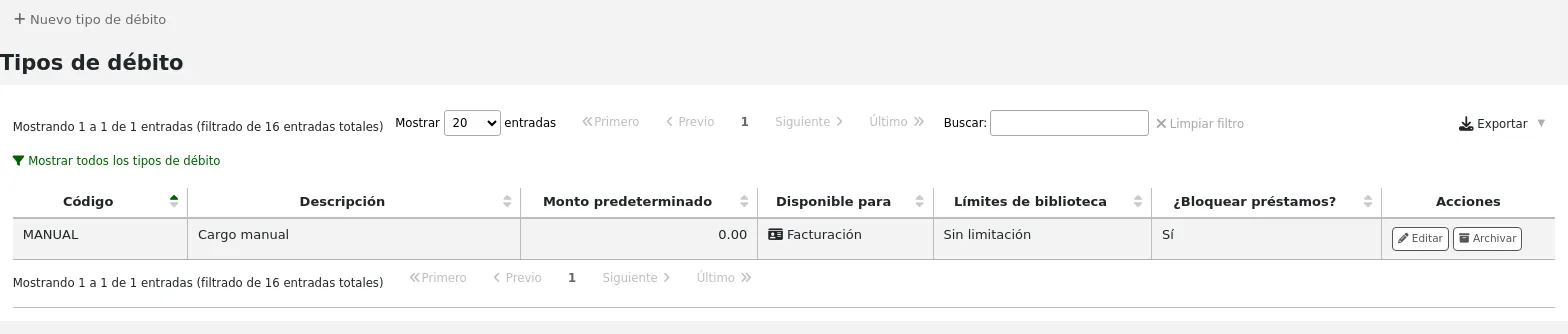
When you first get to the page, you will only see the manual fees that are already defined in your system.
You can see the default system fees by clicking «Show all debit types».
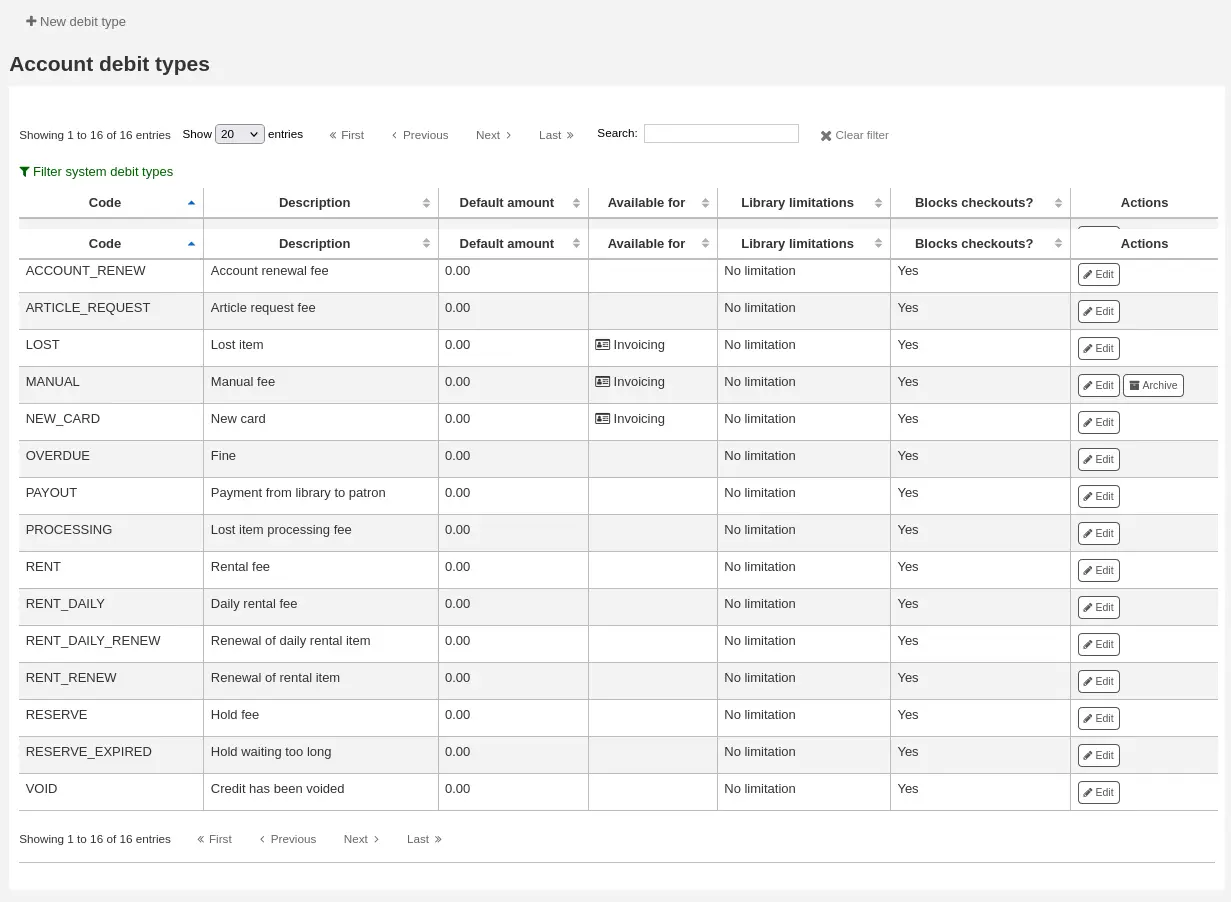
You can go back to seeing only the manual fees by clicking «Filter system debit types».
System debit types
Several debit types come installed with Koha. Most of them are automatic fees that are added according to the policies you set up elsewhere in Koha.
ACCOUNT (Cargo por creación de cuenta): esto es cargado a la cuenta del usuario cuando se registra. La tarifa puede ser cambiada en el patron category settings debajo “Tarifa de inscripción”.
ACCOUNT_RENEW (Account renewal fee): this is charged to the patron’s account when their account is renewed. Like the ACCOUNT debit type above, this can be changed in the patron category settings under “Enrollment fee”.
LOST (Lost item): this is charged to the patron’s account when an item in their file is declared lost. The amount depends on the item’s “replacement cost” field or on the item type’s default replacement cost. It can also be added manually in the manual invoices tab.
MANUAL (Manual fee): this is the default manual fee installed with Koha. This is not charged automatically by Koha, but can be added to a patron’s account manually in the manual invoices tab.
NEW_CARD (New card fee): this is another default manual fee installed with Koha. This will not be charged automatically by Koha, but can be added to a patron’s account manually in the manual invoices tab.
OVERDUE (Overdue fine): this is charged automatically to the patron’s account when they have overdue items. The amount for overdue fines are set in the circulation and fines rules.
PAYOUT (Payment from library to patron): this is used when the library reimburses the patron (for an over payment for example).
PROCESSING (Lost item processing fee): this is charged automatically to the patron’s account when an item in their file is declared lost. The amount is set by item type under “Processing fee (when lost)”.
RENT (Rental fee): this is charged automatically to the patron’s account upon checkout if the item type has a rental charge.
RENT_DAILY (Cargo diario por alquiler): esto es cargado automáticamente a la cuenta del usuario cuando se presta si el tipo de ítem tiene un cargo diario por alquiler.
RENT_DAILY_RENEW (Renewal of daily rental item): this is charged automatically to the patron’s account upon renewal if the item type has a daily rental charge.
RENT_RENEW (Renewal of rental item): this is charged automatically to the patron’s account upon renewal if the item type has a rental charge.
RESERVE (Hold fee): this is charged automatically to the patron’s account upon placing a hold. The amount depends on the “Hold fee” amount in the patron’s category settings.
RESERVE_EXPIRED (Hold waiting too long): this is charged automatically to the patron’s account if they haven’t picked up their hold after the number of days defined in the ExpireReservesMaxPickUpDelay system preference. The amount is set in the ExpireReservesMaxPickUpDelayCharge system preference.
Adding a new debit type
To add a new debit type:
Click “New debit type”
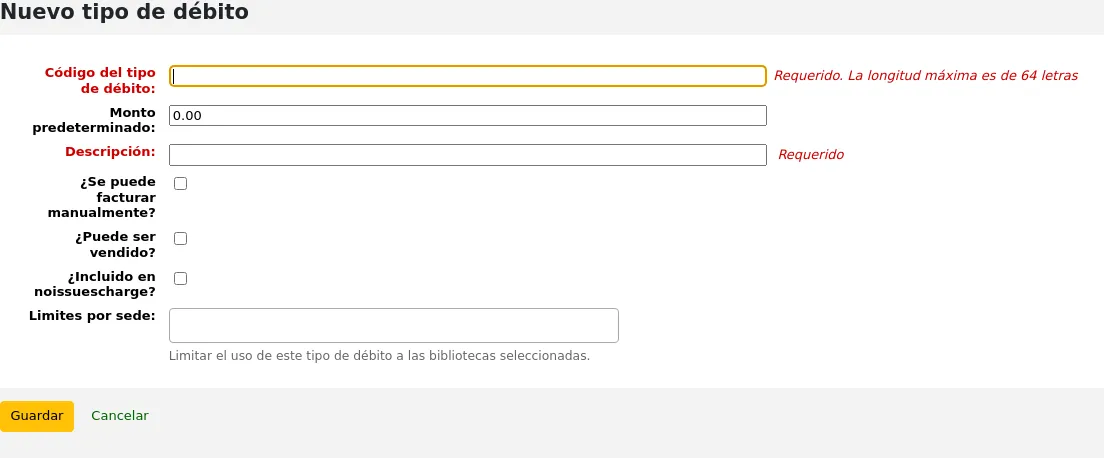
Debit type code: enter a code (limited to 64 letters).
Advertencia
Codes should be limited to letters, numbers, and underscores (_).
Avoid spaces, diacritics, and special characters.
Default amount: enter the default amount.
Nota
Staff will be able to change this amount when adding the charge to the patron’s account, if necessary.
Importante
Do not enter currency symbols. Only write the amount with a decimal point (for example, 5 or 5.00 instead of $5).
Description: write a description, this description will be used in the drop-down menu when adding a new charge to a patron’s account or when making a sale in the point of sale as well as in their transaction history.
Can be manually invoiced: check this box if this debit type can be added manually by staff to a patron’s account via the manual invoices.
Can be sold: check this box if this debit type can be used in the point of sale.
Included in noissuescharge: check this box if this debit type should be included when calculating the amount owed by the patron for the noissuescharge system preference. This system preference is used to block checkouts when a patron owes over a certain amount of money to the library.
Libraries limitation: if necessary, select the libraries where this debit type can be used. Choosing “All libraries” will make the debit type available everywhere.
Nota
You can select more than one library by pressing the “Ctrl” key while selecting.
If you have any additional fields for account debit types (account_debit_types), they will be displayed here.
Haga clic en “Guardar”
Editing an existing debit type
You can only modify the debit types you have added, as well as the “Manual fee”.
To edit a debit type:
Click the “Edit” button to the right of the debit type
Modify any field
Haga clic en “Guardar”
Archiving a debit type
If there is a debit type you don’t need anymore, you can archive it.
Nota
There is no way to delete a debit type since they are used in the patron’s accounting section.
To archive a debit type, simply click the “Archive” button to the right of the debit type.
Restoring an archived debit type
If you need to use an archived debit type again, simply click on the “Restore” button to the right of the debit type.
This will make it available again.
Credit types
Get there: More > Administration > Accounting > Credit types
Nota
Only staff with the manage_accounts permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
This is where you define the manual credits you can give patrons.
When you first get to the page, you will only see the credits that are already defined in your system.
You can see the default system credit types by clicking «Show all credit types».
You can go back to seeing only the manual credit types by clicking «Filter system credit types».
System credit types
Several credit types come installed with Koha. Most of them are automatic credits that are added according to the policies you set up elsewhere in Koha. They can not be deleted.
CANCELLATION (Canceled charge): this is used when canceling a charge in a patron’s account
CREDIT (Credit): this is used for manual credits to give to your patrons.
DISCOUNT (A discount applied to a patrons fine): this is used to discount fines and charges.
FORGIVEN (Forgiven): this is used for manual credits to give to your patrons.
LOST_FOUND (Lost item fee refund): this is used when a previously lost item is returned. If you refund the lost fees (see Default lost item fee refund on return policy), this credit will be applied to refund the fee.
OVERPAYMENT (Over payment refund): this is automatically applied to a patron’s account when they paid too much for a fee. This is mostly used when backdating check-ins where the patron has already paid the full fine.
PAYMENT (Payment): as the name states, this is used to indicate fee payments.
PURCHASE (Purchase): this is used when a payment is made through the point of sale module.
REFUND (A refund applied to a patrons fine): this is used when refunding the payment of a fine or charge.
WRITEOFF (Writeoff): this is used when writing off a fine or charge.
Adding a new credit type
To add a new credit type:
Click “New credit type”
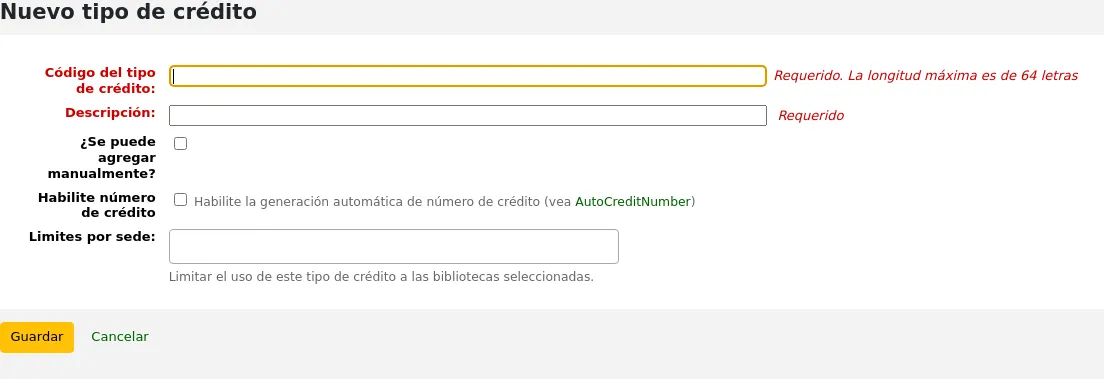
Enter a code (limited to 64 letters)
Advertencia
Codes should be limited to letters, numbers, and underscores (_).
Avoid spaces, diacritics, and special characters.
Write a description
This description will be used in the drop-down menu when adding a new credit to a patron’s account as well as in their transaction history
If this credit type can be added manually by staff to a patron’s account via the manual credit, check the “Can be added manually?” check box
If you need this credit type to be sequentially numbered, check the “Enable credit number”. The format of the number is defined in the AutoCreditNumber system preference.
If this credit type is only to be used in specific branches, you can select the libraries in “Libraries limitation”
Nota
You can select more than one library by pressing the “Ctrl” key while selecting.
If you have any additional fields for account credit types (account_credit_types), they will be displayed here.
Haga clic en “Guardar”
Editing an existing credit type
You can only modify the credit types you have added.
To edit a credit type:
Click the “Edit” button to the right of the credit type
Modify any field
Haga clic en “Guardar”
Archiving a credit type
If there is a credit type you don’t need anymore, you can archive it.
Nota
There is no way to delete a credit type since they are used in the patron’s accounting section.
To archive a credit type, simply click the “Archive” button to the right of the credit type.
Restoring an archived credit type
If you need to use an archived credit type again, simply click on the “Restore” button to the right of the credit type.
This will make it available again.
Cajas registradoras
Get there: More > Administration > Accounting > Cash registers
This feature is enabled through the UseCashRegisters system preference.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_cash_registers permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
If you have no cash registers already defined, you will be invited to create one.
Otherwise, you will see the list of all your cash registers.
In the “Actions” columns, you can choose to edit your cash registers, make one of them default or remove the default status, and archive or restore an archived register.
The default status is only useful in libraries that have more than one register per branch. The default register will be preselected when entering a payment. If there is only one cash register per branch, the branch’s cash register will be selected when paying.
Adding a new cash register
Click on “New cash register”
Give your cash register a name
Optionally you can also add a description
Choose in which library this cash register is located
And finally, enter the initial float, i.e. the amount in the cash register
Click “Add”
Plugins
This section is used to manage all types of plugins.
Importante
Before using plugins, make sure that they are enabled in the configuration file.
Nota
Only staff with the manage permission, the configure permission, or the admin permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will see this section.
See also the tool plugins and report plugins sections.
Get there: More > Administration > Plugins
If there are any administrative plugins installed, they will appear under this section.
Nota
Only staff with the admin permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will be able to use administrative plugins.
Managing plugins
This section is used to view, manage and configure all types of plugins.
Nota
Only staff with the manage permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will be able to install and uninstall plugins.
The page will show all currently installed plugins.
If you have a lot of plugins, you can view a subset by clicking “View plugins by class”.
Installing a plugin
To install a new plugin manually,
Click “Upload plugin”.
Choose the KPZ file on your computer and click “Upload”.
If you configured external plugin repositories, you will have a search box at the top of the page to search these repositories and install directly from there without having to download and upload the KPZ file. To install a plugin from a repository,
Enter a search term in the search box.
Click “Install” to the right of the plugin.
Some plugins might need to be enabled before usage.
To enable a plugin,
Click the “Actions” button to the right of the plugin and choose “Enable”
Using a plugin
All plugins are different. Some might need configuration before usage, others are simply run.
Click the “Actions” button and choose “Configure” or “Run”.
Follow the instructions issued by the plugin’s creator.
Nota
Only staff with the configure permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will be able to access plugin configuration.
Disabling a plugin
If you need to temporarily stop the plugin from taking effect, you can disable it.
Click the “Actions” button to the right of the plugin and choose “Disable”
This will not uninstall the plugin. It will remain installed, but will not have any effect on your Koha installation.
Deleting a plugin
To delete or uninstall a plugin,
Click the “Actions” button to the right of the plugin and choose “Delete”
This will remove the plugin from your Koha installation. Any action or effect it had will stop. If you need to, you can reinstall it later, provided it is still available.
Jobs
This section is used to manage background jobs. Jobs are tasks that are queued in the system to be treated when the server has the resources to do it, such as batch record modification and others.
Get there: More > Administration > Jobs
Nota
Only staff with the manage_background_jobs permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Managing jobs
By default, when accessing the page, you will only see current jobs and jobs enqueued in the last hour.
To see all jobs, uncheck the boxes at the top of the page.
Current jobs only: uncheck this to include finished jobs
Only include jobs enqueued in the last hour: uncheck this to include jobs enqueued earlier
You can search for jobs using the search boxes under the table headings.
To the right of each job, there are action buttons.
View: this will display the details of the job, including, but not limited to:
Job ID: this is the identifier of the job in the Koha database, an incremental number
Status: the status of the job
New: the job has been queued
Cancelled: the job was canceled by a user
Finished: the job was successfully carried out
Started: the job was started, but it is not yet finished
Running: the job is currently being executed
Failed: the job was started, but failed for some reason
Progress: indicates how much of the job is done
Type: indicates the type of job
Batch bibliographic record modification: batch of bibliographic records to be modified.
Batch bibliographic record deletion: batch of bibliographic records to be deleted.
Batch authority record modification: batch of authority records to be modified.
Batch authority record deletion: batch of authority records to be deleted.
Batch item record modification: batch of items to be modified.
Batch item record deletion: batch of items to be deleted.
Batch hold cancellation: a batch of holds to be canceled (when using the “Cancel selected” button).
Create eHoldings titles: titles to be created from a list in the ERM module.
Update Elasticsearch index: bibliographic or authority records, or items to be updated in the Elasticsearch index. Any changes to a bibliographic or authority record, or item trigger an update of the index, including changes in circulation status.
Holds queue update: when the RealTimeHoldsQueue system preference is enabled, changes to holds trigger an update of the holds queue.
Staged MARC records for import: bibliographic or authority records to be staged for import.
Import MARC records: staged bibliographic or authority records to be imported in the catalog.
Revert import MARC records: imported bibliographic or authority records to be reverted.
Queued: date and time when the job was queued
Started: date and time when the job was started
Ended: date and time when the job was finished
Report: this section will contain messages specific to the type of job (for example, number of records modified, in the case of batch record modification)
Detailed messages: this section will contain messages specific to the type of job (for example, which records were modified, in the case of batch record modification)
Cancel: for jobs that are still new or have started, it’s possible to cancel them
Catalog administration
Establecer estos controles antes de empezar a catalogar en su sistema Koha.
Ir a: Más > Administración > Catalogo
MARC bibliographic frameworks
Think of frameworks as templates for creating new bibliographic records. Koha comes with some predefined frameworks that can be edited or deleted, and librarians can create their own frameworks for content specific to their libraries.
Get there: More > Administration > Catalog > MARC bibliographic frameworks
Nota
Only staff with the manage_marc_frameworks permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Importante
Do not delete or edit the Default framework since this will cause problems with your cataloging records - always create a new template based on the Default framework, or alter the other frameworks.
Adding a new framework
Para agregar una nueva hoja de trabajo
Click “New framework”
Code: enter a code of 4 or fewer characters, avoiding spaces, diacritics, or other special characters.
Description: enter a more detailed definition of your framework, this is what will be displayed in Koha.
Haga clic en “Enviar””
Once your framework is added click “Actions” to the right of it on the list of frameworks and choose “MARC structure”
You will be asked to choose a framework to base your new framework on, this will make it easier than starting from scratch

Una vez que su hoja de trabajo aparezca en la pantalla puede editar o eliminar cada campo siguiendo las instrucciones para editar campos y subcampos
Editing existing frameworks
Clicking “Actions” and then “Edit” to the right of a framework will only allow you to edit the description for the framework.

Editing framework fields and subfields
Frameworks are made up of MARC fields (tags) and subfields. To make edits to the fields and subfields associated with the framework you must click on “Actions” and then “MARC structure”.
Importante
Whenever you make changes to the framework fields and subfields, make sure to run the MARC bibliographic framework test.
Editing a MARC field (tag)
After clicking on “MARC structure” you will be taken to a screen listing all the available tags for that framework and you can search for the tag you need. To make edits to a MARC field click on “Actions” on the right of the field and choose “Edit tag”.
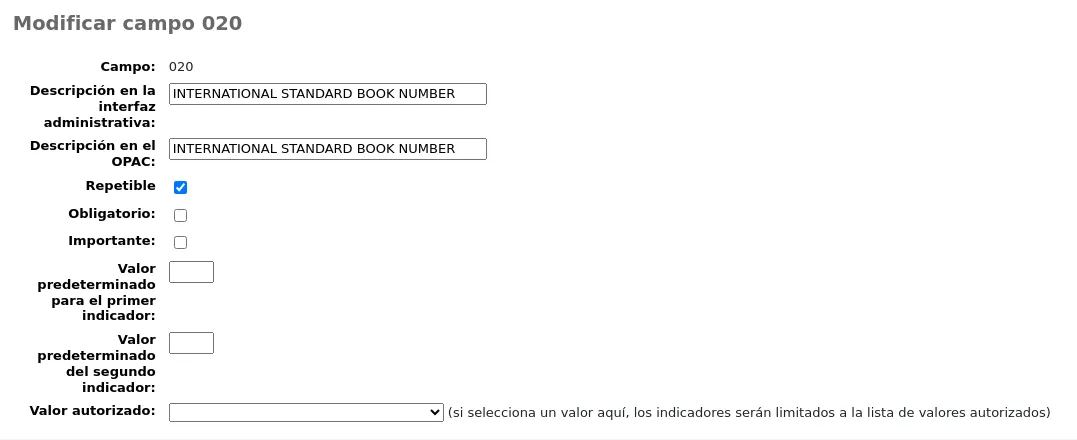
The next screen shows details of the tag.
Tag: the MARC tag, or field number, is uneditable.
Label for lib: text that will show in the staff interface MARC view, and in the basic editor if the advancedMARCeditor system preference is set to display labels.
Nota
If you use XSLT (see the XSLTDetailsDisplay system preference), the labels for the “Normal” view are defined in the XSLT stylesheet.
This will not affect the “Normal” view unless you don’t use XSLT.
Label for OPAC: text that will show on the MARC view in the OPAC.
Nota
If you use XSLT (see the OPACXSLTDetailsDisplay system preference), the labels for the “Normal” view are defined in the XSLT stylesheet.
This will not affect the “Normal” view unless you don’t use XSLT.
Repeatable: when checked, the field will have an icon next to it in the basic editor, allowing you to add multiples of that tag.
Mandatory: when checked, the record cannot be saved unless the field has a value. In the basic editor, a “Required” flag will display as a prompt.
Important: when checked, the field will generate a warning if it is not filled, but unlike “Mandatory”, you will still be able to save your record nonetheless. In the basic editor, an “Important” flag will display as a prompt.
Indicator default values: add default values for indicators here so that they will be prefilled to save time when cataloging, but can still be edited if required.
Authorized value: define an authorized value pull down list for the catalogers
Advertencia
The authorized value option at field level does not work.
Click “Save changes” to save any modification.
Editing a MARC subfield
To edit the subfields associated with the tag, click “Actions” then “Edit subfields” to the right of the tag on the framework field list. Each subfield has its own tab which contains three sections - Basic constraints, Advanced constraints and Other options.
For each subfield you can set the following basic constraint options
Subfield code: this is the MARC subfield code, this wouldn’t normally be changed.
Text for librarian: text that will show in the staff interface MARC view, and in the basic editor if the advancedMARCeditor system preference is set to display labels.
Nota
If you use XSLT (see the XSLTDetailsDisplay system preference), the labels for the “Normal” view are defined in the XSLT stylesheet.
This will not affect the “Normal” view unless you don’t use XSLT.
Text for OPAC: text that will show on the MARC view in the OPAC.
Nota
If left empty, the “Text for librarian” is used instead
Nota
If you use XSLT (see the OPACXSLTDetailsDisplay system preference), the labels for the “Normal” view are defined in the XSLT stylesheet.
This will not affect the “Normal” view unless you don’t use XSLT.
Repeatable: when checked, the field will have an icon next to it in the basic editor, allowing you to add multiples of this subfield.
Mandatory: when checked, the record cannot be saved unless the subfield has a value. In the basic editor, a “Required” flag will display as a prompt.
Important: when checked, the field will generate a warning if it is not filled, but unlike “Mandatory”, you will still be able to save your record nonetheless. In the basic editor, an “Important” flag will display as a prompt.
Managed in tab: defines the tab where the subfield is shown.
Importante
All subfields of a given field must be in the same tab or ignored. Ignore means that the subfield is not managed.
Advertencia
When importing records, or editing existing records, subfields that are managed in tab “ignore” will be deleted. If you still wish to keep the subfields, but hide them, use the “Visibility” options below.
For each subfield you can set the following advanced constraint options
Default value: defines what you want to appear in the field by default, this will be editable, but it saves time if you use the same text over and over or the same value in a field often.
Nota
There are several values that you can use here that will be replaced automatically when a new record is created:
<<MM>> - the current month, 2 digits
<<DD>> - the current day of month, 2 digits
<<YY>> - the current year, 2 digits
<<YYYY>> - the current year, 4 digits
<<USER>> - the username of the currently logged in user
For example: a default of «<<MM>>/<<DD>>/<<YYYY>>» (without quotes) will print the current date in the form of «01/21/2021»
Nota
When those default values are filled depends on the ApplyFrameworkDefaults system preference.
Max length: enter a value here to limit the number of characters that can be entered in the subfield.
Visibility: allows you to select from where this subfield is visible or hidden. Check the boxes where you would like the field to show, and uncheck the boxes where you would like it hidden.
OPAC: when checked, this will make the subfield available for display in the OPAC. For non-XSLT views, the field will be displayed. For XSLT views, it will depend on the stylesheet.
Staff interface: when checked, this will make the subfield available for display in the staff interface. For non-XSLT views, the field will be displayed. For XSLT views, it will depend on the stylesheet.
Editor: when checked, this will make the subfield available for modification in the basic editor.
Collapsed: when checked, the subfield will be hidden in the basic editor, but will display when the field label is clicked to expand all subfields.
Flagged: when checked, the subfield will be unavailable and hidden from all views (equivalent to all boxes being unchecked).
Is a URL: if checked, it means that the subfield is a URL and can be clicked.
Link: if you enter an index name here, a link appears after the subfield in the MARC detail view in the staff interface. If the librarian clicks on the link, a catalog search is done using the index and the content of the subfield.
Koha link: this field is used to create a link between the MARC subfield and a column in the items, biblioitems, and biblio database tables. The mappings can be changed from the Koha to MARC mapping page.
Para cada subcampo puede establecer los siguientes valores de Otras opciones
Authorized value: means the value must be chosen from a drop-down menu generated from the authorized value list.
In the example below, the LANG authorized value category has been set to 041$a.

This creates a drop-down menu in the basic editor.
Thesaurus: means that the value is linked to the authority catalog of the selected category. Authority categories are managed in the Authority types section.
Plugin: means the value is calculated or managed by a cataloging plugin. Cataloging plugins, or value builders, can do almost anything.
Ejemplos:
For call numbers there is an option to add a call number browser next to the call number subfield so that you can identify which call numbers are in use and which are not. Simply choose the cn_browser.pl plugin. Learn more in the cataloging section of this manual.
If you’d like to let file uploads via cataloging you can choose the upload.pl plugin and this will allow you to upload files to Koha to link to your records.
En UNIMARC hay plugins para cada campo 1xx codificado. El plugin es una ayuda enorme para el catalogador. También existen dos plugins (unimarc_plugin_210c y unimarc_plugin_225a) que pueden «mágicamente» encontrar el editor a partir del ISBN y la lista de la colección para el editor
If you would like to enable an autocomplete search for publishers in 260b and 264b you can set the plugin to marc21_field_260b.pl. When you start typing in a publisher name you will be given search results based on publisher names already in the catalog.
To save your changes, click “Save changes”.
Truco
You can drag and drop the subfield tabs to change the order in which they appear when cataloging with the basic editor.
By default, they will appear in alphanumeric order (0-9, then a-z).
Adding fields to frameworks
If a framework doesn’t contain a field that you require, you may need to add it. To add a field to a framework click the “New tag” button at the top of the framework definition.
Esto abrirá un formulario en blanco para introducir los datos de campos MARC
Enter the field number for your new tag. The process for entering the remainder of the settings for the new tag is the same as those found in the editing fields and subfields in frameworks section of this manual.
When you’re finished, click “Save changes” and your new tag will be displayed in the framework field list.
You will need to add at least one subfield to your new tag before it will appear in your framework when you are cataloging.
Click on the “Actions” button for your new tag and then “Edit subfields”. Click on the “New” tab and enter your subfield code. The process for entering the remainder of the settings for the new subfield is the same as those found in the editing fields and subfields in frameworks section of this manual.
Importing and exporting frameworks
Al lado de cada hoja de trabajo hay un enlace tanto para importar o exportar la hoja.
Export framework
To export a framework, click the “Export” option in the “Actions” button to the right of the framework title.
Al hacer clic en “Exportar” se le pedirá que elija el formato para exportar el archivo.
Una hoja de trabajo exportada de esta manera pude ser importada en cualquier otra instalación de Koha, esto se realiza utilizando la opción de importación de hoja de trabajo.
Import framework
Una forma fácil de crear una nueva hoja de trabajo es la de importar una creada desde otra instalación de Koha o desde la suya. Esta hoja de trabajo necesitará de ser exportada de otro sistema utilizando las instrucciones anteriores para que sea posible importarla en este punto.
To import a framework you first need to create a new framework. Once you have that framework, click “Actions” then “Import” to the right of the new framework.

Se le pedirá que busque un archivo en su ordenador para importar en la plantilla.
Se le solicitará que confirme sus acciones antes de importar el archivo.
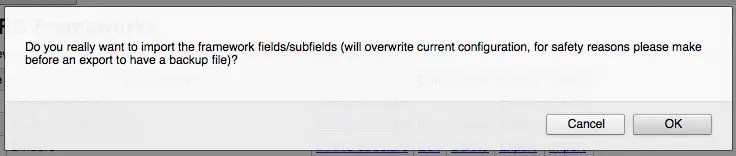
As your file is uploaded, you will see a spinning icon to indicate that the system is working.
Once your import is complete you will be brought to the framework edit tool where you can make any changes you need to the framework you imported.
Correspondencia Koha a MARC
While Koha stores the entire MARC record, it also stores common fields for easy access in various tables in the database (mainly the items, biblioitems, and biblio tables). Koha to MARC mapping is used to tell Koha where to find these values in the MARC record. Whenever a record is added or changed, this mapping will be used to update the linked database column. The information from the database columns is used as a way to quickly look up important information without having to parse the full MARC record. It is used for displaying information in a lot of pages and can also be used in reports.
In many cases, you will not have to change the default values set at the time of the installation, but it is important to know that the tool is here and can be used at any time.
Advertencia
If you change mappings after data has been added to your catalog, ask your system administrator to run misc/batchRebuildBiblioTables.pl. This will update the values in the database columns for all your records.
Get there: More > Administration > Catalog > Koha to MARC mapping
Nota
Only staff with the manage_marc_frameworks permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
La tabla muestra todos los campos de la base de datos que puede ser trazada a los campos de MARC.
To add a new mapping, click on the “Add” button to the right of the appropriate field.
Write in the MARC field and subfield you would like to map, separated by a comma, to this Koha field (for example, «264,a») and click the “OK” button.
Nota
It is possible to link more than one MARC field to a database field. For example, you could link both 260$a and 264$a to the biblioitems.place field.
If you would like to clear the mapping for a database field, click the “Remove” button.
Nota
All changes are immediate. Records created or edited after the change will immediately have the new mappings. However, if you want to update the mappings for records already in the catalog, ask your system administrator to run misc/batchRebuildBiblioTables.pl. This will update the values in the database columns for all your records.
Prueba de las hojas de trabajo bibliográficas MARC
The tool checks the MARC structure of bibliographic frameworks.
Get there: More > Administration > Catalog > MARC bibliographic framework test
Nota
Only staff with the manage_marc_frameworks permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
If you change your MARC bibliographic framework, it’s recommended that you run this tool to test for errors in your definition.
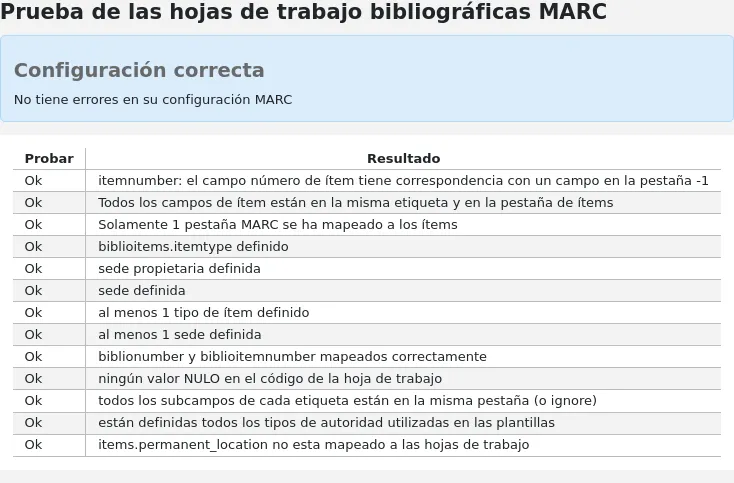
Fuentes de clasificación
Source of classification or shelving scheme are mapped to field 952$2 and 942$2 in Koha’s MARC bibliographic frameworks and stored in the items.cn_source and biblioitems.cn_source fields in the database.
Ir a: Más > Administración > Catalogo > Fuentes de clasificación
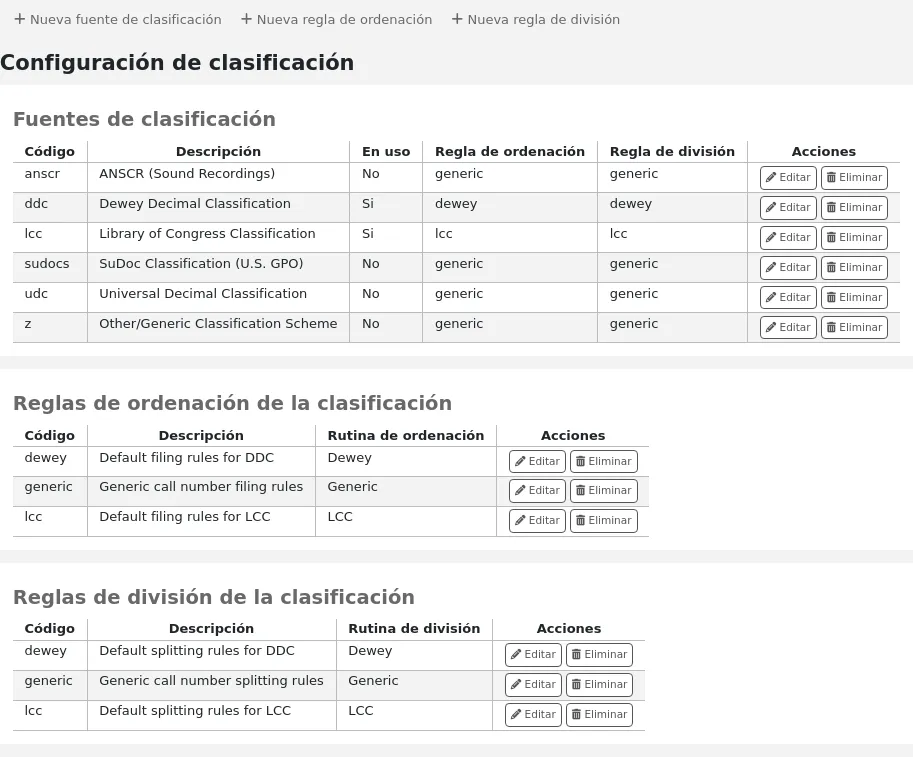
Nota
Only staff with the manage_classifications permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Commonly used classification sources are:
ddc - Clasificación Decimal Dewey
lcc - Clasificación de la Library of Congress
Si decide instalar las fuentes de la clasificación durante la instalación de Koha, vería también otros valores:
ANSCR (grabaciones sonoras)
Clasificación SuDOC
Clasificación decimal universal
Otra/Clasificación genérica
Adding/editing classification sources
You can add your own source of classification by using the “New classification source” button. To edit use the “Edit” button.
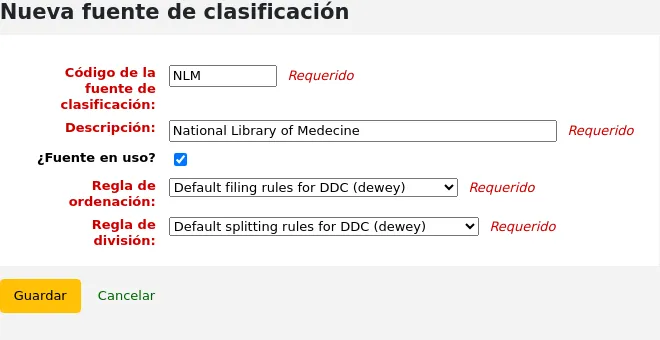
Cuando cree o edite:
Enter a code. The code is limited to 10 characters and must be unique.
Nota
The code is not editable once it has been created.
Enter a description. The description is used in the drop-down lists in the cataloging module.
Check the “Source in use?” checkbox if you want the value to appear in the drop-down list for this category.
Select the appropriate filing rule from the drop-down list.
Select the appropriate splitting rule from the drop-down list.
Reglas de ordenación de la clasificación
Filing rules determine the order in which items are placed on shelves. Filing rules normalize call numbers in order for Koha to be able to compare them and sort them in the right order.
For example, a Dewey call number such as “636.8/07 SHAW” will become “636_800000000000000_07_SHAW” in order to be sorted.
The sorted call number is saved in the items.cn_sort or biblioitems.cn_sort fields in the database
Values that are preconfigured in Koha are:
Dewey
LCC
Genérico
Filing rules are mapped to Classification sources. You can setup new filing rules by using the “New filing rule” button. To edit, use the “Edit” button.
Cuando cree o edite:
Enter a code. The code is limited to 10 characters and must be unique.
Nota
The code is not editable once it has been created.
Enter a description. The description is used in the drop-down list when creating or editing a classification source.
Seleccione una rutina de clasificación apropiada - dewey, genérica o lcc
The Dewey filing routine generates a sorted call number by following these rules:
Concatenates classification and item parts.
Converts to uppercase.
Removes any leading or trailing white spaces, and forward slashes (/)
Separates alphabetic prefix from the rest of the call number
Splits into tokens on white spaces and periods.
Leaves first digit group as is.
Converts second digit group to 15-digit long group, padded on right with zeroes.
Converts each whitespace to an underscore.
Removes any remaining non-alphabetical, non-numeric, non-underscore characters.
The generic filing routine generates a sorted call number by following these rules:
Concatenates classification and item parts.
Removes any leading or trailing white spaces.
Converts each whitespace to an underscore.
Converts to uppercase.
Removes non-alphabetical, non-numeric, non-underscore characters.
The LCC filing routine generates a sorted call number by following these rules:
Classification splitting rules
Splitting rules determine how call numbers are split when printed on a spine label.
Nota
Splitting rules are only used if your label layout specifies to split call numbers.
For example, a Dewey call number such as “636.8/07 SHAW” will become
636.807
SHAW
once printed on a spine label.
Values that are preconfigured in Koha are:
Dewey
LCC
Genérico
Splitting rules are mapped to Classification sources. You can setup new splitting rules by using the “New splitting rule” button. To edit, use the “Edit” button.
Cuando cree o edite:
Enter a code. The code is limited to 10 characters and must be unique.
Nota
The code is not editable once it has been created.
Enter a description. The description is used in the drop-down list when creating or editing a classification source.
Choose an appropriate splitting routine - Dewey, Generic, LCC or RegEx
The Dewey splitting routine looks for the three digits and the decimal, puts it on one line with the other parts (Cutter, prefix, etc.) each on a separate line (generally split on spaces).
The Generic splitting routine splits on spaces.
The LCC splitting routine puts each component on a separate line.
The RegEx splitting routine allows you to create a custom splitting routine.
Some examples of RegEx splitting routines:
Split on spaces:
s/\s/\n/g
Split on equal signs (=):
s/(\s?=)/\n=/g
Split on forward slashes (/):
s/(\s?\/)/\n/g
Remove first split if call number starts with J or K:
s/^(J|K)\n/$1 /
Cut after 9 characters:
s/(^.{9})/$1\n/
It is possible to mix and match RegEx splitting routines by clicking the “New” link just under the RegEx input box.
For example, if you want to cut after nine characters AND split on spaces, you can write both and the call number “971.42805092 C669r” will be split
971.42805
092
C669r
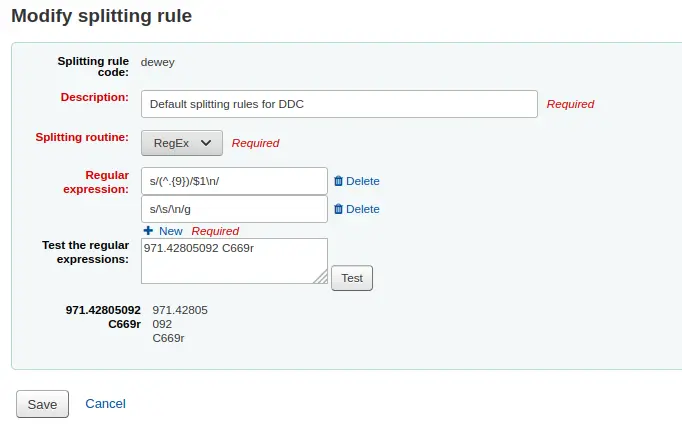
Regla de coincidencia de registro
Las reglas de registros coincidentes se utilizan en la importación de registros MARC en Koha.
Get there: More > Administration > Catalog > Record matching rules
Nota
Only staff with the manage_matching_rules permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Las reglas que se configuran aquí serán referenciadas en Preparar registros MARC para la importación.
It is important to understand the difference between “Match points” and “Match checks” before adding new matching rules to Koha.
Match points are the criteria that you enter that must be met in order for an incoming record to match an existing MARC record in your catalog. You can have multiple match points on an import rule each with its own score. An incoming record will be compared against your existing records (“one record at a time”) and given a score for each match point. When the total score of the match points matches or exceeds the threshold given for the matching rule, Koha assumes a good match and imports/overlays according your specifications in the import process. An area to watch out for here is the sum of the match points. Double check that the matches you want will add up to a successful match.
Ejemplo:
Umbral de coincidencia: 100
Match point on 020$a 1000
Match point on 022$a 1000
Match point on 245$a 500
Match point on 100$a 100
En el ejemplo anterior, una concidencia del 020$a o el 022$a re sultara en una considencia4a exitosa. Una concidencia en un título 245$a y autor 100$a (y no en 020$a o 022$a) solo agregara hasta 600 y no sera concidencia. Y una concidencia en 020$a y 245$a resultara en 1500 y mientras sea una concidencia exitosa, los 500 extra puntos para el 245$a título de concidencia son superfluo. El registro entrante concidio en el 020$a sin la necesidad de la concidencia 245$a. De todas maneras si asigna un puntaje de 500 al de 100$a Puntos Iguales, una concidencia en el título 245$a y 100$a autor sera considerado una concidencia exitosa (total de 1000) aunque si el 020$a no iguale.
Match checks are not commonly used in import rules. However, they can serve a couple of purposes in matching records. First, match checks can be used as the matching criteria instead of the match points if your indexes are stale and out of date. The match checks go right for the data instead of relying on the data in the indexes. (If you fear your indexes are out of date, a rebuild of your indexes would be a great idea and solve that situation!) The other use for a match check is as a “double check” or “veto” of your matching rule. For example, if you have a matching rule as below:
Umbral de coincidencia: 100
Match point on 020$a 1000
Match check on 245$a
Koha will first look at the 020$a tag/subfield to see if the incoming record matches an existing record. If it does, it will then move on to the Match Check and look directly at the 245$a value in the incoming data and compare it to the 245$a in the existing “matched” record in your catalog. If the 245$a matches, Koha continues on as if a match was successful. If the 245$a does not match, then Koha concludes that the two records are not a match after all. The Match Checks can be a really useful tool in confirming true matches.
When looking to create matching rules for your authority records the following indexes will be of use:
Index name |
Matches MARC tag |
|---|---|
LC-cardnumber |
010$a |
Personal-name |
100$a |
Corporate-name-heading |
110$a |
Meeting-name |
111$a |
Title-uniform |
130$a |
Chronological-term |
148$a |
Subject-topical |
150$a |
Name-geographic |
151$a |
Term-genre-form |
155$a |
Table: Authority indexes
Adding matching rules
Para crear una nueva regla de coincidencia:
Click “New record matching rule”
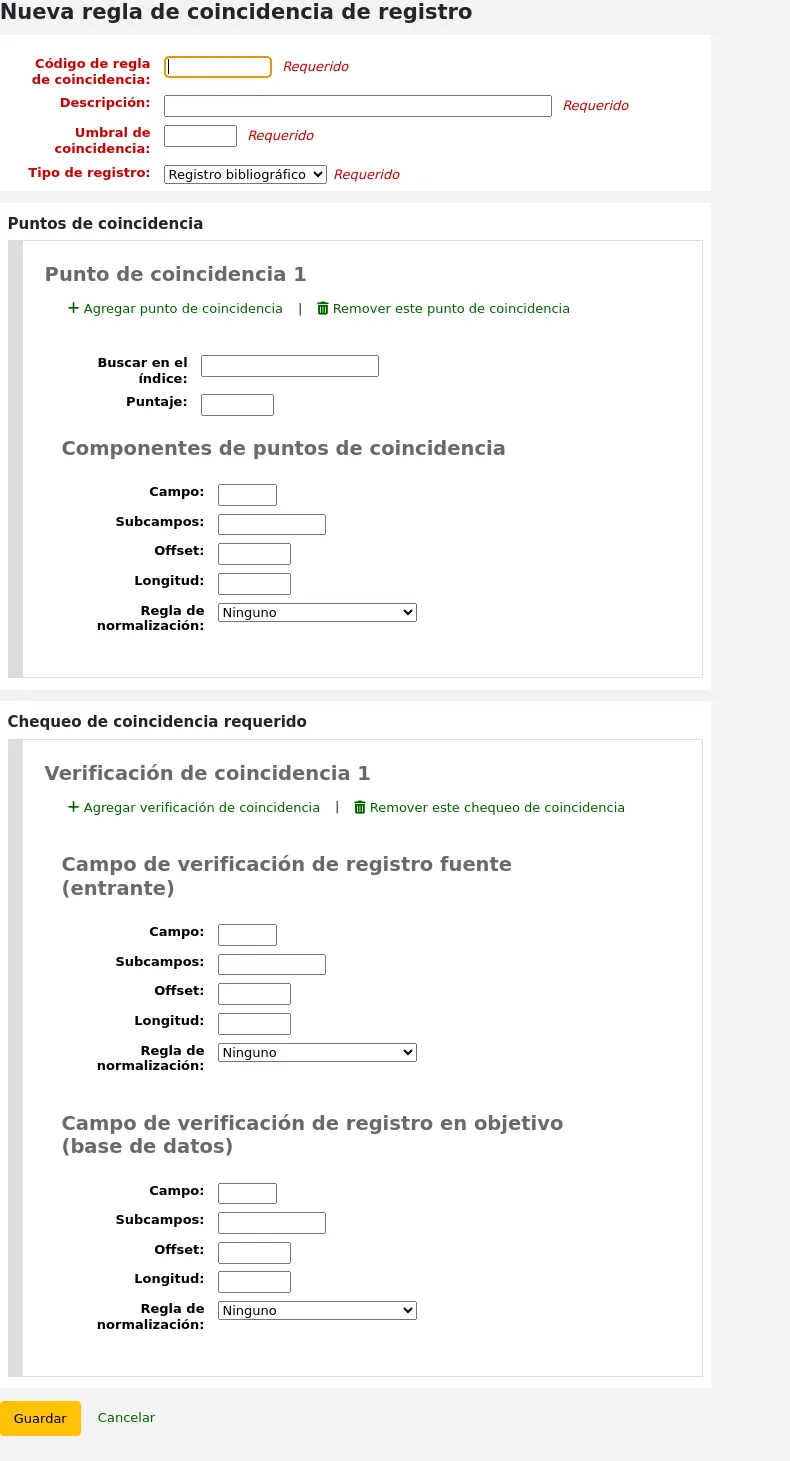
Seleccione un nombre único e ingréselo en el campo “Código de regla de coincidencia”
“Descripción” puede ser cualquier cosa que deje en claro qué regla está eligiendo
“Límite de coincidencia” - El total de “puntos” que debe sumar un registro para considerarse una “coincidencia”
“Record type” is the type of import this rule will be used for - either authority or bibliographic
Los puntos de coincidencia se establecen para determinar cuales campos deben coincidir
“Search index” can be found by looking at the index configuration on your system. For Zebra you might find the right index names in your ccl.properties file. You can also find useful information in the Koha search indexes chapter of this manual.
“Score” - The number of “points” a match on this field is worth. If the sum of each score is equal or greater than the match threshold, the incoming record is a match to the existing record.
Enter the MARC tag you want to match on in the “Tag” field.
Enter the MARC tag subfield you want to match on in the “Subfields” field. For matching on controlfields like 001 the subfields input field can be left empty.
“Offset” - Para usar en campos de control, 001-009
“Longitud” - Para usar en campos de control, 001-009
There are currently several options for “Normalization rules”:
None - no normalization rule will be applied
Remove spaces
Uppercase
Lowercase
Legacy default - this option was added to maintain the behavior form before the other normalization rules became available.
ISBN - using this option will improve matching on ISBN. If your incoming records ISBN fields contain extra text, like “9780670026623 (alk. paper)”, they will still match correctly.
“Required match checks” - While match points work on the search index, match checks work directly on the data and can be used as the matching criteria instead of the match points or in addition to them to confirm true matches.
Sample bibliographic record matching rule: Control number
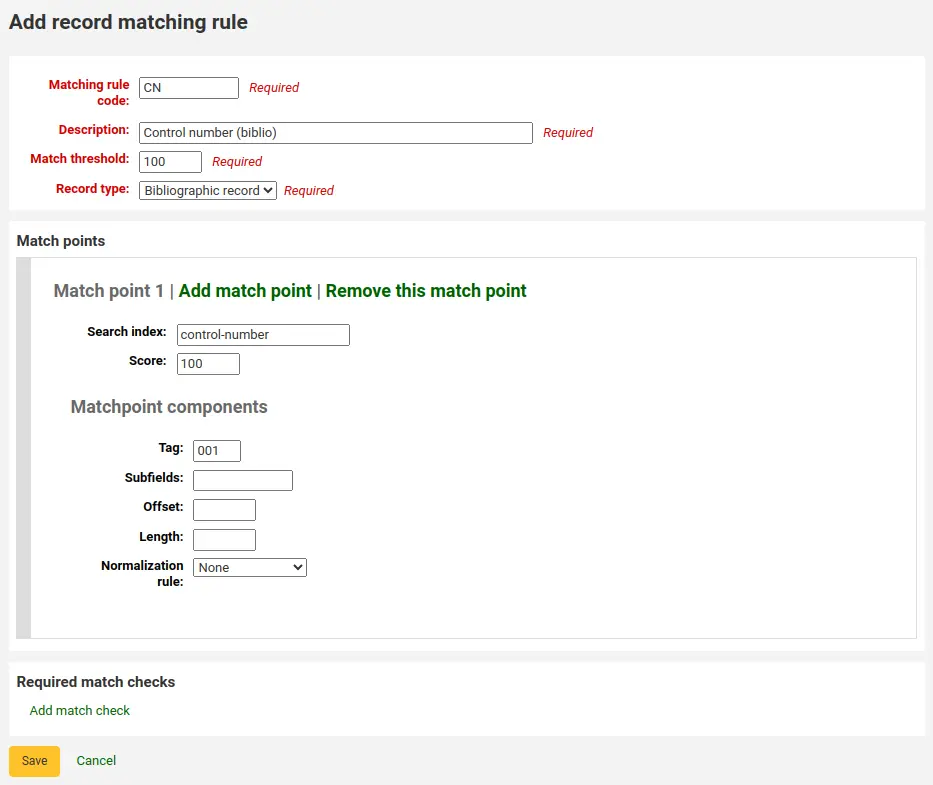
Umbral de coincidencia: 100
Record type: Bibliographic record
Nota
In order to match on the 001 in authority records, you will need to create a second rule, repeating all of these values and change just the record type to “Authority record”.
Puntos de coincidencia (solo uno):
Search index: control-number
Score: 100
Etiqueta: 001
Nota
In MARC21, this field is for the control number assigned by the organization creating, using, or distributing the record.
Subfields: empty
Offset: 0 or empty
Length: 0 or empty
Normalization rule: None
Required match checks: none (click “Remove this match check”)
Record sources
Version
This section was added to Koha in version 24.05.
Record sources are used to indicate where records come from and optionally prevent records from specific sources to be edited in Koha.
This is particularly useful in instances where records are cataloged in another system and pushed to Koha. Sometimes, in those cases, it’s best to edit the records in the source system rather than in Koha.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_record_sources permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Adding a record source
To add a record source,
Click “New record source”

Fill out the form
Name: enter the name of the source
Can be edited: if this box is checked, records from this source will be editable in Koha. If it is not checked, only staff members with the edit_locked_records permission will be able to edit the records.
Haga clic en “Enviar””
Editing a record source
To edit a record source, click the “Edit” button next to the source.

Deleting a record source
To delete a record source, click the “Delete” button next to the source and confirm.

Record overlay rules
Record overlay rules allow for defining rules for how incoming and original MARC records should be merged on a field tag and context basis when a MARC record is updated.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_marc_overlay_rules permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Contexts
Let’s first focus on understanding the concept of contexts.
Contexts are defined by «module» and «filter» enabling separate rule sets for different contexts.
By setting different filter values for these modules, rules are applied only when the filter value matches for a particular module. A wildcard; «*», can be used to match all possible filter values.
There are three different context modules:
- borrower
Allows for defining rules that will be applied if the currently logged in user’s borrowernumber matches the filter condition.
- categorycode
Allows for defining rules that will be applied if the currently logged in users’s category code matches the filter condition.
- source
Allows for defining rules that will be applied if the record is updated in a particular part of Koha. The following update methods are supported:
batchimport
z39.50
intranet
bulkmarcimport
import_lexile
batchmod
A context is really nothing but a module and filter combination. Every time a record is updated i Koha, a context is set an filter values populated with context dependent values.
Examples of two different contexts are saving record in the staff client or the currently logged in user having a particular borrowernumber, for example «12».
These two contexts are define as:
Module: source, filter: intranet
Module: borrower, filter: 12
Only the rules of one context, that is a module and filter combination, are applied. If multiple contexts matches they are not merged together.
If we have the following rules:
Module: source, filter: *, tag: 650, preset: Protect
Module: source, filter: *, tag: 500, preset: Protect
Module: borrower, filter: 12, tag: *, preset: Overwrite
And the context of the update where the rules are applied is:
source => "intranet" (wildcard match)
borrower => 1 (no match)
Only the first two rules will be applied.
If instead the context of rule evaluation was:
source => "intranet" (wildcard match)
borrower => 12 (an exact match, which is considered more specific than a wildcard match)
Only the second rule would be applied, even though the first two rules also matches they will be discarded since the context match of that rule set is of lower specificity because of the wildcard.
Context specificity is ranked in the following way:
First all the rules are grouped into rule sets identified by a unique filter and module combination.
If one or more contexts have a non wildcard filter condition match, the rule set of the context with the module of highest specificity is selected. (The modules are listed in order of specificity above).
If no exact context match is found, but one or more wildcard matches are, the rule set of the context with the module of highest specificity is selected.
If no context matches the default behavior is to overwrite, the original record with the incoming record.
Rules
A rule consists of a three different parts:
- Context
A module and filter to match against as described above.
- Tag
A field tag expression for defining which tag(s) the rule should be applied on. Three different tag expressions are supported:
An exact tag, for example «650».
A regular expression, for example «6..» matching all 6XX tags.
A wildcard, «*», matching all tags
When rules for a specific context are evaluated, the most specific match is selected. The tag expressions above are listed in order of specificity.
- Actions
Each rule defines a set of actions to take depending on the type of update. There are four types of update events: Added, Appended, Removed and Deleted. For each event an action is specified, whether to perform the update, or to skip it.
By enabling/disabling updates for these different events 16 different update behaviors can be defined. There are presets available for the most common/useful combinations:
Preset |
Added |
Appended |
Removed |
Deleted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Protect |
Skip |
Skip |
Skip |
Skip |
Overwrite |
Add |
Append |
Remove |
Delete |
Add new |
Add |
Skip |
Skip |
Skip |
Add and append |
Add |
Append |
Skip |
Skip |
Protect from deletion |
Add |
Append |
Remove |
Delete |
Protect
Added: Skip, Appended: Skip, Removed: Skip, Deleted: Skip
The «Protect» preset will prevent all updates on matching fields, protecting them from being overwritten.
Given this rule:
Module: source, filter: *, Tag: 650, Preset: Protect
And the following original and incoming records:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
650 #0$aTelevision serials$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision pilot programs$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
The 650 field of the original record will retain its original value after the update (but since the default behavior if no rule matches is to overwrite, the 500 field will be added):
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision serials$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
Overwrite
Added: Add, Appended: Append, Removed: Remove, Deleted: Delete
The «Overwrite» preset will allow all updates on matching fields.
Since the default behavior is to overwrite if no rule matches, adding a rule with the overwrite preset only makes sense if there is some other rule with a lower tag specificity with a different behavior, for example a wildcard tag rule.
So given these two rules:
Module: source, filter: *, Tag: *, Preset: Protect
Module: source, filter: *, Tag: 650, Preset: Overwrite
And the following original and incoming records:
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision serials$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
Incoming record:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision pilot programs$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
All fields but 650 will be protected on the original record, and the resulting record will be:
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision pilot programs$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
Add new
Added: Add, Appended: Skip, Removed: Skip, Deleted: Skip
The «Add new» allow updates only if the incoming field is new, that is there exists no fields with this tag in the original record.
Given this rule:
Module: source, filter: *, Tag: 650, Preset: Add
And the following original and incoming records:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
650 #0$aTelevision serials$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision pilot programs$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
The 650 in the incoming record will not overwrite the 650 field in the original record since the original record contains one or more 650 fields. The 500 field will be added since the default rule is to overwrite. The resulting record will be:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision serials$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
On the other hand, if the original record was:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
The resulting record will be:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision pilot programs$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
This is because there were no 650 fields in the original record, so adding new ones is permitted.
Add and append
Added: Add, Appended: Append, Removed: Skip, Deleted: Skip
In the «Add and append» preset, appending is also permitted, but not removing or deleting.
So if we have the following rule:
Module: source, filter: *, Tag: 650, Preset: Add and append
And the following original and incoming records:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
650 #0$aTelevision serials$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision pilot programs$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
The resulting record will be:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision serials$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
650 #0$aTelevision pilot programs$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
Note that the «old» 650 field from the original record was not removed since we only allow adding or appending new values.
If we instead used the «Overwrite» preset the resulting record would instead be:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision pilot programs$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
with the 650 field of the original record removed.
Protect from deletion
Added: Add, Appended: Append, Removed: Remove, Deleted: Skip
The preset «Protect from deletion» will allow all update operations except deletion. Deletion is defined as when there are no fields of the matching tag in the incoming record so that all of the fields with this tag would be removed on the original record.
So given the following rule:
Module: source, filter: *, Tag: 650, Preset: Protect from deletion
And the following original and incoming records:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
650 #0$aTelevision serials$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision pilot programs$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
The resulting record will be:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision pilot programs$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
On the other hand, if the incoming record was:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
In this case the deletion of 650 would not be permitted and the value of the field on the original record would be protected. The resulting record would instead be:
100 1#$aTerrace, Vincent,$d1948-
500 ##$aIncludes index.
650 #0$aTelevision serials$zUnited States$vCatalogs.
Custom presets
To work with custom presets, a more complete understanding of the update events is required:
- Added
For a matching rule with a tag, the action configured for the «Added» event is applied for new fields in the incoming record if the original record has no fields with that tag. If the action is «Add» they will be added to the original record, if «Skip» they will be thrown away.
- Appended
If the two record have common fields with the rule tag, that is one or more fields with identical subfield and identifier values, the action configured for the «Appended» event is applied for fields found in incoming record but not in original record. If the action is «Append» they will be added to the original record, if «Skip» they will be thrown away.
- Removed
If the two records have common fields with the rule tag, the action configured for the «Removed» action is applied for fields found in original record but not in incoming record. If the action is «Remove» they will removed from the original record, if «Skip» they will be kept.
- Deleted
If the original record have fields with the rule tag, but no fields with this tag is found in the incoming record, the action configured for the «Deleted» event is applied for the fields in the incoming record. If the action is «Delete» the fields will be removed from the original record, if «Skip» they will be kept.
Configuración de conjunto OAI
En esta página puede crear, modificar y eliminar conjuntos OAI-PMH
Nota
Only staff with the manage_oai_sets permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Crear un conjunto
Para crear un conjunto:
Haga clic en el enlace “Agregar un nuevo conjunto”
Rellene los campos obligatorios “setSpec” y “setName”
Entonces puede agregar descripciones para este conjunto. Para hacerlo haga clic en “Agregar descripción” y rellene la casilla de texto creada. Puede agregar cuantas descripciones desee.
Haga clic en al botón “Guardar”
Modify/delete a set
Para modificar un conjunto, haga clic en el enlace “Modificar” en la mísma línea del conjunto que desea modificar. Aparecerá un formulario similar al de creación y le permitirá modificar setSpec, setName y descripciones.
Para eliminar un conjunto, solo haga clic en el enlace “Eliminar” en la misma línea del conjunto que desea eliminar.
Defina correspondencias
Here you can define how a set will be build (what records will belong to this set) by defining mappings. Mappings are a list of conditions on record content.
Cumplimente los campos “Campo”, “Subcampo” y “Valor”. Por ejemplo si quiere incluir en este conjunto todos los registros que tengan un 999$9 con valor “XXX”. Cumplimente “Campo” con 999, “Subcampo” con 9 y “Valor” con XXX.
If you want to add another condition, click on “Add” button and repeat step 1. You can choose between “and” or “or” Boolean operators to link your conditions.
Haga clic en “Guardar”
Para eliminar una condición, solo deje al menos uno de “Campo”, “Subcampo” o “Valor” y haga clic en “Guardar”.
Nota
En realidad, una condición es verdadera si el valor en el subcampo correspondiente es estrictamente igual a lo que se define si “Valor”. Un registro que cuenta con 999$9 = “XXX YYY «no pertenecer a un conjunto donde la condición es de 999$9 =”XXX “.
Y es sensible a mayúsculas: un registro que tiene 999$9 = “xxx” no pertenecerá a un conjunto cuya condición sea 999$9 = “XXX”.
Crear conjuntos
Una vez haya configurado todos sus conjuntos, deberá construirlos. Este se hace invocando el script misc/migration_tools/build_oai_sets.pl.
Campos para búsqueda en ítems
Get there: More > Administration > Catalog > Item search fields
This section allows you to add custom search fields to the item search option in the staff interface.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_item_search_fields permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Adding a custom item search field
To add a new search field, click the “New search field” button.
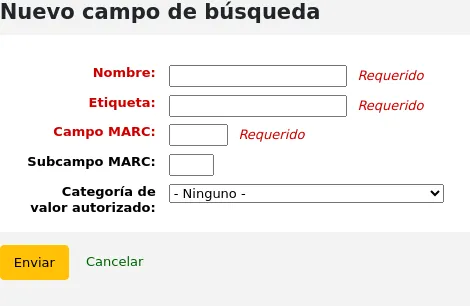
Name: enter the search field’s name
Label: enter the label of the search field as it will appear on the item search page
MARC field: enter the MARC field number to search in; the MARC field will also appear on the item search page
MARC subfield: enter the MARC subfield code to search in
Authorized value category: if needed, choose an authorized value category for this search field; this will effectively turn this search field in a dropdown menu instead of a free text field
Click “Submit”.
Once the new field is added, it will be visible on the item search page, in the dropdown that starts with “Barcode”.
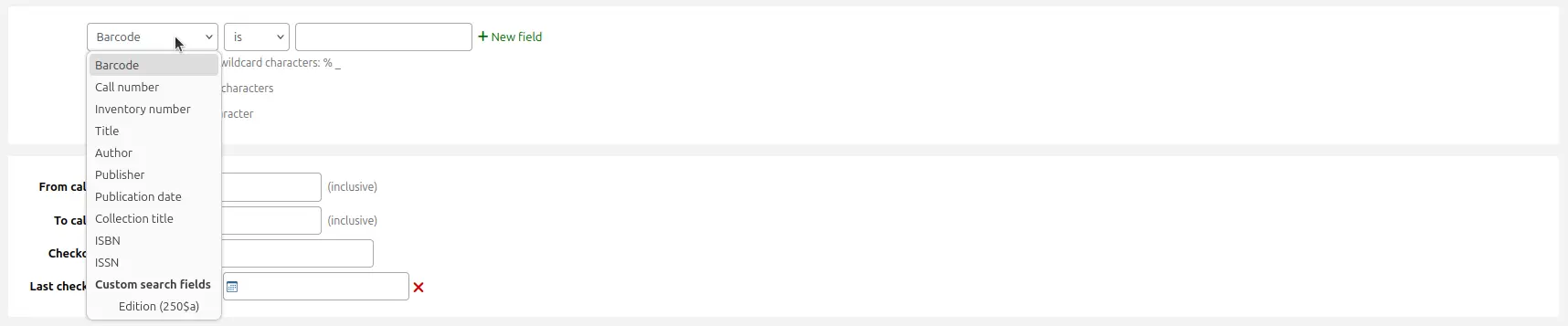
Editing a custom item search field
To edit an item search field, click the “Edit” button next to the search field in the table.
Make the changes and click “Submit”.
Deleting a custom item search field
To delete an item search field, click the “Delete” button next to the search field in the table and confirm the deletion.

Search filters
Search filters are custom searches or filters that can be applied to search results.
This functionality is enabled on using the SavedSearchFilters system preference.
Nota
This section will only be visible if the SavedSearchFilters system preference is enabled.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_search_filters permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Search filters are added by searching the catalog through the staff interface.
This page is used to manage existing search filters.
You can make changes to each search filter by clicking on the action buttons on the right.
Edit filter: change the name of the filter, and its availability in the OPAC or staff interface
Edit search: clicking this button will bring you to the advanced search form, with the filter already applied. You can change the search parameters, and click “Save filter” at the top of the page.
Delete: clicking this button will delete the filter.
Advertencia
There is no confirmation when deleting a search filter. Once you click “Delete”, the filter will be deleted immediately.
Nota
Search filters can be used as predefined search URLs that you can use on your website or in HTML customizations.
Search filters are available through relatively short links.
<OPACBaseURL>/cgi-bin/koha/opac-search.pl?limit=search_filter:<Id of filter>
Use this URL anywhere to link directly to the search.
Search engine configuration
Once you have switched to Elasticsearch in your SearchEngine system preference, you’ll see a new link for Search engine configuration in the Catalog section of Administration. Here you will manage indexes, facets, and their mappings to MARC fields and subfields.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_search_engine_config permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
The page is separated in three tabs: search fields, bibliographic records, and authority records.
Importante
If you change anything in this page, you need to completely reindex your records, otherwise, only records added or edited after the change will be affected.
Peligro
Any change done through the interface will be lost if you click on
“Reset mappings” or if the rebuild command is run with the --reset
or -r parameter. The “Reset mappings” button and the --reset
parameter reset the settings to the defaults.
Search fields
The search fields tab in the search engine configuration page show all the search fields used by Elasticsearch in Koha.
The table shows:
Name: the name of the search field, as defined in the mappings file.
Aliases: some fields have aliases, for example, «author» can also be «au». These are hard-coded and cannot be changed.
Label: some fields have labels that are different from their name. These are used as the facet header when the field is used as a facet.
Type: the type influences how the data is stored and how it is searched.
Boolean: a 0 / 1 (no / yes) value.
Call Number: a call number influenced by the classification source.
Date: a date stored in ISO format.
Geo point: a geographic latitude and longitude value.
Version
The Geo point type was added to Koha in version 24.05.
ISBN: ISBN standard number.
Number: a number.
Std. Number: a number.
String: a simple string of characters.
Sum: a sum of values.
Year: a four-digit year number.
Weight: a positive numerical value assigned to that search field to make it more «important» in a simple search. The higher the value, the more «important» this field is in the relevancy sorting.
Nota
Weighted search only works for bibliographic search, not authority search. It also only works for the simple search, unless the “Apply field weights to search” option in the advanced search is selected.
Searchable: whether this field is used in the staff interface or the OPAC.
Adding search fields
Version
The possibility of adding search fields was added to Koha in version 24.05.
It is possible to add search fields from this table. Add the search field information in the last row of the table, and click the “Add” button at the end of the row.
Deleting search fields
Version
The possibility of deleting added search fields was added to Koha in version 24.05.
It is possible to delete search fields that were added manually. The default search fields cannot be deleted because they are necessary for Koha to work properly.
To delete a search field, click the “Delete” button at the end of the row.
Bibliographic records
The bibliographic records tab in the search engine configuration page shows the MARC mappings for each search field used by Elasticsearch in Koha.
Nota
The default mappings are described in the Elasticsearch indexes section of the Searching chapter.
The table shows:
Search field: the corresponding search field (as defined in the search fields tab). Search fields can be repeated to include several MARC fields.
Sortable: indicates whether this mapping should be used in the sorting for this search field. For example, in MARC21, the title index has several different title fields, but only the 245 field is used for sorting.
Facetable: indicates whether this mapping can be used in the facets.
Version
Facet configuration was added to Koha in version 24.05.
Suggestible: indicates whether this mapping is used in the browse search.
Searchable: indicates whether this mapping is used for searching.
Filter: the type influences the way values are indexed.
Punctuation: removes punctuation.
None: values are indexed as they are.
Version
Filters were added to Koha in version 23.11.
Mapping: indicates the MARC field mapped to that search field.
Nota
Mappings can include whole fields or only specific subfields. In the case of subfields, they can be indexed individually or as a single value.
For example:
520will index all the contents of the 520 field. Each subfield in the field will be indexed individually.100awill index only the contents of 100$a.020azwill index only the contents of subfields $a and $z of field 020. They will be indexed individually.245(abp)will index only the contents of subfields $a, $b and $p of field 245. They will be indexed as one entry.
For fixed-length fields, the syntax is as follows :
leader_/6will index position 6 of the leader (000).007_/0will index position 0 of field 007.008_/39will index position 39 of field 008.008_/15-17will index positions 15 to 17 of field 008, as one entity.
Adding mappings
To add a mapping, add the information in the last row of the table and click the “Add” button at the end of the row.
Importante
Remember that if you change anything in this page, you need to completely reindex your records, otherwise, only records added or edited after the change will be affected.
Peligro
Any change done through the interface will be lost if you click on
“Reset mappings” or if the rebuild command is run with the --reset
or -r parameter. The “Reset mappings” button and the --reset
parameter reset the settings to the defaults.
Deleting mappings
To delete a mapping, click the “Delete” button at the end of the row.
Some mappings are necessary for Koha to function properly and cannot be deleted.
Importante
Remember that if you change anything in this page, you need to completely reindex your records, otherwise, only records added or edited after the change will be affected.
Peligro
Any change done through the interface will be lost if you click on
“Reset mappings” or if the rebuild command is run with the --reset
or -r parameter. The “Reset mappings” button and the --reset
parameter reset the settings to the defaults.
Facet order
This section allows you to customize the facets, as displayed in the search results in the OPAC and staff interface.
Search field: the corresponding search field (as defined in the search fields tab).
Label: the search field’s label (as defined in the search fields tab).
Version
This column was added to Koha in version 23.11.
Authorized value category: for some facets, it is possible to define an authorized value category that will manage the text displayed for the facet items. Some facets have hard-coded authorized value categories, such as LOC for location and CCODE for collections.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 23.11.
To reorder the facets, simply drag and drop the row where you want it.
To rename facets, you need to change the label in the search fields tab.
To delete a facet, click the “Delete” button.
Atención
In Koha versions 23.11 and earlier, it is not possible to delete facets. But it is possible to uncheck the “Display” checkbox to hide them from the search results.
To add a new facet,
first, add the search field,
then add mappings to that search field, making sure to set “Facetable” to “Yes”,
finally, add the facet in the facet order table, using the last row to enter the values, and click the “Add” button at the end of the row.
Version
The option to add facets was added to Koha in version 24.05.
Adquisiciones
El módulo de adquisiciones de Koha proporciona una forma para que la biblioteca haga los pedidos a sus proveedores y gestione los presupuestos de adquisiciones.
Before using the acquisitions module, you will want to make sure that you have completed all of the set up.
Ir a: Más > Administración > Adquisiciones
Monedas y tipo de cambio
Si usted hace pedidos a más de un país debe completar la entrada de cambio de divisas para que el módulo de adquisiciones pueda calcular correctamente los totales.
Nota
Only staff with the currencies_manage permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Get there: More > Administration > Acquisitions > Currencies and exchange rates
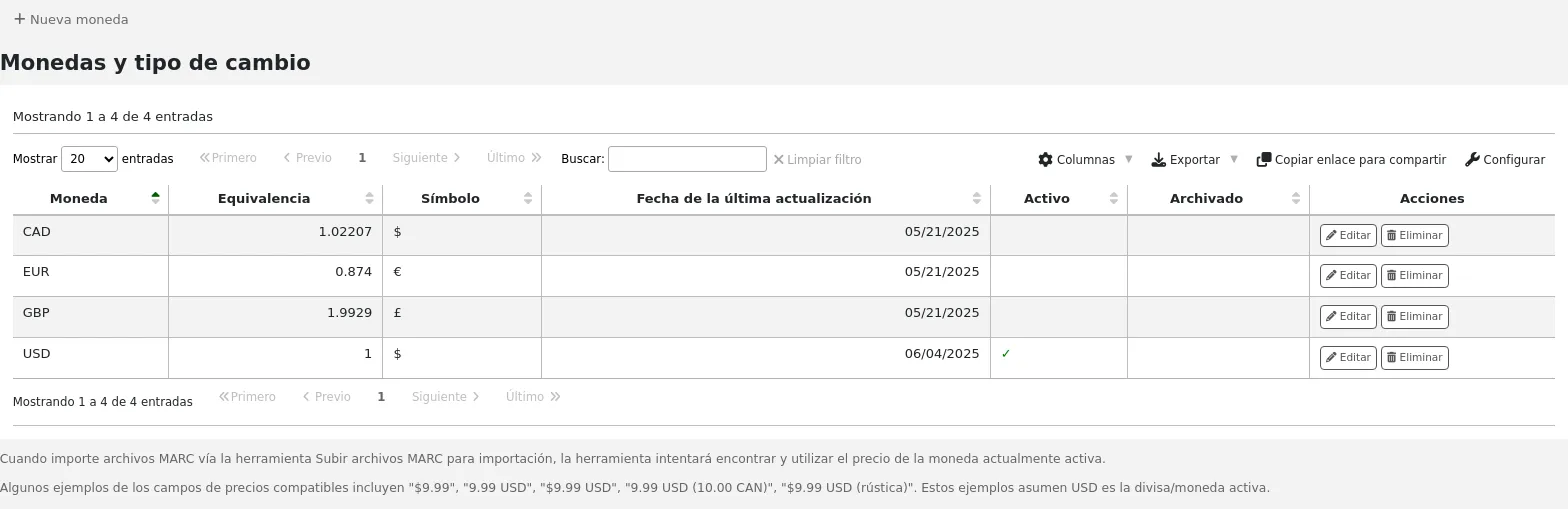
Nota
You can customize the columns of this table in the Table settings section of the Administration module (table id: currency).
Currency: this is the code for the currency. For default currencies, the ISO code is used as currency code (for example “USD” for the US dollar). The ISO code will be used when importing MARC files via the staging tools. The tool will attempt to find and use the price of the currently active currency.
Rate: the rate will be used to calculate the price in the active currency.
Nota
Estos datos no se actualizan automáticamente, así que asegúrese de mantenerlos al día para que su contabilidad se mantenga correcta.
Symbol: this is the symbol for the currency (for example, $ for USD, or € for EUR).
Last updated: this is the date when the currency was last updated in Koha.
Active: the active currency is the main currency you use in your library. The active currency will have a check mark in the “Active” column. If you don’t have an active currency you will see an error message telling you to choose an active currency.

The active currency must have a rate of 1. There can only be one active currency.
Archived: archived currencies will have “Yes” in this column. Archived currencies cannot be used in the acquisitions module.
Nota
It is currently not possible to manually archive currencies. Currencies will be archived if Koha is updated and a currency that was used previously in the acquisitions module was deleted.
Actions: use the buttons to edit or delete currencies.
Nota
If a currency was used at least once, it will not be possible to delete it.
Adding a new currency
If a currency that you use is not already in your system, you can create it.
Click “New currency”.
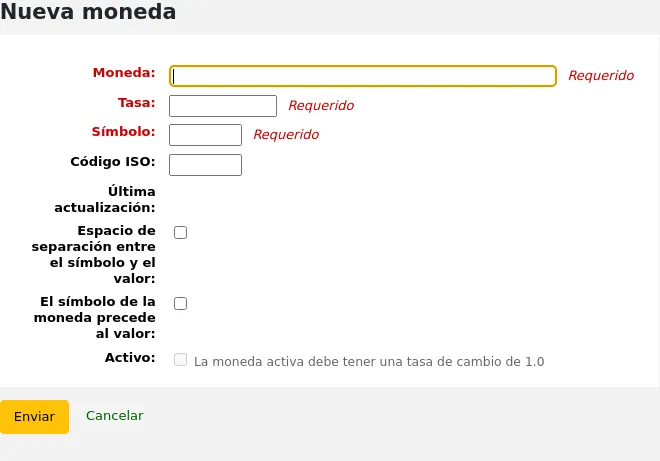
Fill out the form.
Currency: enter a code for the currency, this can be the ISO code, or another code. This is what will be displayed in the acquisitions module.
Nota
If you decide to use a custom code here, make sure to fill out the ISO code with the correct code for the currency. This will ensure that prices are calculated according to the rate.
Nota
This field is limited to 10 characters.
Rate: enter the rate of this currency relative to your active currency.
Symbol: enter the symbol for the currency (for example, $ for USD, or € for EUR).
ISO code: enter the ISO code for the currency (for example “USD” for the US dollar). This field is optional. If this field is empty, Koha will use the currency code (above) as the ISO code for price calculations.
Last updated: this will be filled automatically with today’s date, it is not possible to manually change this date.
Space separation between symbol and value: if checked, Koha will display the price with a space before the currency symbol (for example, 10.99 $ rather than 10.99$).
Currency symbol precedes value: if checked, Koha will display the currency symbol before the price (for example, $10.99 rather than 10.99$).
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 24.11.
Active: check this box if this currency is the default currency used in the acquisitions module. Note that there can only be one active currency and that the active currency’s rate must be 1.
Click “Submit”.
Editing a currency
If you often order from other countries, it will be necessary to update the exchange rate regularly in order to calculate the prices precisely.
To edit an existing currency,
Click the “Edit” button to the right of the currency in the currencies table.
Change the rate, or other value.
Nota
Note that the currency code and the last updated date cannot be edited.
Click “Submit”.
Deleting a currency
If there are currencies that you never use, it is possible to delete them.
From the currencies table, click the “Delete” button to the right of the currency.
Advertencia
Currencies that have been used at least once in the acquisitions module cannot be deleted.
Presupuestos
Budgets are used for tracking accounting values related to acquisitions. For example you could create a budget for the current year (ex. 2015) and then break that into funds for different areas of the library (ex. Books, Audio, etc).
Ir a: Más > Administración > Adquisiciones > Presupuestos
Nota
Staff members must have the period_manage permission (or the superlibrarian permission) in order to access the budgets administration page.
It is recommended to minimally give the following permissions to staff members who need to manage budgets, since these are interdependent:
Cuando visite la administración principal de presupuestos verá dos pestañas, una para presupuestos activos y otra para inactivos.
Adding budgets
Budgets can either be created from scratch or by duplicating the previous year’s budget.
Nota
Staff members must have the period_manage permission (or the superlibrarian permission) in order to create new budgets or duplicate existing budgets.
Adding a new budget
If you haven’t used Koha before for acquisitions, you’ll need to start fresh with a new budget.
To add a new budget,
Click the “New budget” button.
Fill out the form:
Start date (mandatory): choose the starting date for the time period this budget is for. This can be the start of the calendar year, fiscal year, academic year, quarter, etc.
End date (mandatory): choose the ending date for the time period this budget is for.
Description (mandatory): enter a description for this budget. The description should be something that will help you identify the budget when ordering.
Total amount: enter the amount for the budget. Do not use any symbols, simply enter the amount of the budget with numbers and decimals.
Make budget active: marking a budget as active makes it usable when placing orders in the acquisitions module, even if the order is placed after the budget end date. This will allow you to record orders that were placed in a previous budget period.
Lock budget: locking a budget means that you will not be able to add funds or add sub funds to this budget, and you will not be able to plan spending. Lock the budget once it is set as you wish.
Click “Save”.
You will be brought back to the list of existing budgets.
Proceed to add funds to the budget.
Duplicating a budget
At the end of the year, or the end of your budget period, you can duplicate the current budget. This will also duplicate all funds, so you don’t have to start from scratch each year or period.
To duplicate a budget,
From the list of budgets, click the “Actions” button on the right.

Choose “Duplicate”.
Alternatively,
From the list of budgets, click on the budget name.

On the screen listing the budget breakdown, click the “Edit” button at the top and choose to “Duplicate budget”.
In both cases, you will be presented with a form to duplicate the budget.
Start date (mandatory): choose the starting date for the time period this new budget is for.
End date (mandatory): choose the ending date for the time period this budget is for.
Description (mandatory): enter a description for this new budget.
Change amounts by: by default, the total amount from the duplicated budget and the original amounts for each fund will be used. However, if needed, you can indicate to change the amounts by a percentage, that can be positive or negative. For example, if your new budget was increased by 2%, enter 2. Inversely, if your new budget was decreased by 2%, enter -2.
If amounts changed, round to a multiple of: if you entered a value in “Change amounts by”, Koha will calculate the amounts automatically. You can force it to round down the amounts. For example, entering “100”, will round down the amounts to the hundreds (5542 will become 5500).
Mark the original budget as inactive: check this box if the original budget should no longer be used, effective immediately. You can always edit the budget later to make it inactive.
Set all funds to zero: check this box if you wish the new budget to contain all the same fund structures as the previous budget but no allocations until you manually enter an amount in the fund.
This will not only duplicate the budget, but all of the funds associated with that budget so that you can reuse budgets and funds from year to year.
When the time comes, you can close the previous budget to move unreceived orders, and, if desired, unspent funds to the new budget.
Editing a budget
Nota
Staff members must have the period_manage permission (or the superlibrarian permission) in order to edit existing budgets.
You can edit existing budgets to make them inactive or lock them to prevent fund changes, for example.
To edit a budget,
From the list of budgets, click the “Actions” button on the right.

Choose “Edit”.
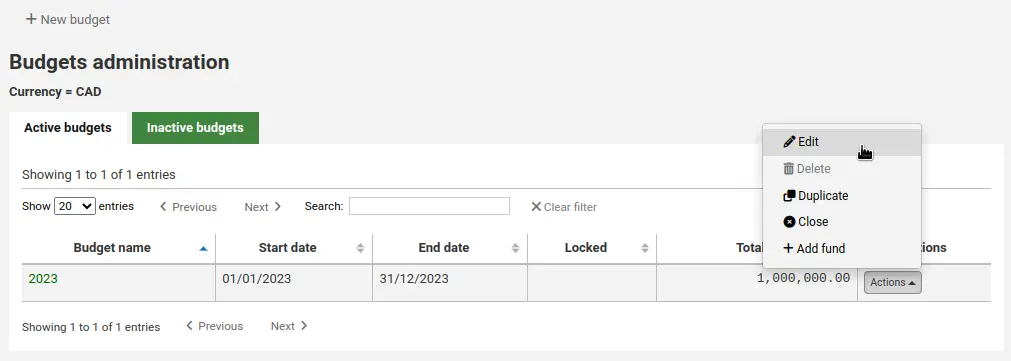
Alternatively,
From the list of budgets, click on the budget name.

On the screen listing the budget breakdown, click the “Edit” button at the top and choose to “Edit budget”
In both cases, you will be presented with a form to duplicate the budget.
Make your changes (see the field descriptions above).
Click “Save”.
Closing a budget
Cierre un presupuesto para mover o pasar pedidos sin recibir y, si se desea, fondos no gastados de un presupuesto previo a un nuevo presupuesto. Antes de cerrar su presupuesto es posible que desee duplicar el presupuesto del año anterior para que tenga un lugar al cual pasar los pedidos sin recibir.
Nota
Staff members must have the period_manage permission (or the superlibrarian permission) in order to close existing budgets.
To close a budget,
From the list of budgets, click the “Actions” button on the right.

Choose “Close”
Nota
Budgets without unreceived orders cannot be closed.
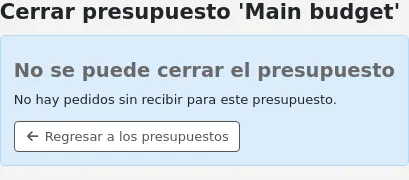
Fill out the form.
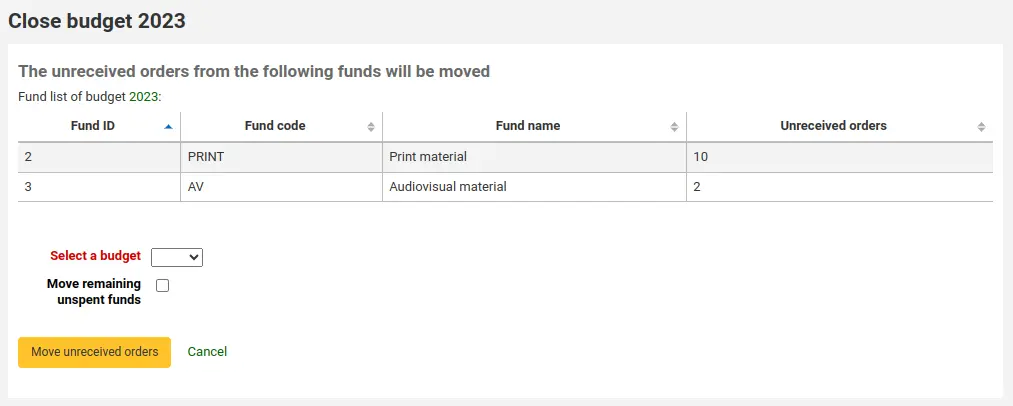
Select a budget: choose the new budget for the unreceived orders from the dropdown.
Nota
In order for the unreceived orders to be automatically moved to the new budget, the fund structures in the previous budget must exist in the new budget.
Move remaining unspent funds: check this box to move the unspent amounts from the funds of the budget being closed to the selected budget.
Click the “Move unreceived orders” button.
You will be presented with a dialog box that says “You have chosen to move all unreceived orders from “Budget X” to “Budget Y”. This action cannot be reversed. Do you wish to continue?” Budget X is the budget to be closed and Budget Y is the selected budget.
Si todo parece correcto haga clic en “Aceptar” y los pedidos sin recibir y, si esta seleccionado, se trasladarán los fondos no gastados.
Espere hasta que el “Informe después de mover pedidos sin recibir del presupuesto X a Y” sea desplegado. Esto mostrará una lista de los números de pedido que han sido impactados (agrupados por el fondo) y detalla si el pedido sin recibir fue movido o si hubo un problema. Por ejemplo, si el nuevo presupuesto no contiene un fondo con el mismo nombre que el presupuesto anterior, el pedido no será movido.
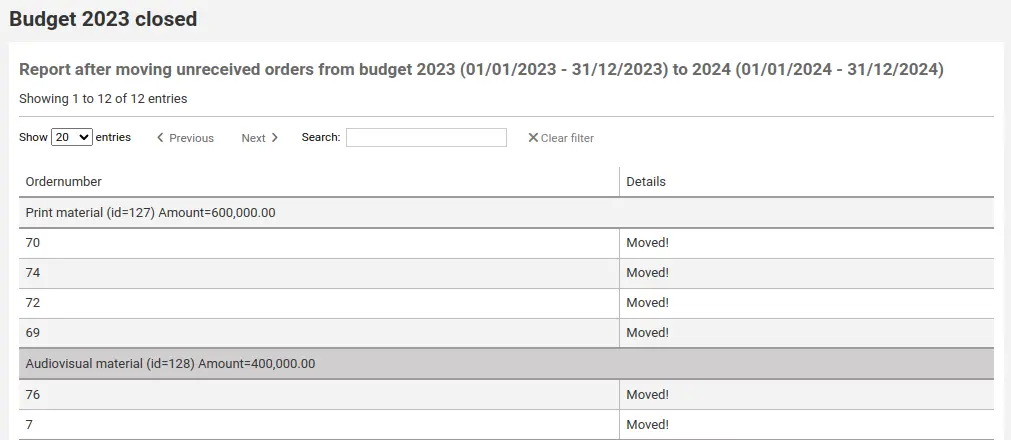
Deleting a budget
In order to delete a budget, it must not have funds. Start by deleting the funds.
Advertencia
This cannot be undone. Make sure you are certain this budget needs to be deleted. You can make it inactive or close it, instead.
To delete a budget,
From the list of budgets, click the “Actions” button on the right.

Choose “Delete”.
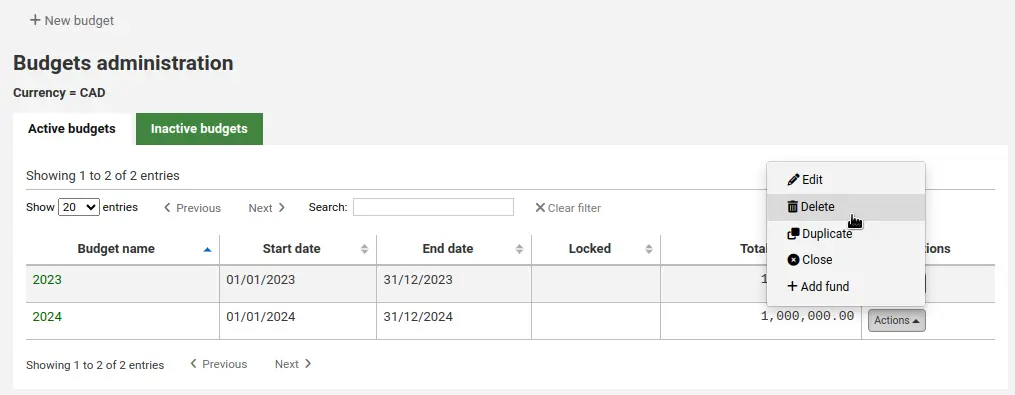
Click “Yes, delete”.
Fondos
Funds are divisions of a budget. For example you could have a budget for the current year (ex. 2015) and then break that into funds for different areas of the library (ex. Books, Audio, etc).
Ir a: Más > Administración > Adquisiciones > Fondos
Adding a fund to a budget
A fund is added to a budget. Make sure to add a budget before adding funds.
Nota
If a budget is locked, it will not be possible to add funds.
To add a new fund,
From the list of budgets, click the “Actions” button on the right.

Choose “Add fund”.
Alternatively,
From the list of budgets, click on the budget name.

On the screen listing the budget breakdown, click the “New” button at the top and choose the “New fund for…” option.
In both cases, you will be presented with a form to create the new fund.
Fund code (mandatory): enter a unique identifier for your fund.
Fund name (mandatory): enter a name for the fund. This should be something that staff will understand, as this is what will be displayed when ordering.
Amount (mandatory): enter the amount with only numbers and decimals, no other characters.
Warning at (%): enter a percentage value to have Koha warn you when you have spent this percentage of the fund, to prevent overspending. For example, if you enter 90%, Koha will warn you for each order after 90% of the fund is spent.
Warning at (amount): same as above but for a specific amount of money spent. For example, if you enter 5000, Koha will warn you for each order after 5000 is spent in the fund.
Owner: you can choose to assign this fund to a staff member.
Click “Select owner”.
Search for the staff member in the patron search form.
Nota
Only staff with the budget_modify permission (or the superlibrarian permission) are returned in the search results.
Click “Select” to the right of the staff member’s result.
Nota
A fund can only have one owner.
Nota
In order to limit the use of this fund to the owner, you must choose either “Owner”, “Owner and users” or “Owner, users and library” in the “Restrict access to” field below. Otherwise, adding users will not have any restricting effect.
Nota
Staff members with the order_manage_all permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will be able to use funds regardless of restrictions.
Make sure your staff doesn’t have that permission if you want to restrict access to funds.
Users: you can also add users who will be able to spend in that fund.
Nota
In order to limit the use of this fund to the users, you must choose either “Owner and users” or “Owner, users and library” in the “Restrict access to” field below. Otherwise, adding users will not have any restricting effect.
Nota
Staff members with the order_manage_all permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will be able to use funds regardless of restrictions.
Make sure your staff doesn’t have that permission if you want to restrict access to funds.
Click “Add users”
Search for the staff member in the patron search form.
Nota
Only staff with the budget_modify permission (or the superlibrarian permission) are returned in the search results.
Click “Add” to the right of the staff member’s result.
Nota
You can add as many users as you need.
Click “Close” once all the users have been added.
Library: If this fund is for a specific library, choose it here.
Nota
In order to limit the use of this fund to the library, you must choose “Owner, users and library” in the “Restrict access to” field below. Otherwise, choosing a library will not have any restricting effect.
Nota
Staff members with the order_manage_all permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will be able to use funds regardless of restrictions.
Make sure your staff doesn’t have that permission if you want to restrict access to funds.
Restrict access to: you can restrict who can order from this fund by choosing either the “owner”, “owner and users” or “owner, users and library”.
Advertencia
Without an owner, the access restriction will be ignored, be sure to enter an owner as well as choose a restriction.
Nota
Staff members with the order_manage_all permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will be able to use funds regardless of restrictions.
Make sure your staff doesn’t have that permission if you want to restrict access to funds.
Notes: any descriptive notes about this fund.
Nota
Notes will only appear on this screen (when editing the fund).
Statistic 1 done on: this is used for statistical purposes. Choose an authorized value category from which to choose values when placing orders using this fund. You will then be able to plan spending and report on spending according to those categories. The default authorized value category Asort1 is created specifically for this purpose, but you can use any authorized value category in this field (CCODE for example to plan spending according to collections).
Statistic 2 done on: same as above, for a second statistical category. The default authorized value category Asort2 is created specifically for this purpose, but you can use any authorized value category.
Nota
To learn more about planning categories, check out the Planning category FAQ.
Click “Submit”.
You will be brought to a list of all of the funds for the budget.
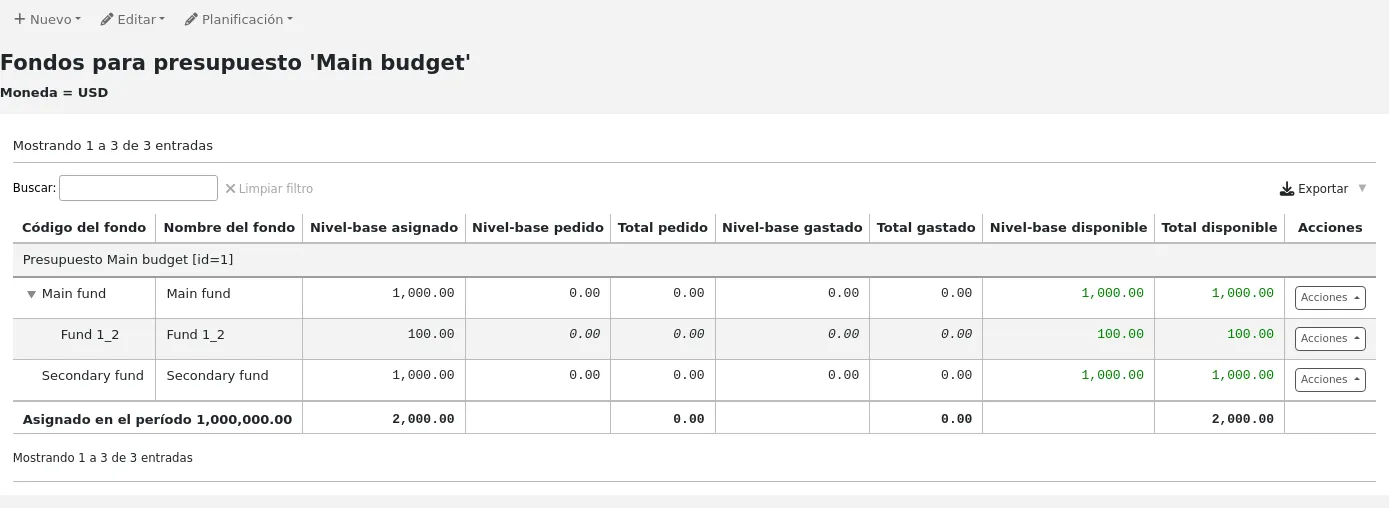
The monetary columns in the fund table break down as follows:
Base-level allocated is the “Amount” value you defined when creating the fund
Base-level ordered is the ordered amount for this fund (without child funds)
Total ordered is the base-level ordered for this fund and all its child funds
Base-level spent is the spent amount for this fund (without child funds)
Total spent is the base-level spent for this fund and all its child funds
Base-level available is 1 - 2
Total available is 1 - 3
To the right of each fund you will find the “Actions” button under which you will find the “Edit,” “Delete,” and “Add sub fund” options.
Adding a sub fund
A sub fund is a more granular division of the fund. An example would be to have a fund for “Fiction” and under that have a fund for “New releases” and a fund for “Science Fiction.” It is an optional way to further organize your finances.
Nota
If a budget is locked, it will not be possible to add sub funds.
To add a sub fund to a fund,
From the list of all funds, or from the list of funds of a specific budget, click the “Actions” button on the right.

Choose “Add sub fund”.
Fill out the new sub fund form. Fields are the same as for adding a new fund. The only difference is that the form will state the “parent” fund.
Click “Submit”.
Funds with sub funds will show with a small arrow to the left. Clicking that will show you the sub funds.
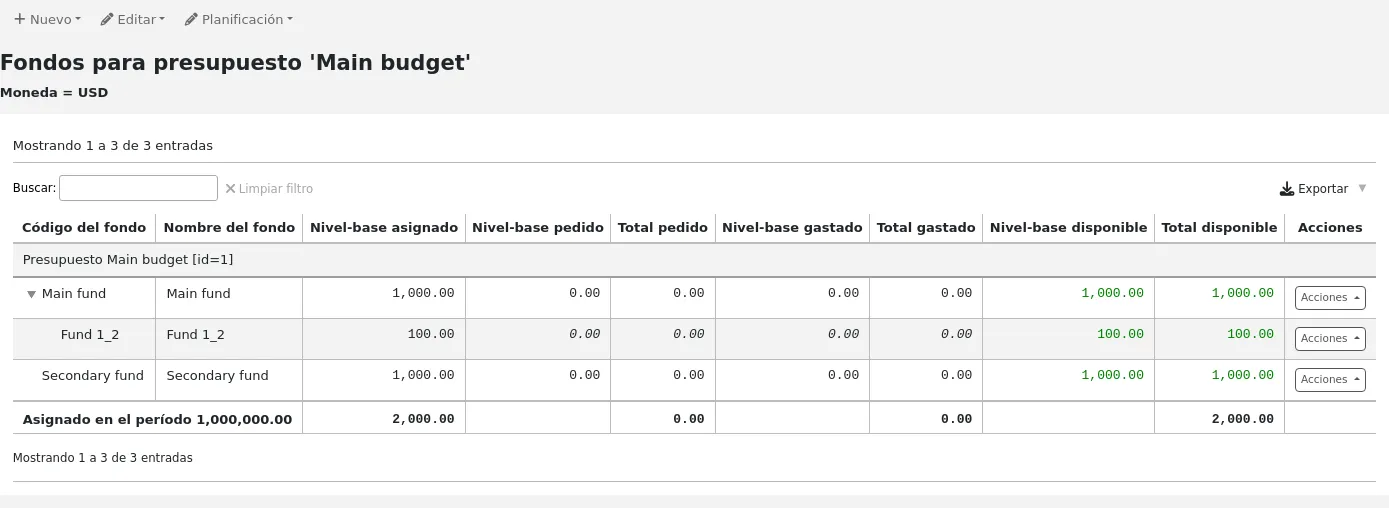
Deleting funds
It is possible to delete funds, if necessary.
Advertencia
Deleting a fund in which there are orders will delete those orders. Only delete funds if you are certain it needs to be deleted. It is not possible to undo this.
To delete a fund,
From the list of all funds, or from the list of funds of a specific budget, click the “Actions” button on the right.

Choose “Delete”.
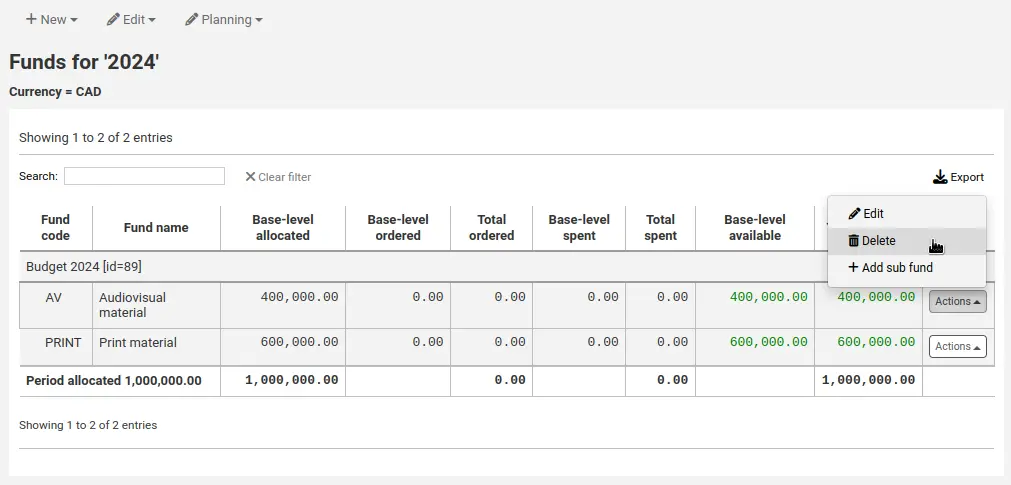
Click “Yes, delete this fund” in the warning message.
Budget planning
Nota
Staff members must have the planning_manage permission, the budget_manage permission, and the period_manage permission (or the superlibrarian permission) in order to access budget planning.
Cuando vea la lista de fondos haga clic en el botón “Planificación” y seleccione como planifica gastar su presupuesto.
If you choose “Plan by months” you will see the budgeted amount broken down by months.
On the left are filters that can be used to limit what is shown in the table.

Select planning type: choose to plan by months, libraries, item types, or any authorized value category used as statistic 1 or 2 in the funds.
Show my funds only: this will filter out funds of which you are not the owner.
Show active funds only: this will filter out funds that have not been used (no ordered amount).
Show actual/estimated values: this will alter the table to show the ordered amounts as well.
To hide some of the columns, uncheck the boxes at the top of the table.
From here, you can plan your budget spending by manually entering values or by clicking the “Auto-fill row” button. If you choose to auto-fill the form the system will try to divide the amount accordingly, you may have to make some edits to split things more accurately.
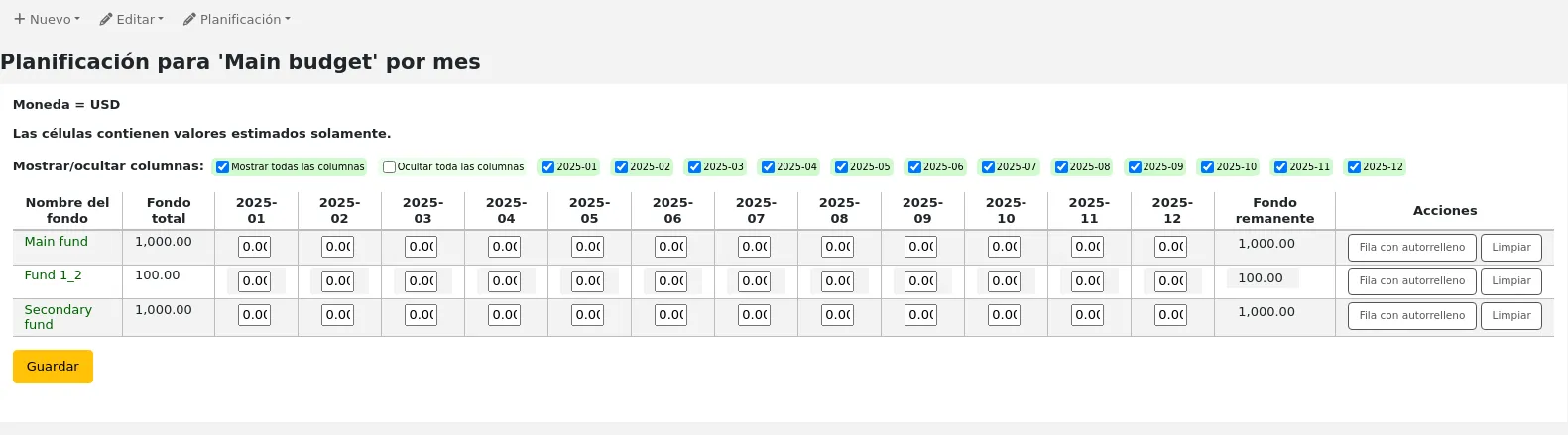
Once your changes are made, click the “Save” button.
Nota
If a budget is locked, it will not be possible to edit the values.
To export your data as a CSV file, enter a file name in the “Output to a file named” field, in the “Export” section on the left, and click the “Submit” button.
Cuentas EDI
From here you can set up the information needed to connect to your acquisitions vendors.
Nota
This section will only appear if the EDIFACT system preference is enabled.
Nota
Only staff with the edi_manage permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Nota
Before you begin you will need at least one vendor set up in acquisitions.
To add account information click the “New account” button.
Enter your vendor’s information in the form.
See the EDI questions for vendors section of the acquisitions module chapter for a description of each field.
Cada proveedor tendrá una cuenta.
Biblioteca EANs
Un EAN de biblioteca es el identificador que un proveedor proporciona a una biblioteca para devolver información a ellos, de esta manera, ellos saben cual cuenta usar cuando facturan. Una cuenta EDI puede tener varios EANs.
Nota
This section will only appear if the EDIFACT system preference is enabled.
Nota
Only staff with the edi_manage permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
To add an EAN click the “New EAN” button.
En el formulario que aparece deberá introducir al menos una fecha para realizar la búsqueda.
See the EDI questions for vendors section of the acquisitions module chapter for a description of each field.
Parámetros adicionales
Get there: More > Administration > Additional parameters
Identity providers
This section is used to define and manage external identity providers for Koha users. This is used when your users come from an external source, such as student management system, active directory, or other similar databases.
Get there: More > Administration > Additional parameters > Identity providers
Nota
Only staff with the manage_identity_providers permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Adding an identity provider
To add an identity provider, click the “New identity provider” button.

Basic configuration
Code: enter a code for this provider.
Nota
The code for the identity provider is limited to 20 characters and can only be composed of letters, numbers, and underscore (_).
Description: enter a name for this provider. This is what you will see in the interface.
Protocol: choose which protocol this identity provider uses.
OAuth
OIDC
Advanced configuration
Configuration: Use this field to enter the configuration specific to the protocol chosen above.
You can click on the “Add default OAuth configuration” button or the “Add default OIDC configuration” button to prefill the field with some default values, which you can change for your own values.
The default OAuth configuration is:
{ "key": "<enter client id>", "secret": "<enter client secret>", "authorize_url": "<enter authorization endpoint>", "token_url": "<enter token endpoint>", "userinfo_url": "<enter user info endpoint (optional)>", "scope": "email" }
The default OIDC configuration is:
{ "key": "<enter client id>", "secret": "<enter client secret>", "well_known_url": "<enter openid configuration endpoint>", "scope": "openid email" }
Mapping: Use this field to define the field mappings from the external database to the Koha borrower fields.
The key is the Koha field from the borrowers table, and the value is the external field.
Nota
You can find all fields for the borrowers table in the database structure.
You can click on the “Add default OAuth mapping” button or the “Add default OIDC mapping” button to prefill the field with some default values, which you can change for your own values.
Both the default OAuth mapping and default OIDC mapping are:
{ "email": "email", "firstname": "given_name", "surname": "family_name" }
If the external fields are nested, you can use periods to separate the levels.
For example, if the firstname is nested like so:
<user> <given_name>First name</given_name> <family_name>Family name</family_name> <email>Email address</email> </user>
Use:
"firstname": "user.0.given_name"
This will fetch the «given_name» field in the first «user» field (0 = first).
Importante
If you plan on using the auto register function (see below), make sure either «userid» or «cardnumber» are present in the mappings.
Importante
Make sure the field for the matchpoint (see below) is included in the mappings.
Matchpoint: choose which field is used to match incoming users to existing users.
Nota
The field chosen here must be included in the mappings (see above).
Icon URL: if you want an icon to show on the login screen for this provider, enter the URL to the image file here.
Domain configuration
Nota
Enter at least one domain for this provider. Once it is saved, you will be able to add more domains to this provider.
Domain: enter the email domain for incoming users.
Nota
Enter an asterisk (*) to include all domains.
Default library: if auto register is enabled, choose at which library new users will be registered.
Default category: if auto register is enabled, choose which patron category will be assigned to new users.
Allow OPAC: choose if patrons of this domain can log into the OPAC with their credentials from this identity provider.
Allow staff: chose if staff members of this domain can log into the staff interface with their credentials from this identity provider.
Auto register: choose whether or not a new patron account is created in Koha when a user from this domain logs in for the first time with their credentials from this identity provider.
Nota
If auto register is enabled, make sure the «userid» or «cardnumber» fields are included in the mappings (see above).
Also make sure the default library and default category are set correctly for new patrons. These will be assigned to the new patrons.
Update on login: choose whether or not the patron account in Koha is updated with the external information when a user from this domain logs in with their credentials from this identity provider.
Advertencia
Information may be lost if you change it directly in Koha.
Once the form is completed, click “Submit” to save the new identity provider.
You will need to restart Koha once the identity provider is added.
Adding an email domain to an existing identity provider
You will need to add at least one email domain when creating a new identity provider. You can add more by clicking the “Manage domains” button to the right of the identity provider from the main identity providers page, and clicking “New email domain”.
Domain: enter the email domain for incoming users.
Nota
Enter an asterisk (*) to include all domains.
Update on login: choose whether or not the patron account in Koha is updated with the external information when a user from this domain logs in with their credentials from this identity provider.
Advertencia
Information may be lost if you change it directly in Koha.
Auto register: choose whether or not a new patron account is created in Koha when a user from this domain logs in for the first time with their credentials from this identity provider.
Nota
If auto register is enabled, make sure the «userid» or «cardnumber» fields are included in the mappings of the identity provider.
Also make sure the default library and default category are set correctly for new patrons. These will be assigned to the new patrons.
Default library: if auto register is enabled, choose at which library new users will be registered.
Default category: if auto register is enabled, choose which patron category will be assigned to new users.
Allow OPAC: choose if patrons of this domain can log into the OPAC with their credentials from this identity provider.
Allow staff: chose if staff members of this domain can log into the staff interface with their credentials from this identity provider.
Once the form is completed, click “Submit” to save the new email domain.
Servidores Z39.50/SRU
Z39.50 is a client/server protocol for searching and retrieving information from remote computer databases. In short, it’s a tool used for copy cataloging.
SRU (Search/Retrieve via URL) is a standard XML-based protocol for search queries, utilizing CQL (Contextual Query Language), a standard syntax for representing queries.
Using Koha you can connect to any Z39.50 or SRU target that is publicly available or that you have the log in information to and copy bibliographic or authority records from that source.
Get there: More > Administration > Additional parameters > Z39.50/SRU servers
Nota
Only staff with the manage_search_targets permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Koha comes with a default list of Z39.50/SRU targets set up that you can add to, edit or delete.
Adding a Z39.50 target
To find additional Z39.50 targets, you can use Index Data’s IRSpy https://irspy.indexdata.com or the Library of Congress’s list of targets https://www.loc.gov/z3950/. You can also contact individual libraries and ask for their Z39.50 information.
From the main Z39.50 page, click “New Z39.50 server”.
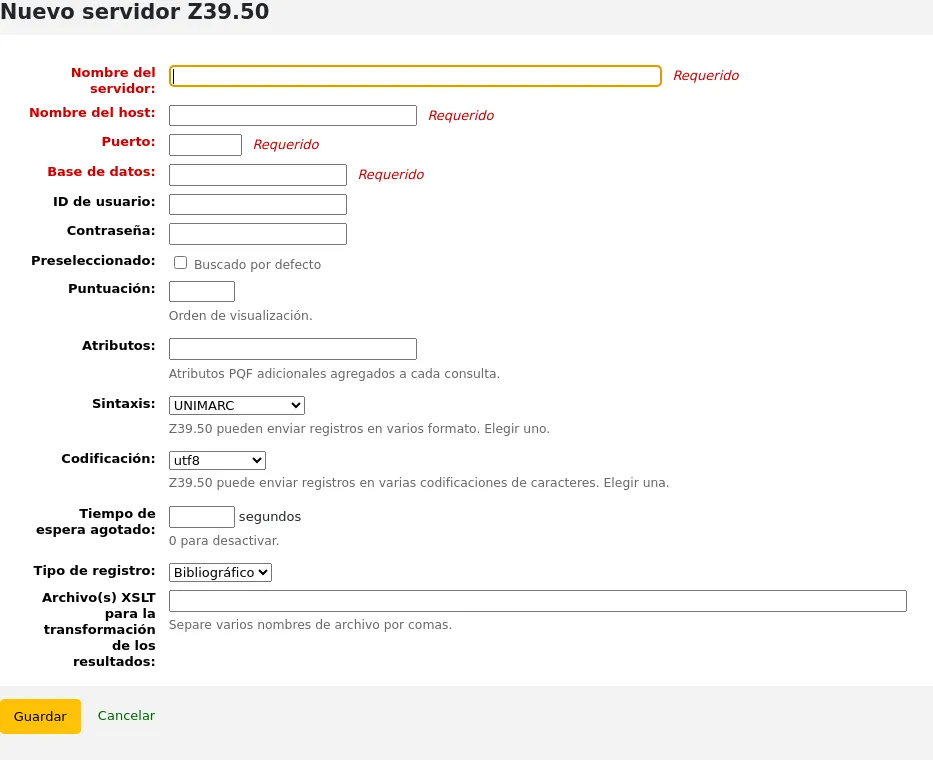
Server name: enter a name that will help you identify the source (such as the library name). It will be saved in capital letters.
Hostname: enter the address to the Z39.50 target.
Port: enter the port number to listen on to get results from this target.
Database: enter the name of the database.
Userid: some servers might be password protected. If that is the case for the server you are trying to add, enter your user ID for that source.
Password: if the server is password protected, enter your password for that source.
Preselected: check this box if you want this target to always be selected by default.
Rank: enter a number representing where in the list you’d like this target to appear. 0 is the top position, then 1, 2, etc.
Si se deja en blanco los objetivos estarán en orden alfabético.
Attributes: enter PQF attributes to be added to all queries.
Syntax: choose the MARC flavor used by this target.
Encoding: choose the character encoding used by this target.
Nota
If you notice special characters don’t appear correctly when you import records through Z39.50, it means the encoding is wrong. Change it to another and try importing again.
Timeout: enter a number of seconds after which to stop trying to search the target if results aren’t found in a reasonable amount of time. It is helpful for targets that take a long while.
Record type: choose if this is a bibliographic or an authority target.
XSLT file(s) for transforming results: enter one or more (comma-separated) XSLT file names that you want to apply on the search results.
Al recuperar los registros de servidores externos puede que desee automatizar algunos cambios en esos registros. Los XSLTs le permiten hacer esto. Koha incluye algunos archivos XSLT de ejemplo listos para su uso en el directorio /koha-tmpl/intranet-tmpl/prog/en/xslt/:
Del952.xsl: Remove Koha items (field 952) (MARC21)
Del995.xsl: Remove Koha items (field 995) (UNIMARC)
Del9LinksExcept952.xsl: Remove links to authorities in bibliographic records ($9), except in the case of 952$9 (itemnumber) (MARC21)
Del9LinksExcept995.xsl: Remove links to authorities in bibliographic records ($9), except in the case of 995$9 (itemnumber) (UNIMARC)
Click “Save”.
Suggested bibliographic Z39.50 targets
Koha libraries that have shared their Z39.50 targets are listed on the Koha wiki at https://wiki.koha-community.org/wiki/Koha_Open_Z39.50_Sources.
Known publicly available targets are listed on the Koha wiki at https://wiki.koha-community.org/wiki/Configure_Z39.50/SRU_targets.
You can also find open Z39.50 targets listed on the IRSpy website at https://irspy.indexdata.com/.
These targets are known to work:
LIBRARY OF CONGRESS
- Server name:
LIBRARY OF CONGRESS
- Hostname:
lx2.loc.gov
- Port:
210
- Database:
LCDB
- Preselected:
select to search by default
- Rank:
enter a value for the display order, for example 1
- Syntax:
MARC21/USMARC
- Encoding:
utf8
- Timeout:
0
- Record type:
Bibliographic
OHIOLINK
- Server name:
OHIOLINK
- Hostname:
olc1.ohiolink.edu
- Port:
210
- Database:
INNOPAC
- Preselected:
select to search by default
- Rank:
enter a value for the display order, for example 1
- Syntax:
MARC21/USMARC
- Encoding:
utf8
- Timeout:
0
- Record type:
Bibliographic
Adding an SRU target
From the main Z39.50/SRU page, click “New SRU server”
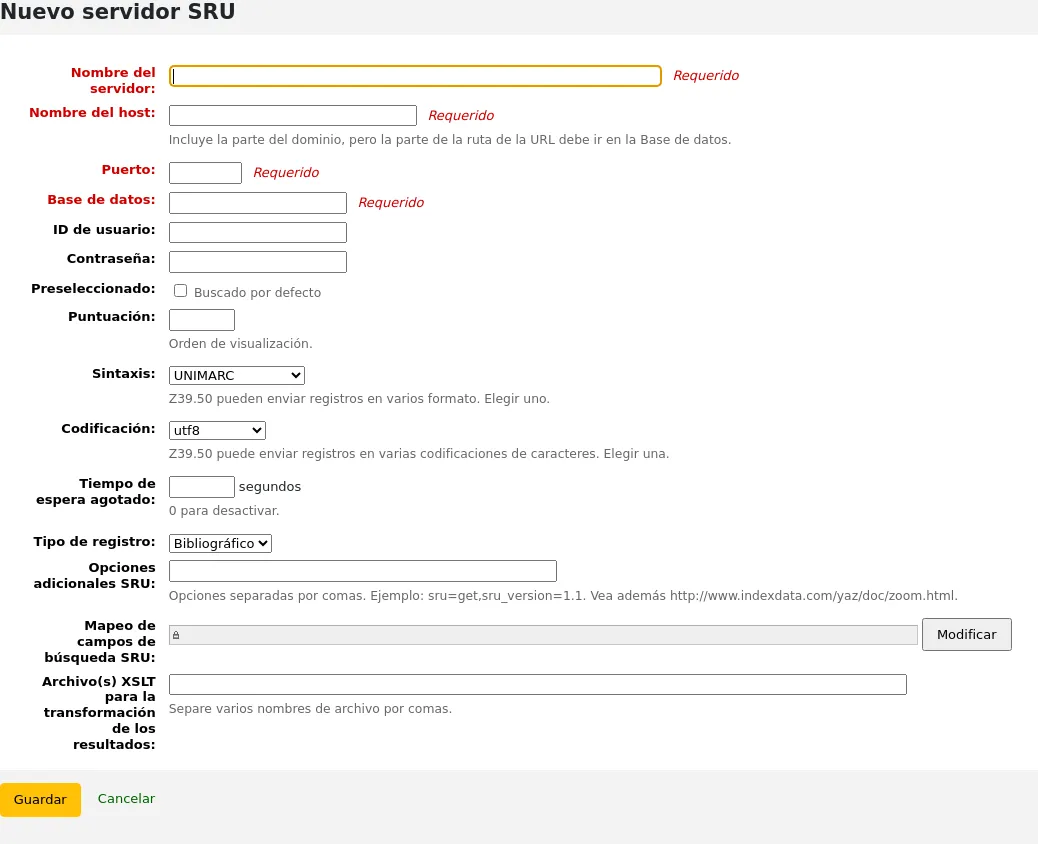
Server name: enter a name that will help you identify the source (such as the library name).
Hostname: enter the address (URL) to the SRU target.
Port: enter which port to listen on to get results from this target.
Database: enter the name of the database.
Userid: some servers might be password protected. If that is the case for the server you are trying to add, enter your user ID for that source.
Password: if the server is password protected, enter your password for that source.
Preselected: check this box if you want this target to always be selected by default.
Rank: enter a number representing where in the list you’d like this target to appear. 0 is the top position, then 1, 2, etc.
Si se deja en blanco los objetivos estarán en orden alfabético.
Syntax: choose the MARC flavor used by this target.
Encoding: choose the character encoding used by this target.
Nota
If you notice special characters don’t appear correctly when you import records through Z39.50, it means the encoding is wrong. Change it to another and try importing again.
Timeout: enter a number of seconds after which to stop trying to search the target if results aren’t found in a reasonable amount of time. It is helpful for targets that take a long while.
Record type: choose if this is a bibliographic or an authority target.
Additional SRU options: enter additional options of the external server here, like
sru_version=1.1orschema=marc21, etc. Note that these options are server dependent.SRU Search field mapping: click “Modify” to add or update the mapping from the available fields on the Koha search form to the specific server dependent index names.
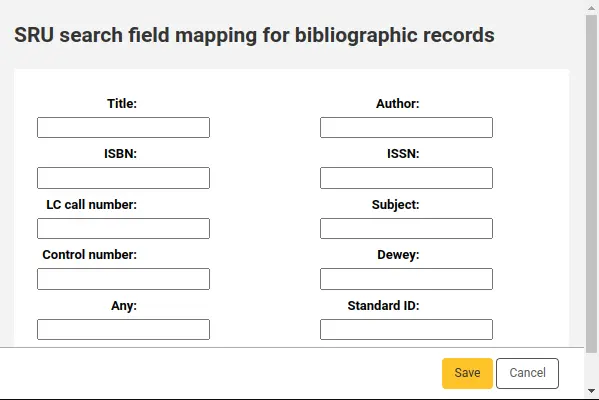
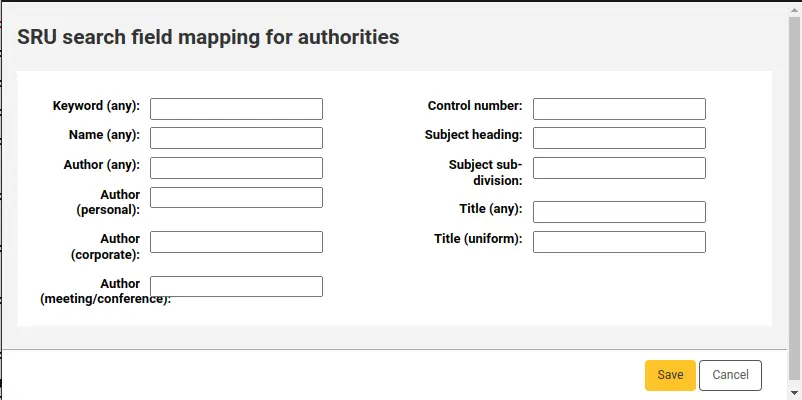
Para refinar aún más sus búsquedas, puede agregar los siguientes nombres de índice al Mapeo de campo de búsqueda SRU. Para ello, edite el servidor y haga clic en el botón Modificar junto a este campo.
Título
dc.title
ISBN
bath.isbn
Cualquiera
cql.anywhere
Autor
dc.author
ISSN
bath.issn
Tema
dc.author
ID estándar
bath.standardIdentifier
Table: SRU mapping
XSLT file(s) for transforming results: enter one or more (comma-separated) XSLT file names that you want to apply on the search results.
Al recuperar los registros de servidores externos puede que desee automatizar algunos cambios en esos registros. Los XSLTs le permiten hacer esto. Koha incluye algunos archivos XSLT de ejemplo listos para su uso en el directorio /koha-tmpl/intranet-tmpl/prog/en/xslt/:
Del952.xsl: Remove Koha items (field 952) (MARC21)
Del995.xsl: Remove Koha items (field 995) (UNIMARC)
Del9LinksExcept952.xsl: Remove links to authorities in bibliographic records ($9), except in the case of 952$9 (itemnumber) (MARC21)
Del9LinksExcept995.xsl: Remove links to authorities in bibliographic records ($9), except in the case of 995$9 (itemnumber) (UNIMARC)
Click “Save”.
SMTP servers
Get there: More > Administration > Additional parameters > SMTP servers
This section is used to configure SMTP servers to send emails through Koha.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_smtp_servers permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
The default STMP configuration is set in the koha-conf.xml file. But this section allows you to add additional servers.
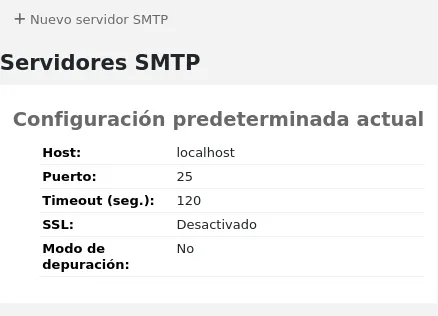
To add a new server,
Click “New SMTP server”
Name (required): give the server a significant name, this is the name that will be displayed in Koha
Host (required): enter the host name or IP address of the server
Port (required): enter the port number provided by your administrator
Timeout (seconds): enter the number of seconds after which an unsent email will result in an error
SSL: choose the security protocol provided by your administrator
Disabled: no security (not recommended)
SSL
STARTTLS
Username: enter the username provided by your administrator
Password: enter the password provided by your administrator
Debug mode: choose whether to enable the debug mode to send additional output to the logs
Default server: choose whether this server is the default one to be used by all libraries
Haga clic en “Enviar””
Once the server is added, you can select it in the library’s details.
¿Quiso decir?
Get there: More > Administration > Additional parameters > Did you mean?
Nota
Only staff with the manage_didyoumean permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Koha can offer “Did you mean?” options on searches based on values in your authorities.
Importante
¿Quizás quiso decir? sólo funciona en el OPAC, por ahora. Las opciones de interfaz administrativa están aquí para un desarrollo futuro.
Utilizando esta página puede controlar cuales opciones presenta Koha a usuarios en sus resultados de búsqueda.

Para habilitar la barra “¿Quiso decir?” en sus resultados de búsqueda deberá seleccionar la casilla al lado de cada plugin que dese utilizar. Los dos plugins que tiene para elegir son:
El plugin ExplodedTerms sugiere que el usuario pruebe buscar por términos más generales/específicos/relacionados para una dada búsqueda (ej. un usuario buscando por «Nueva York (Estado)» puede hacer clic el enlace para términos específicos si está también interesado en «Nueva York (Ciudad)». Esto solo es relevante para bibliotecas con datos de autoridades altamente jerárquicos.
El plugin AuthorityFile busca el archivo de autoridades y sugiere que el usuario podría estar interesado en libros enlazados a las primeras 5 autoridades
Si desea que un plugin tenga prioridad sobre otro arrástrelo simplemente encima del otro.

If you choose both plugins you will see several options at the top of your search results
If you choose just the AuthorityFile you’ll see just authorities.
Table settings
This administration area will help you hide or display columns on fixed tables throughout the staff interface and OPAC.
Get there: Administration > Additional parameters > Table settings

Nota
Only staff with the manage_column_config permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Al hacer clic en el módulo que desee editar las tablas, se le mostrará las opciones disponibles para usted.
This area lets you control the columns that show in the table in question. If nothing is hidden you will see no check marks in the “is hidden by default” column.
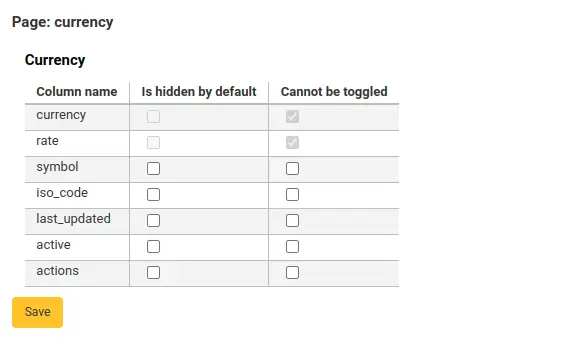
And will see all of the columns when viewing the table on its regular page.
If columns are hidden they will have checks in the “is hidden by default” column.
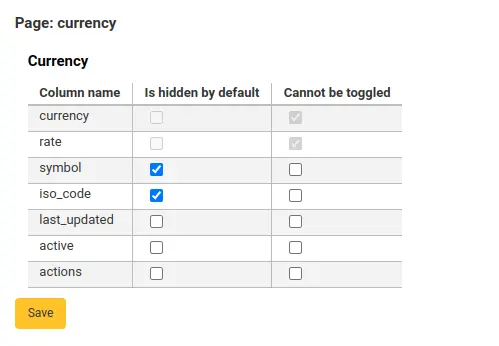
And hidden when you view the table.
The “Cannot be toggled” column is used to prevent individual users from showing or hiding this column when viewing the table.
Individual users can toggle columns using the “Columns” button at the top of the table.
For example, in the Currencies table, the “Currency” and “Rate” columns cannot be toggled. When the user clicks on the “Columns” button, they are not able to choose whether these two columns are hidden or visible.
Note that using the “Columns” button show or hide columns will only toggle them for the current user and session. Once the user logs out, the columns will go back to their default settings as set in the table settings administration page. It will not affect any other user.
Módulo |
Tables |
|---|---|
Adquisiciones |
|
Administración |
|
Authorities |
There aren’t any tables that can be configured from the Authorities module. |
Catálogo |
|
Catalogación |
|
Circulación |
|
Course reserves |
|
E-resource management |
|
Préstamos interbibliotecarios |
|
Usuarios |
|
Point of sale |
|
Herramientas |
|
OPAC |
|
Informes |
|
Publicaciones periódicas |
|
Nota
Patrons in the OPAC can’t toggle column visibility. For OPAC tables this feature only allows to control the visibility of columns.
Nota
Any tables with columns listed here also have the option to export to Excel, export to CSV, copy, or print within the table header.
Alertas audibles
If you have your AudioAlerts preference set to “Enable” you will be able to control the various alert sounds that Koha uses from this area.
Get there: More > Administration > Additional parameters > Audio alerts
Nota
Only staff with the manage_audio_alerts permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Each dialog box in Koha has a CSS class assigned to it that can be used as a selector for a sound.
You can edit the defaults by clicking the “Edit” button to the right of each alert.
You can assign alerts to other CSS classes in Koha by entering that information in the selector box. For example if you enter
body:contains('Check in message')
Then when you visit the check-in page you will hear an alert.
Every page in Koha has a unique ID in the body tag which can be used to limit a sound to a specific page
Any ID selector (where HTML contains id=»name_of_id» ) and can also be a trigger as: #name_of_selector
Proveedores de telefonía móvil SMS
Importante
- This option will only appear if the
SMSSendDriver, SMSSendMaxChar preference is set to “Email”.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_sms_providers permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
Nota
Many mobile providers have deprecated support for the SMS::Send::Email feature. It is not recommended for use unless you have a dedicated SMS to Email gateway.
From here you can enter as many cellular providers as you need to send SMS notices to your patrons using the email protocol.
Algunos ejemplos de valores son:
Mobile carrier |
SMS gateway domain |
|---|---|
Alltel |
sms.alltelwireless.com |
AT&T |
txt.att.net |
Boost Mobile |
sms.myboostmobile.com |
Project Fi |
msg.fi.google.com |
Predeterminado: pública |
text.republicwireless.com |
Sprint |
messaging.sprintpcs.com |
T-mobile |
tmomail.net |
U.S. Cellular |
email.uscc.net |
Verizon Wireless |
vtext.com |
Virgin Mobile |
vmobl.com |
Table: SMS provider examples
To add new providers enter the details in the form and click “Add new” to save.
These options will appear in the OPAC for patrons to choose from on the messaging tab if you have EnhancedMessagingPreferences enabled.
Campos adicionales
This section is used to add custom fields to order baskets, invoice, serial subscriptions, and accountlines.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_additional_fields permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
To add a new field, first choose which table you want to add it to.
Acquisitions
Invoices (aqinvoices): a field added to aqinvoices will appear when viewing an invoice in the acquisitions module.
Order baskets (aqbasket): a field added to aqbasket will appear upon the creation of a new order basket or the modification of an existing order basket in the acquisitions module.
Order lines (aqorders): a field added to aqorders will appear when adding orders to a basket or editing orders in open baskets.
Administration
Libraries (branches): a field added to branches will appear when editing libraries.
Version
Additional fields for libraries were added to Koha in version 25.05.
ERM
Agreements (erm_agreements): a field added to erm_agreements will appear when creating or editing agreements in the ERM module.
Version
Additional fields for ERM agreements were added to Koha in version 24.11.
Licenses (erm_licenses): a field added to erm_licenses will appear when creating or editing agreements in the ERM module.
Version
Additional fields for ERM licenses were added to Koha in version 24.11.
Packages (erm_packages): a field added to erm_packages will appear when creating or editing packages in the ERM module.
Version
Additional fields for ERM packages were added to Koha in version 24.11.
Patrons
Account lines (credit) (accountlines:credit): a field added to account line credits will appear when paying or writing off charges in a patron’s account or when creating manual credits.
Account lines (debit) (accountlines:debit): a field added to account line debit will appear when creating a manual invoice
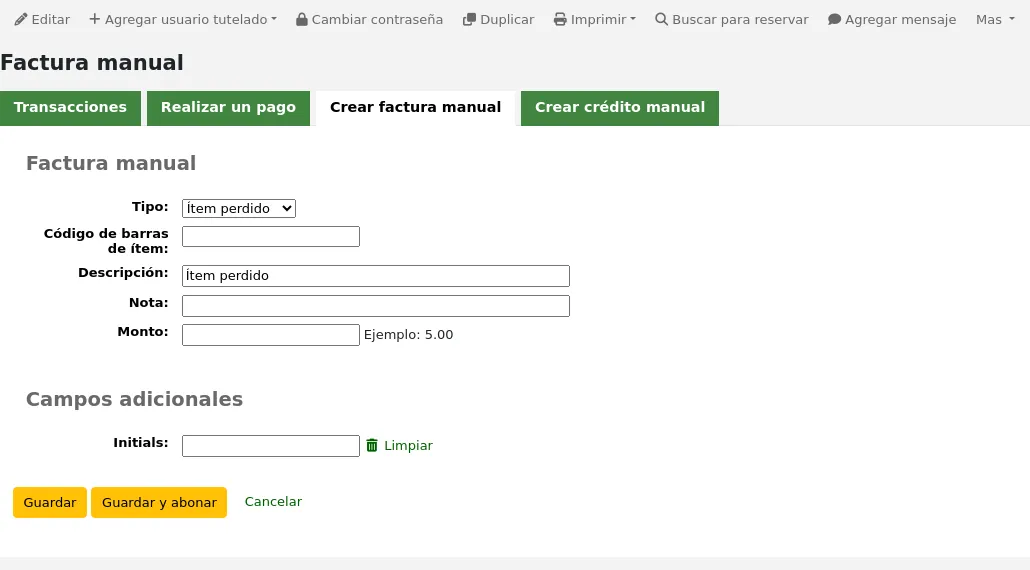
Account credit types (account_credit_types): a field added to account credit types will appear when adding or editing credit types.
Version
Additional fields for credit types were added to Koha in version 25.05.
Account debit types (account_debit_types): a field added to account debit types will appear when adding or editing debit types.
Version
Additional fields for debit types were added to Koha in version 25.05.
Serials
Subscriptions (subscription): a field added to subscription will appear when creating a new subscription or when editing an existing subscription in the serials module.
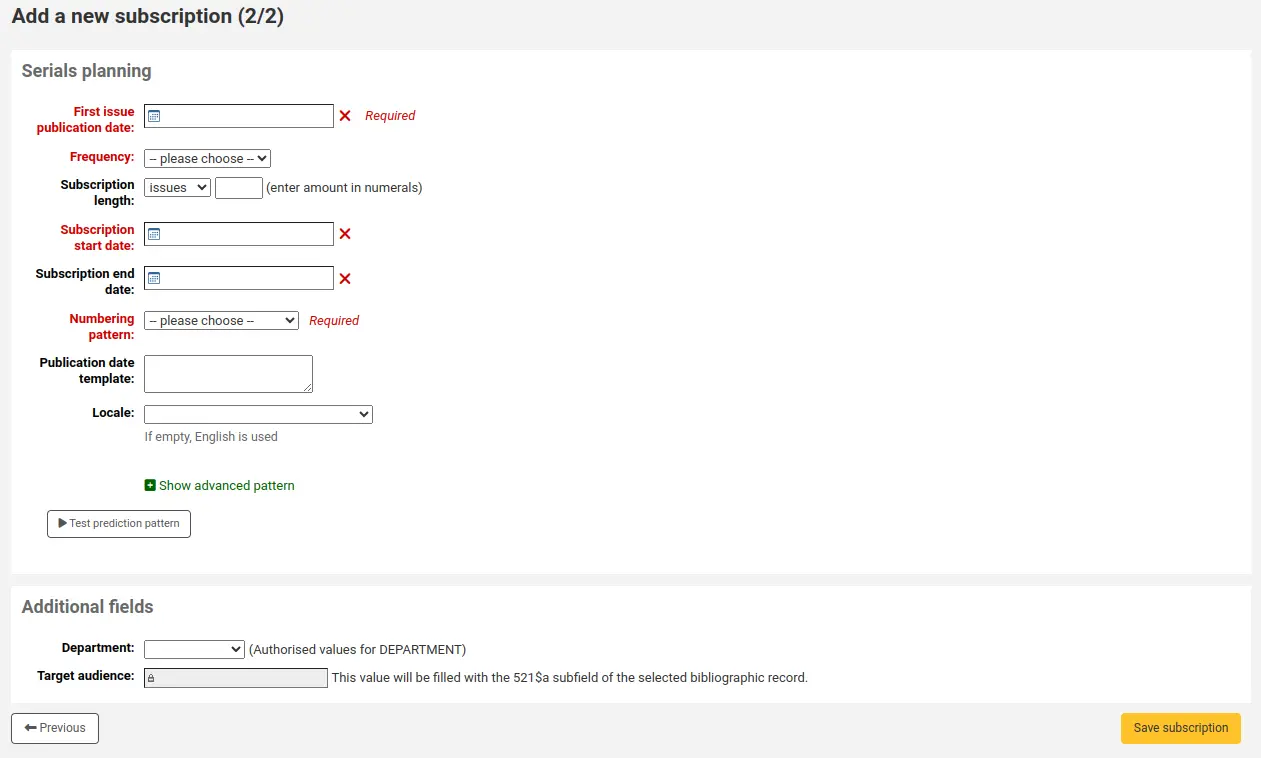
Click on “New field”.
Fill out the form.
Name: this is the name of the field as you want it to appear.
Authorized value category: if you want to add a dropdown menu to the field choose an authorized value category here (you can also create a new authorized value category if you need to).
Repeatable: if you want the field to be repeatable, check this box. For free text fields, it will add a “New” button next to the field so that staff can repeat the field and add a new value. For fields with authorized value categories, it will create a list of checkboxes instead of a dropdown menu allowing staff to choose more than one option.
Version
This option was added to Koha in version 24.11.
MARC field: for additional subscription fields, it is possible to link the field to a MARC field. The additional field will be automatically populated with the corresponding record’s value for this MARC field.
Nota
You can only choose one of the two options (authorized value OR MARC field)
Advertencia
If you choose the MARC field, make sure you enter it in this format: field$subfield
For example: 590$a
Searchable: check this box if you want to be able to search baskets or subscriptions based on this field
Order basket searchable additional fields will be available in the orders advanced search form
Invoice searchable additional fields will be available in the invoice search form
Subscription searchable additional fields will be available in the subscription advanced search form
Examples of additional fields
Ejemplo 1: Campo para suscripción adicional usando valores autorizados
You might want to track which department you’re ordering this serial for
In the “Name” field, enter “Department”
In the “Authorized value category” field, choose DEPARTMENT
Check the “Searchable” box
When you are adding a subscription, the field will be in the “Additional fields” section with its authorized values drop-down menu.

When you view the subscription, the field will appear under “Additional fields”.
Because we made the field searchable, it will also be in the serials subscription search.
Example 2: Additional subscription field using MARC field
This is particularly useful if you want to view bibliographic information in the subscription detail page. In this example, we will add the 521$a field, which is, in MARC21, the target audience note.
In the “Name” field, enter “Target audience”
In the “MARC field” field, enter “521$a”
Nota
You will not be able to edit this field from the subscription form. If you need to add or change the value in this field, you must go through the cataloging module.
When you view the subscription, the field and the information from the bibliographic record will appear under “Additional fields”.

Example 3: Free text invoice additional field
If you need to enter additional information in invoices, such as the number of the check used to pay for the invoice, you can choose not to use an authorized value at all.
In the “Name” field, enter “Check #”
Check the “Searchable” box
The new fields will be displayed when viewing the invoice in the acquisitions module.

Because we made the field searchable, it will also be in the invoice search.
Keyboard shortcuts
This section is used to redefine the keyboard shortcuts used in the advanced cataloging editor.
Nota
This section will only appear if the EnableAdvancedCatalogingEditor system preference is enabled.
Nota
Only staff with the manage_keyboard_shortcuts permission (or the superlibrarian permission) will have access to this section.
To change a shortcut, enter the combination of keys to use in the field in the “Shortcut keys” column, and click “Save shortcuts”.
Make sure to follow the key map rules when entering your key combinations:
Separate keys using a hyphen “-”
Control key is “Ctrl”
Alt key is “Alt”
Shift is “Shift”
If combining multiple keys they must be in specified order: Shift-Cmd-Ctrl-Alt